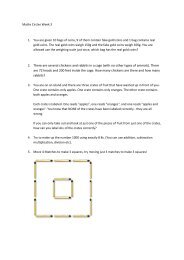
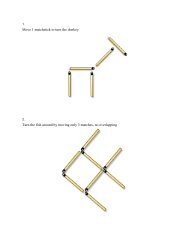
1. A mail-order computer business has six telephone lines. Let X ...
1. A mail-order computer business has six telephone lines. Let X ...
1. A mail-order computer business has six telephone lines. Let X ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
15. A random sample of n bike helmets manufactured by a certain company<br />
is selected. <strong>Let</strong> X = the number among the n that are flawed<br />
and let p = P (flawed). Assume that only X is observed, rather than<br />
the sequence of Successes and Failures. Derive the Maximum Likelihood<br />
Estimator of p. If n = 20 and x = 3, what is the estimate? Is<br />
this estimator unbiased?<br />
Ans This is a Binomial model. Therefore, p.d.f. is<br />
P [X = x] =<br />
n<br />
x<br />
<br />
p x (1 − p) n−x<br />
Because we have just a single observation, the jt. p.d.f itself is this,<br />
and probability in this case is not 0, we can take log,<br />
<br />
n<br />
ln P [X = x] = ln[ ]x ln p + (n − x) ln(1 − p)<br />
x<br />
Maximizing w.r.t. p,<br />
∂ ln P [X = x]<br />
∂p<br />
= x<br />
p<br />
n − x<br />
+ (−1) = 0<br />
1 − p<br />
(n − x)p = x(1 − p) ⇒ np = x ⇒ ˆp = x<br />
n<br />
To show unbiasedness, use the fact that X is binomial,<br />
E[X/n] = (1/n)E[X] = np/n = p<br />
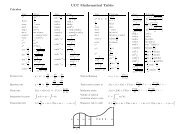
The following page contains a table of cumulative standard normal probabilities<br />
x<br />
Φ(x) = P [Z < x] =<br />
For x < 0, Φ(−x) = 1 − Φ(x).<br />
10<br />
−∞<br />
1 x2<br />
− √ e 2 dx<br />
2π