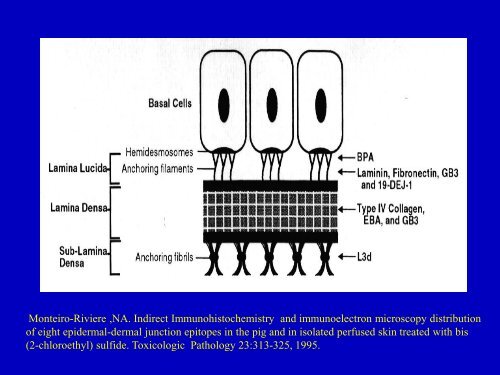
Monteiro-Riviere ,NA. Indirect Immunohistochemistry
Monteiro-Riviere ,NA. Indirect Immunohistochemistry
Monteiro-Riviere ,NA. Indirect Immunohistochemistry
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>Monteiro</strong>-<strong>Riviere</strong> ,<strong>NA</strong>. <strong>Indirect</strong> <strong>Immunohistochemistry</strong> and immunoelectron microscopy distribution<br />
of eight epidermal-dermal junction epitopes in the pig and in isolated perfused skin treated with bis<br />
(2-chloroethyl) sulfide. Toxicologic Pathology 23:313-325, 1995.
<strong>Monteiro</strong>-<strong>Riviere</strong> <strong>NA</strong>: Integument. In Eurell J, Frappier B, eds. Dellman’s Textbook of<br />
Veterinary Histology, Blackwell Publishing, Ames, Iowa, 6 th ed., pp.320-349, 2006.
Experimental Model Systems
• Practicality<br />
• Absorption<br />
Animal Models<br />
• Toxicology - Increased absorption compared to man to<br />
assess worse case scenario<br />
• Rats, Mice, Rabbits<br />
• Pharmacology - Similar absorption to man<br />
• Toxicity<br />
• Pigs, Primates, Hairless Rodents<br />
• Immunological considerations<br />
• Rabbits, Guinea Pigs, Rodents<br />
• Species differences for different mechanisms are<br />
independent ∴one species is not the best model for all<br />
endpoints in humans!
Species Differences<br />
• Anatomical factors such as thickness,<br />
adnexial structures, etc.<br />
• Biochemical differences in lipid<br />
composition, enzymes, etc.<br />
• Different receptors for immunological or<br />
pharmacological agents<br />
• Physiological differences including blood<br />
flow, etc.
Body Site Differences<br />
• The rate of penetration and absorption differs<br />
across various body sites<br />
• Scrotum > Forehead > Axilla > = Scalp > Back =<br />
Abdomen > Palm and Plantar surface<br />
• Seen in humans and animals making route to<br />
route extrapolations “interesting.”<br />
• The major reasons are due to:<br />
– Differences in anatomy:skin thickness<br />
– Differences in physiology: blood flow and distribution<br />
of blood vessels<br />
– Stratum corneocyte cell size ?
Pig Skin is Similar to Human Skin<br />
• Similar surface characteristics<br />
• Body masses and skin to body surface area ratio<br />
• Sparse hair coat<br />
• Thick epidermis<br />
• Hair follicle density<br />
• Epidermal turnover kinetics<br />
• Lipid composition<br />
• Biophysical properties of lipid<br />
I like pigs. Dogs look up to us.<br />
Cats look down on us.<br />
Pigs treat us as equals.<br />
Don’t use skin from an abattoir if hide is scalded!
Differences Between Pig and<br />
Human Skin<br />
• Pig skin has an additional interfollicular<br />
muscle<br />
• Young pigs have hair follicles that occur<br />
in a triad<br />
• Pigs have only apocrine sweat glands over<br />
most of the body<br />
• Immunological and drug metabolism<br />
differences not well characterized
<strong>Monteiro</strong>-<strong>Riviere</strong>, <strong>NA</strong>. Comparative Anatomy, Physiology, and Biochemistry<br />
of Mammalian Skin . In Hobson DW (ed) Dermal and Ocular Toxicology:<br />
Fundamentals and Methods, Boca Raton, FL, CRC Press, Chpt. 1, 3-71, 1991.
Porcine Skin<br />
Stromberg MW, Huang YC, <strong>Monteiro</strong>-<strong>Riviere</strong> <strong>NA</strong>. Interfollicular smooth muscle in the<br />
skin of the domesticated pig. The Anatomical Record 201:455-462, 1981.
Porcine Skin
Human Skin
Monkey Skin
Nude Guinea Pig Skin
Mouse Skin
Nude Mouse
Rat Skin
Rabbit Skin
Cow Skin
Cow Skin
Dog Skin<br />
<strong>Monteiro</strong>-<strong>Riviere</strong> <strong>NA</strong>: Integument. In Eurell J, Frappier B, eds. Dellman’s Textbook of<br />
Veterinary Histology, Blackwell Publishing, Ames, Iowa, 6 th ed., pp.320-349, 2006.
Dog Skin<br />
<strong>Monteiro</strong>-<strong>Riviere</strong> <strong>NA</strong>: Integument. In Eurell J, Frappier B, eds. Dellman’s Textbook<br />
of Veterinary Histology, Blackwell Publishing, Ames, Iowa, 6 th ed., pp.320-349, 2006.
Cat Skin
Cat Skin<br />
<strong>Monteiro</strong>-<strong>Riviere</strong> <strong>NA</strong>: Integument. In Eurell J, Frappier B, eds. Dellman’s Textbook<br />
of Veterinary Histology, Blackwell Publishing, Ames, Iowa, 6 th ed., pp.320-349, 2006.
Cat Foot Pad<br />
<strong>Monteiro</strong>-<strong>Riviere</strong> <strong>NA</strong>: Integument. In Eurell J, Frappier B, eds. Dellman’s Textbook of<br />
Veterinary Histology, Blackwell Publishing, Ames, Iowa, 6th ed., pp.320-349, 2006.
Comparative Epidermal Thickness and Number<br />
of Cell Layers From the Back of Nine Species<br />
Species Epidermis Stratum Corneum Number of Cell Layers<br />
(µm) (µm)<br />
Cat 12.97 + 0.93 5.84 + 1.02 1.28 + 0.13<br />
Cow 36.76 + 2.95 8.65 + 1.17 2.22 + 0.11<br />
Dog 21.16 + 2.55 5.56 + 0.85 1.89 + 0.16<br />
Horse 33.59 + 2.16 7.26 + 1.04 2.50 + 0.25<br />
Monkey 26.87 + 3.14 2.05 + 2.30 2.67 + 0.24<br />
Mouse 13.32 + 1.19 2.90 + 0.12 1.75 + 0.08<br />
Pig 51.89 + 1.49 12.28 + 0.72 3.94 + 0.13<br />
Rabbit 10.85 + 1.00 6.56 + 0.37 1.22 + 0.11<br />
Rat 21.66 + 2.23 5.00 + 0.85 1.83 + 0.17<br />
<strong>Monteiro</strong>-<strong>Riviere</strong> et al. Interspecies and interegional analysis of the comparative<br />
histological thickness and laser Doppler blood flow measurements at five cutaneous<br />
sites in nine species. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 95:582-586, 1990.
Blood Flow Measurements of Nine Species at<br />
Five Cutaneous Sites<br />
Species BUT EAR HSJ TLJ VAB<br />
Cat 1.82 + 0.59 6.46 + 2.30 1.86 + 0.70 2.39 + 0.35 6.19 + 0.94<br />
Cow 6.03 + 1.84 6.98 + 2.19 5.51 + 2.32 5.49 + 1.49 10.49 + 2.13<br />
Dog 2.21 + 0.67 5.21 + 1.53 5.52 + 1.31 1.94 + 0.27 8.78 + 1.40<br />
Horse 3.16 + 1.22 ----- 6.76 + 1.49 2.99 + 0.86 8.90 + 1.46<br />
Monkey 3.12 + 0.58 20.93 + 5.37 8.49 + 3.28 2.40 + 0.82 3.58 + 0.41<br />
Mouse 3.88 + 0.92 1.41 + 0.48 10.10 + 3.51 20.56 + 4.69 36.85 + 8.14<br />
Pig 3.08 + 0.48 11.70 + 3.02 6.75 + 2.09 2.97 + 0.56 10.68 + 2.14<br />
Rabbit 3.55 + 0.93 8.38 + 1.53 5.38 + 1.06 5.46 + 0.94 17.34 + 6.31<br />
Rat 4.20 + 1.05 9.13 + 4.97 6.22 + 1.47 9.56 + 2.17 11.35 + 5.53<br />
Units=ml/min/100g (mean + SE)<br />
But = buttocks; Ear = pinnae; HSJ = humeroscapular joint; TLJ = thoracolumbar junction;<br />
VAB = ventral abdomen.<br />
<strong>Monteiro</strong>-<strong>Riviere</strong> et al. Interspecies and interegional analysis of the comparative histological<br />
thickness and laser Doppler blood flow measurements at five cutaneous sites in nine species.<br />
Journal of Investigative Dermatology 95:582-586, 1990.
Hair Follicle Density<br />
Species Area of Skin Number of Hair<br />
Follicles/cm 2<br />
Human Abdomen 11 + 1<br />
Pig Back 11 + 1<br />
Rat Back 289 + 21<br />
Mouse Back 658 + 38<br />
Hairless Mouse Back 75 + 6<br />
Bronaugh et al. Methods for in vitro percutaneous absorption studies II. Animal<br />
models for human skin. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology 62, 481-488, 1982.