Zbornik - Društvo genetičara Srbije
Zbornik - Društvo genetičara Srbije
Zbornik - Društvo genetičara Srbije
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
V-Usm-2 ZBORNIK ABSTRAKATA III KONGRESA GENETIÈARA SRBIJE 185<br />
Subotica, 30. novembar - 4. decembar 2004.<br />
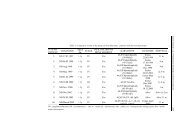
MULTIPLEKS PCR KAO BRZ, SENZITIVAN I SPECIFIÈAN METOD ZA<br />
DETEKCIJU PATOGENIH MIKROORGANIZAMA<br />
Nataša Goliæ, L. Ranin, M. Kojiæ, Ivana Strahiniæ, Ð. Fira, Maja Vukašinoviæ,<br />
Amarela Terziæ-Vidojeviæ, Jelena Begoviæ, Jelena Lozo, Katarina Krstiæ, B. Jovèiæ,<br />
Maja Tolinaèki, Milica Nikoliæ i Lj. Topisiroviæ<br />
Institut za molekularnu genetiku i genetièko inenjerstvo, Beograd<br />
U poslednjih deset godina su razvijene razlièite metode za identifikaciju i tipizaciju<br />
prokariotskih i eukariotskih organizama na DNK nivou. PCR metod omoguæava brzu i<br />
specifiènu detekciju širokog spektra bakterijskih vrsta. Multipleks PCR je brz, senzitivan i<br />
specifièan metod za detekciju patogenih mikroorganizama u jednoj PCR reakciji. Metod je<br />
zasnovan na PCR reakciji u kojoj se koristi nekoliko parova prajmera. Jedan set prajmera je<br />
najèešæe specifièan za vrstu i potièe iz regiona 16S rDNK, te se na osnovu dobijenog<br />
produkta nedvosmisleno detektuje prisustvo specifiènog mikroorganizma. Drugi set<br />
prajmera je obièno specifièan za gene koji su prisutni samo kod patogenih serotipova. PCR<br />
metod je izuzetno senzitivan i moe da detektuje vrlo mali broj patogenih æelija u uzorku<br />
(oko 10 æelija). Štaviše, ovaj metod je brz i rezultati se dobijaju u toku jednog radnog dana.<br />
Dobijeni rezultati su nedvosmilseni. Prednost multipleks PCR metoda je da omoguæuje<br />
detekciju specifiènih mikroorganizama odmah nakon infekcije, pre pojave prvih simptoma<br />
i stvaranja antitela, kao i nakon infekcije kada je titar antitela blizu normalnih vrednosti<br />
(ELISA test). U ovom radu predstavljamo multipleks PCR, kao metod za detekciju Listeria<br />
monocytogenes, Yersinia enterocolitica, Helicobacter pylori, Mycoplasma pneumoniae,<br />
Chlamidia trachomatis, Chlamidia pneumonie, Campilobacter jejuni, Borrelia burgdoferi,<br />
i Brucella sp. iz klinièkih uzoraka.<br />
MULTIPLEX PCR AS A RAPID, SENSITIVE AND SPECIFIC METHOD FOR<br />
DETECTION OF PATHOGEN MICROORGANISMS<br />
In the past decade, various methods have been developed for the identification and typing<br />
of prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms at the DNA level. The PCR approach allows<br />
rapid and specific detection of a wide range of bacterial species. Multiplex PCR is rapid,<br />
sensitive and specific method for detection of pathogen microorganisms in one PCR reaction.<br />
The method is based on PCR reaction in which several sets of primers are used.<br />
One set of primers is usually species specific, originated from 16S rDNA, that<br />
unumbiguos detect the presence of a specific microorganism. The other set of primers is<br />
commonly specific for the genes that are predominantly present in pathogen serotypes.<br />
PCR method is extremely sensitive and very low amount of pathogen cells in the sample<br />
could be detected (aproximatelly 10 cells). Moreover, this method is fast and the analysis<br />
could be completed in one working day. The results obtained by this method are<br />
unambiguos. The most important is that by using the multiplex PCR method it becomes<br />
possible to detect the presence of the specific microorganism immediately after infection,<br />
before the apearence of the first symptoms and the antibody generation, as well as after<br />
the infection when the titer of antibodies is close to referent values (ELISA test). In this<br />
work we describe the multiplex PCRs that are used for detection of Listeria<br />
monocytogenes, Yersinia enterocolitica, Helicobacter pylori, Mycoplasma pneumoniae,<br />
Chlamidia trachomatis, Chlamidia pneumonie, Campilobacter jejuni, Borrelia burgdoferi,<br />
and Brucella sp. from the clinical specimens.