Residual Strength and Fatigue Lifetime of ... - Solid Mechanics
Residual Strength and Fatigue Lifetime of ... - Solid Mechanics
Residual Strength and Fatigue Lifetime of ... - Solid Mechanics
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
was used to monitor 3D surface displacements <strong>and</strong> 2D surface strains continuously during the<br />
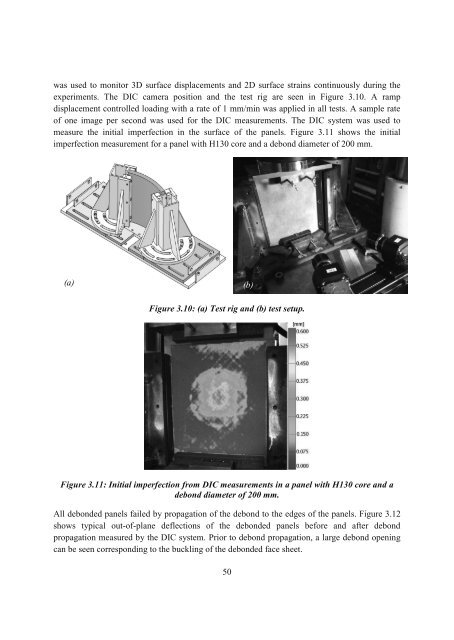
experiments. The DIC camera position <strong>and</strong> the test rig are seen in Figure 3.10. A ramp<br />
displacement controlled loading with a rate <strong>of</strong> 1 mm/min was applied in all tests. A sample rate<br />
<strong>of</strong> one image per second was used for the DIC measurements. The DIC system was used to<br />
measure the initial imperfection in the surface <strong>of</strong> the panels. Figure 3.11 shows the initial<br />
imperfection measurement for a panel with H130 core <strong>and</strong> a debond diameter <strong>of</strong> 200 mm.<br />
(a) (b)<br />
Figure 3.10: (a) Test rig <strong>and</strong> (b) test setup.<br />
Figure 3.11: Initial imperfection from DIC measurements in a panel with H130 core <strong>and</strong> a<br />
debond diameter <strong>of</strong> 200 mm.<br />
All debonded panels failed by propagation <strong>of</strong> the debond to the edges <strong>of</strong> the panels. Figure 3.12<br />
shows typical out-<strong>of</strong>-plane deflections <strong>of</strong> the debonded panels before <strong>and</strong> after debond<br />
propagation measured by the DIC system. Prior to debond propagation, a large debond opening<br />
can be seen corresponding to the buckling <strong>of</strong> the debonded face sheet.<br />
50