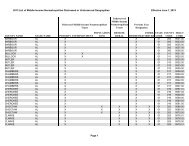
Annual Report 2012 - ffiec
Annual Report 2012 - ffiec
Annual Report 2012 - ffiec
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Policy decisions are implemented<br />
by the FRB or under delegated<br />
authority to the Director for the<br />
Division of Banking Supervision<br />
and Regulation, the Director for<br />
the Division of Consumer and<br />
Community Affairs, and to the<br />
12 Federal Reserve Banks—each<br />
of which has operational responsibility<br />
within a specific geographical<br />
area. The Reserve Bank<br />
Districts are headquartered in<br />
Boston, New York, Philadelphia,<br />
Cleveland, Richmond, Atlanta,<br />
Chicago, St. Louis, Minneapolis,<br />
Kansas City, Dallas, and San Francisco.<br />
Each Reserve Bank has a<br />
president (chief executive officer)<br />
who serves for five years and is<br />
appointed by the Reserve Bank’s<br />
class B and class C directors,<br />
and other executive officers who<br />
report directly to the president.<br />
Among other responsibilities, a<br />
Reserve Bank employs a staff of<br />
examiners who examine state<br />
member banks and Edge Act and<br />
agreement corporations, conduct<br />
BHC inspections, and examine the<br />
international operations of foreign<br />
banks—whose head offices are<br />
usually located within the Reserve<br />
Bank’s District. When appropriate,<br />
examiners also visit the overseas<br />
offices of U.S. banking organizations<br />
to obtain financial and<br />
operating information to evaluate<br />
adherence to safe and sound banking<br />
practices.<br />
National banks, which must be<br />
members of the Federal Reserve<br />
System, are chartered, regulated,<br />
and supervised by the OCC. Statechartered<br />
banks may apply to<br />
and be accepted for membership<br />
in the Federal Reserve System,<br />
after which they are subject to the<br />
supervision and regulation of the<br />
FRB, which is coordinated with the<br />
state’s banking authority. Insured<br />
state-chartered banks that are not<br />
members of the Federal Reserve<br />
System are regulated and supervised<br />
by the FDIC. The FRB also<br />
has overall responsibility for foreign<br />
banking operations, including<br />
both U.S. banks operating abroad<br />
and foreign banks operating<br />
branches within the United States.<br />
The Dodd-Frank Act directs the<br />
FRB to collect assessments, fees,<br />
and other charges that are equal<br />
to the expenses incurred by the<br />
Federal Reserve to carry out its<br />
responsibilities with respect to<br />
supervision of (1) BHCs and<br />
SLHCs with assets equal to or<br />
greater than $50 billion and (2)<br />
all nonbank financial companies<br />
supervised by the FRB.<br />
Additionally, the Dodd-Frank<br />
Act created an independent CFPB<br />
within the Federal Reserve System.<br />
The FRB covers the expenses of the<br />
CFPB’s operations with revenue it<br />
generates principally from assessments<br />
on the 12 Federal Reserve<br />
Banks.<br />
23