Evaluation of Plastic Waste Management in Thailand Using Material ...
Evaluation of Plastic Waste Management in Thailand Using Material ...
Evaluation of Plastic Waste Management in Thailand Using Material ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
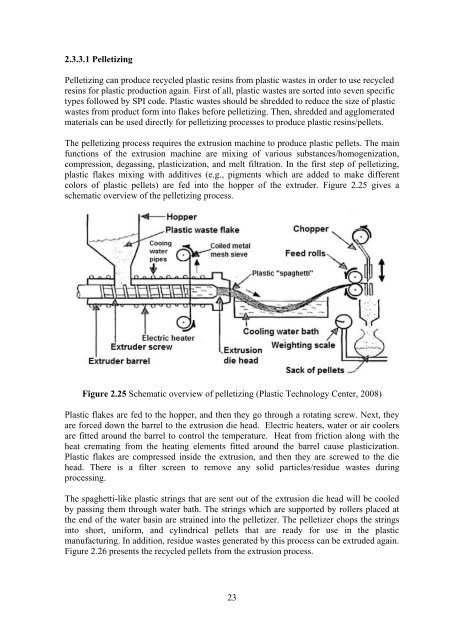
2.3.3.1 Pelletiz<strong>in</strong>g<br />
Pelletiz<strong>in</strong>g can produce recycled plastic res<strong>in</strong>s from plastic wastes <strong>in</strong> order to use recycled<br />
res<strong>in</strong>s for plastic production aga<strong>in</strong>. First <strong>of</strong> all, plastic wastes are sorted <strong>in</strong>to seven specific<br />
types followed by SPI code. <strong>Plastic</strong> wastes should be shredded to reduce the size <strong>of</strong> plastic<br />
wastes from product form <strong>in</strong>to flakes before pelletiz<strong>in</strong>g. Then, shredded and agglomerated<br />
materials can be used directly for pelletiz<strong>in</strong>g processes to produce plastic res<strong>in</strong>s/pellets.<br />
The pelletiz<strong>in</strong>g process requires the extrusion mach<strong>in</strong>e to produce plastic pellets. The ma<strong>in</strong><br />
functions <strong>of</strong> the extrusion mach<strong>in</strong>e are mix<strong>in</strong>g <strong>of</strong> various substances/homogenization,<br />
compression, degass<strong>in</strong>g, plasticization, and melt filtration. In the first step <strong>of</strong> pelletiz<strong>in</strong>g,<br />
plastic flakes mix<strong>in</strong>g with additives (e.g., pigments which are added to make different<br />
colors <strong>of</strong> plastic pellets) are fed <strong>in</strong>to the hopper <strong>of</strong> the extruder. Figure 2.25 gives a<br />
schematic overview <strong>of</strong> the pelletiz<strong>in</strong>g process.<br />
Figure 2.25 Schematic overview <strong>of</strong> pelletiz<strong>in</strong>g (<strong>Plastic</strong> Technology Center, 2008)<br />
<strong>Plastic</strong> flakes are fed to the hopper, and then they go through a rotat<strong>in</strong>g screw. Next, they<br />
are forced down the barrel to the extrusion die head. Electric heaters, water or air coolers<br />
are fitted around the barrel to control the temperature. Heat from friction along with the<br />
heat cremat<strong>in</strong>g from the heat<strong>in</strong>g elements fitted around the barrel cause plasticization.<br />
<strong>Plastic</strong> flakes are compressed <strong>in</strong>side the extrusion, and then they are screwed to the die<br />
head. There is a filter screen to remove any solid particles/residue wastes dur<strong>in</strong>g<br />
process<strong>in</strong>g.<br />
The spaghetti-like plastic str<strong>in</strong>gs that are sent out <strong>of</strong> the extrusion die head will be cooled<br />
by pass<strong>in</strong>g them through water bath. The str<strong>in</strong>gs which are supported by rollers placed at<br />
the end <strong>of</strong> the water bas<strong>in</strong> are stra<strong>in</strong>ed <strong>in</strong>to the pelletizer. The pelletizer chops the str<strong>in</strong>gs<br />
<strong>in</strong>to short, uniform, and cyl<strong>in</strong>drical pellets that are ready for use <strong>in</strong> the plastic<br />
manufactur<strong>in</strong>g. In addition, residue wastes generated by this process can be extruded aga<strong>in</strong>.<br />
Figure 2.26 presents the recycled pellets from the extrusion process.<br />
23