UPGRADING REPAIRING PCs
UPGRADING REPAIRING PCs
UPGRADING REPAIRING PCs
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
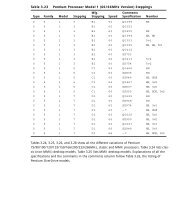
Memory Types 41<br />
transfers to and from a 128-bit memory bus instead of the slower<br />
(100MHz or 66MHz), 32-bit or 64-bit data transfers of SDRAM and<br />
previous memory types.<br />
RDRAM modules are called RIMMs (Rambus Inline Memory Module),<br />
and any unused RIMM slots on a motherboard must be filled with<br />
a continuity module to permit a continuous high-speed data pathway<br />
through the RIMMs (see Figure 2.10). Each RIMM represents<br />
multiple memory banks, and thus a single RIMM at a time can be<br />
added to a system—much the way installation of DIMMs works,<br />
although the memory types are not interchangeable.<br />
1.00 [0.039] 3.00 [0.118]<br />
Detail A<br />
4.00 [0.157]<br />
5.675 [0.2234]<br />
REF.<br />
A-1<br />
+<br />
COMPONENT AREA<br />
(A SIDE)<br />
+<br />
B-1<br />
133.35 +0.15<br />
-0.15 5.250+0.006<br />
-0.006<br />
+<br />
Detail B<br />
1.00[0.039]<br />
11.50[0.453]<br />
4.50[1.772]<br />
45.00[1.777]<br />
27.50[1.083]<br />
45.00[1.772]<br />
+0.08<br />
55.18<br />
-0.08<br />
78.17[3.078]<br />
REF.<br />
2.172+0.003<br />
-0.003<br />
-A-<br />
+<br />
+<br />
COMPONENT AREA<br />
(B SIDE)<br />
+<br />
+<br />
+<br />
B-92<br />
17.78 [0.700]<br />
0.85 [0.033]<br />
4.00 +0.15<br />
-0.15 0.157+0.006<br />
-0.006<br />
-B-<br />
A-92<br />
1.27 +0.10<br />
-0.10<br />
0.050 +0.004<br />
-0.004<br />
+0.10<br />
3.00<br />
-0.10<br />
0.80 +0.10<br />
Detail B<br />
-0.10<br />
TYP. 184 PLCS<br />
0.15 +0.10<br />
-0.10<br />
3XScale<br />
2.99 +0.05<br />
-0.05<br />
Capacitor<br />
CSP<br />
Note: Components<br />
Not Always Present<br />
on B side<br />
0.75-1.35<br />
[0.030-0.053]<br />
-C-<br />
+<br />
3XScale<br />
Figure 2.10 Typical RDRAM bus layout, showing two RIMMs and one<br />
continuity module installed.<br />
DDR SDRAM<br />
Double Data Rate (DDR) SDRAM memory is an improved version of<br />
standard SDRAM in which data is transferred twice as fast. Instead<br />
of doubling the actual clock rate, DDR memory achieves the doubling<br />
in performance by transferring twice per transfer cycle—once<br />
at the leading (falling) and once at the trailing (rising) edge of the<br />
cycle. This is similar to the way RDRAM operates and effectively<br />
doubles the transfer rate, even though the same overall clock and<br />
timing signals are used.<br />
DDR SDRAM is supported by many of the newest server chipsets<br />
and provides a design alternative to the more radical RDRAM. The<br />
DDR Consortium—an industry panel consisting of Fujitsu, Ltd.;<br />
Hitachi, Ltd.; Hyundai Electronics Industries Co.; Mitsubishi<br />
Electric Corp.; NEC Corp.; Samsung Electronics Co.; Texas<br />
Instruments, Inc.; and Toshiba Corp.—undertook official standardization<br />
of DDR.<br />
2.00 +0.10<br />
-0.10<br />
3.99 +0.10<br />
-0.10<br />
DDR-SDRAM uses a new DIMM module design with 184 pins.<br />
Figure 2.11 shows the DDR SDRAM DIMM.