Zbornik - Društvo genetičara Srbije
Zbornik - Društvo genetičara Srbije
Zbornik - Društvo genetičara Srbije
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
218 ZBORNIK ABSTRAKATA III KONGRESA GENETIÈARA SRBIJE V-Pos-15<br />
Subotica, 30. novembar - 4. decembar 2004.<br />
MUTACIJE C- MYC I C-ERB2 GENA KOD PLANOCELULARNOG<br />
KARCINOMA USNE DUPLJE<br />
B. Popoviæ 1 , J. Milašin 1 , B. Jekiæ 2 , I. Novakoviæ 2 i Lj. Lukoviæ 2<br />
1<br />
Stomatološki fakultet, Institut za Biologiju, Univerzitet u Beogradu, Beograd<br />
2<br />
Medicinski fakultet, Institut za biologiju i humanu genetiku, Univerzitet u Beogradu, Beograd<br />
Planocelularni karcinomi, kao i veæina malignih tumora, rezultat su akumulacije<br />
molekularno-genetièkih lezija, koje obuhvataju protoonkogene i tumor supresorske gene.<br />
Najèešæe aktivirani geni, odgovorni za gubitak kontrole tokom transdukcije mitogenog<br />
signala, kod velike grupe humanih tumora, ukljuèujuæi i planocelularni karcinom su<br />
protoonkogeni c-erb2 i c-myc. Produkt c-erb2 gena je transmembranski glikoproteinski<br />
receptor sa tirozin kinaznom aktivnošæu, dok je produkt c-myc protoonkogena,<br />
transkripcioni faktor ukljuèen u kontrolu æelijske proliferacije. Osnovni mehanizam<br />
njihove onkogene aktivacije je genska amplifikacija.<br />
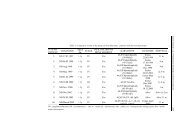
U našoj studiji, genska amplifikacija c-myc i c-erb2 gena ispitana je metodom<br />
diferencijalnog PCR-a, a zatim je stopa amplifikacije korelisana sa klinièko–patološkim<br />
parametrima. Kod 14/70 (20%) PCR analiziranih parafinskih uzoraka, pokazana je<br />
amplifikacija c-erb2 gena, dok je kod 12/70 (17%) uzoraka utvrðena amplifikacija c-myc<br />
gena. Iako se procenat genske amplifikacije poveæava sa stadijumom bolesti, korelacija<br />
izmeðu prisustva ovih genetièkih markera i klinièkih parametara nije najjasnija.Tumori<br />
sa amplifikacijom, bez obzira na stadijum i mesto nastanka predstavljaju podgrupu sa<br />
lošijom prognozom, ali je ipak potrebno pratiti pacijente u duem vremenskom periodu,<br />
da bi mogli pouzdani zakljuèci da se donesu o korelaciji genotip-fenotip.<br />
C- MYC AND C-ERB2 MUTATIONS IN ORAL SQUAMOUS<br />
CELL CARCINOMA<br />
Oral squamous cell carcinomas (OSCC), like most other malignancies, result from an accumulation<br />
of molecular lesions in proto-oncogene and tumour suppressor genes. The<br />
most commonly activated genes responsible for the loss of control in signal transduction<br />
pathways in a wide range of human tumours including OSCC are proto-oncogenes -<br />
c-erb2 and c-myc. The product of c-erb2 is a transmembrane glycoprotein receptor with<br />
tyrosine kinase activity while the product of c-myc is a transcriptional factor which is involved<br />
in the control of cell proliferation. The principle mechanism of their oncogenic<br />
activation is gene amplification.<br />
In our study, amplification status for c-myc and c-erb2 was evaluated using double differential<br />
PCR and the level of amplification was correlated with clinicopathological<br />
markers. 14 out of 70 PCR analyzed paraffin embedded samples, showed amplification<br />
of c-erb2 (20%) and 12 (17%) of the c-myc gene. Although the percentage of gene amplification<br />
tended to increase in high grade, high stage tumours, the correlation between the<br />
presence of amplification and tumour staging was not so clear. Tumours with amplification,<br />
regardless of their stage and site represent a subgroup with worse prognosis but a<br />
longer follow-up of the patients is still necessary.