Zbornik - Društvo genetičara Srbije
Zbornik - Društvo genetičara Srbije
Zbornik - Društvo genetičara Srbije
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
V-Pos-2 ZBORNIK ABSTRAKATA III KONGRESA GENETIÈARA SRBIJE 205<br />
Subotica, 30. novembar - 4. decembar 2004.<br />
THE IMPOIRTANCE OF ENZYMATIC ANALYSIS IN THE CELLS FOR<br />
DETERMINATION OF SPECIFIC TYPES OF MUCOPOLYSACCHARIDOSES<br />
J. Durkoviæ 1 , I. Kremensky 2 and I. Sinigerska 2<br />
1<br />
Health Center Subotica, Department of Medical Genetics, Subotica<br />
2<br />
Laboratory of Molecular Pathology, University Hospital, Sofia, Bulgaria<br />
Mucopolysaccharidoses are recessive very heterogenic group of diseases caused by<br />
storages in lysosomes. The substances stored are partially degraded mucopolysaccharides.<br />
Degradation of acid mucopolysaccharides begins by separation of glucoseaminoglycans<br />
(GAG) from the proteins. Due to the inherited defectiveness of specific<br />
lysosomal hydrolase enzymes, incompletely hydrolyzed molecules are accumulated in<br />
tissues and they are increasingly excreted in urine. The detection of urinary GAG excess<br />
is the first step in diagnostic work-up of a patient with such clinical features. In case the<br />
increased excretion of GAG is confirmed, examination directed to discriminate the types<br />
of the disease is necessary and that is very important in terms of prognostics and further<br />
treatment of the diseased.<br />
In our case report clinically suspected mucopolysaccharidosis called for metabolic<br />
screening of first morning urine and the positive toluidine blue test result indicated the increased<br />
excretion of mucopolysaccharides. The electrophoretical fractionation of excreted<br />
GAG showed, that heparan sulphate was the predominant component. One dimensional<br />
barium acetate electrophoresis is more suitable than thin layer chromatography for<br />
separation of heparan sulphate. Blood sample was tested for specific enzyme deficiency<br />
in white blood cells. Since the enzyme analysis indicated deficiency of heparin<br />
sulphamidase, MPS III the A type was diagnosed. This enzyme is a specific hydrolase involved<br />
in separating sulphate bonds from amino groups of glucosamines. Heparin<br />
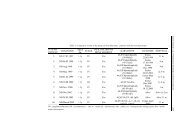
sulfamidase enzyme activities of patient with MPS IIIA in leukocytes is 0,38 nmol/17<br />
h/mg and control subjects is 1,8-6,8 nmol/17 h/mg.<br />
The gene for this enzymes has not been cloned yet. Mucopolysaccharidoses are of special<br />
genetic interest since they show mutation in various loci as well as more than one mutation<br />
in one single locus. Multiple alleles give a similar phenotype but different enzyme<br />
deficiency that results in different products of hydrolysis. This means that DNA diagnosis<br />
(PCR) is made more difficult and therefore making diagnosis of mucopolysaccharidosis<br />
is based on enzyme analyses.