UPGRADING REPAIRING PCs
UPGRADING REPAIRING PCs
UPGRADING REPAIRING PCs
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
8<br />
Chapter 1—General Technical Reference<br />
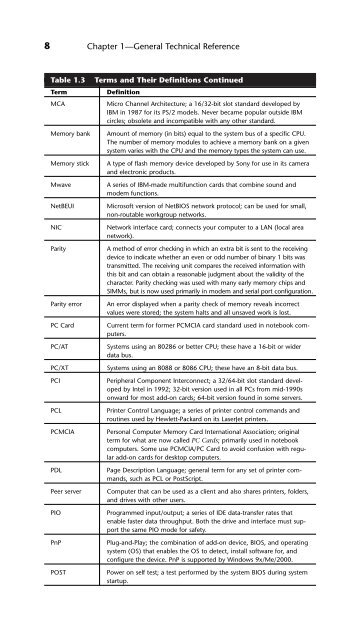
Table 1.3 Terms and Their Definitions Continued<br />
Term Definition<br />
MCA Micro Channel Architecture; a 16/32-bit slot standard developed by<br />
IBM in 1987 for its PS/2 models. Never became popular outside IBM<br />
circles; obsolete and incompatible with any other standard.<br />
Memory bank Amount of memory (in bits) equal to the system bus of a specific CPU.<br />
The number of memory modules to achieve a memory bank on a given<br />
system varies with the CPU and the memory types the system can use.<br />
Memory stick A type of flash memory device developed by Sony for use in its camera<br />
and electronic products.<br />
Mwave A series of IBM-made multifunction cards that combine sound and<br />
modem functions.<br />
NetBEUI Microsoft version of NetBIOS network protocol; can be used for small,<br />
non-routable workgroup networks.<br />
NIC Network interface card; connects your computer to a LAN (local area<br />
network).<br />
Parity A method of error checking in which an extra bit is sent to the receiving<br />
device to indicate whether an even or odd number of binary 1 bits was<br />
transmitted. The receiving unit compares the received information with<br />
this bit and can obtain a reasonable judgment about the validity of the<br />
character. Parity checking was used with many early memory chips and<br />
SIMMs, but is now used primarily in modem and serial port configuration.<br />
Parity error An error displayed when a parity check of memory reveals incorrect<br />
values were stored; the system halts and all unsaved work is lost.<br />
PC Card Current term for former PCMCIA card standard used in notebook computers.<br />
PC/AT Systems using an 80286 or better CPU; these have a 16-bit or wider<br />
data bus.<br />
PC/XT Systems using an 8088 or 8086 CPU; these have an 8-bit data bus.<br />
PCI Peripheral Component Interconnect; a 32/64-bit slot standard developed<br />
by Intel in 1992; 32-bit version used in all <strong>PCs</strong> from mid-1990s<br />
onward for most add-on cards; 64-bit version found in some servers.<br />
PCL Printer Control Language; a series of printer control commands and<br />
routines used by Hewlett-Packard on its LaserJet printers.<br />
PCMCIA Personal Computer Memory Card International Association; original<br />
term for what are now called PC Cards; primarily used in notebook<br />
computers. Some use PCMCIA/PC Card to avoid confusion with regular<br />
add-on cards for desktop computers.<br />
PDL Page Description Language; general term for any set of printer commands,<br />
such as PCL or PostScript.<br />
Peer server Computer that can be used as a client and also shares printers, folders,<br />
and drives with other users.<br />
PIO Programmed input/output; a series of IDE data-transfer rates that<br />
enable faster data throughput. Both the drive and interface must support<br />
the same PIO mode for safety.<br />
PnP Plug-and-Play; the combination of add-on device, BIOS, and operating<br />
system (OS) that enables the OS to detect, install software for, and<br />
configure the device. PnP is supported by Windows 9x/Me/2000.<br />
POST Power on self test; a test performed by the system BIOS during system<br />
startup.