Zbornik - Društvo genetičara Srbije
Zbornik - Društvo genetičara Srbije
Zbornik - Društvo genetičara Srbije
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
IV-Pos-14 ZBORNIK ABSTRAKATA III KONGRESA GENETIÈARA SRBIJE 131<br />
Subotica, 30. novembar - 4. decembar 2004.<br />
GENETIÈKA VARIJABILNOST I KOEFICIJENTI KORELACIJE<br />
NAJVANIJIH AGRONOMSKIH SVOJSTAVA SELEKCIONISANIH<br />
POPULACIJA CRVENE DETELINE (Trifolium pratense L.)<br />
Z. Lugiæ, J. Radoviæ i G. Jevtiæ<br />
Institut za istraivanja u poljloprivredi «SRBIJA», Centar za krmno bilje, Kruševac<br />
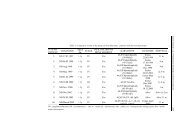
U radu su prikazani osnovni parametri varijabilnosti, kao i genetièki i fenotipski<br />
koeficijenti korelacije dve selekcionisane populacije crvene deteline (A i B) za sledeæe<br />
osobine: prinos suve mase po biljci, visinu biljke, broj izdanaka po biljci, broj internodija<br />
na glavnom izdanku, sadraj sirovih proteina (SSP), sadraj sirove celuloze (SSC) i<br />
sadraj ukupnih šeæera (SUŠ). Varijabilnost pojedinaènih biljaka za sva ispitivana<br />
svojstva je bila visoka i najveæa za prinos suve mase po biljci (CVF 17,78-22,42%) i broj<br />
izdanaka po biljci (CVF 20,74-21,21%). Najnia varijabilnost je konstatovana za visinu<br />
biljke i SSP. Populacija A je ostvarila veæe srednje vrednosti i intervale varijacije za sve<br />
ispitivane osobine. Pozitivne, jake i vrlo znaèajne genetièke korelacije kod populacije A<br />
zabeleene su za prinos suve mase, kao najvaniju osobinu, visinu biljke i SSC (0,776**<br />
i 0,754**). Srednje jake, pozitivne korelacije su konstatovane za prinos suve mase po<br />
biljci i visinu biljke, kao i za SSC i visinu biljke. Korelativni odnos SSP i SUŠ je sa<br />
ostalim svojstvima bio slabo pozitivan do jako i znaèajno negativan. Negativne genetièke<br />
korelacije dobijene su za visinu biljke, broj izdanaka po biljci i SUŠ, dok su visina biljke<br />
i SSP, kao i SSP i SSC bili u znaèajnom negativnom korelativnom odnosu (- 0,404* i<br />
-0,832**). Kod populacije B su dobijene nie vrednosti genetièkih koeficijenata<br />
korelacije, ali su odnosi ispitivanih osobina bili slièni kao kod populacije A. Visoka<br />
varijabilnost pojedinaènih biljaka za sve ispitivane osobine ukazuje na to da su<br />
prouèavane populacije perspektivne za dalje programe oplemenjivanja.<br />
GENETIC VARIABILITY AND COEFFICIENTS OF CORRELATION FOR<br />
AGRONOMIC MOST IMPORTANT TRAITS OF SELECTED POPULATIONS<br />
OF RED CLOVER (Trifolium pratense L.)<br />
The objective of this work was investigation of two selected population of red clover (A<br />
and B). The traits dry matter yield (DMY), plant height, number of tillers per plant, number<br />
of internodes on main shot, crude protein content (CPC), crude fiber content (CFC)<br />
and total sugar content (TSC) was determined during this research. Average values, interval<br />
of variation, coefficient of variation and genetic and phenotypic coefficient of correlations<br />
were calculated for all investigated traits. Plant variability of all traits was very<br />
high and highest for DMY per plant and number of tillers per plant (CVF 17,78-22,42%<br />
and 20,74-21,21%, respectively). Lowest variability is detected for plant height and CPC.<br />
Highest averages and interval of variation were detected for population A. Positive,<br />
strong and high significant genetic coefficient of correlations for population A are estimated<br />
between DMY (most important agronomic trait) and plant height (0,776**) and<br />
between DMY and CFC (0,754**). Correlation coefficients of medium intensity were<br />
calculated for DMY and plant height and for CFC and plant height. Negative genetic correlations<br />
were detected for plant height, number of tillers per plant ant TSC, while plant<br />
height and CPC and CPC and CFC show significant negative coefficient of correlation (-<br />
0,404* i -0,832**, respectively). For population B significantly lower coefficients of correlation<br />
were calculated, but relationships among traits were similar to population A.<br />
High variability of all plants for all examined traits shows that populations are very perspective<br />
for further breeding process.