UPGRADING REPAIRING PCs
UPGRADING REPAIRING PCs UPGRADING REPAIRING PCs
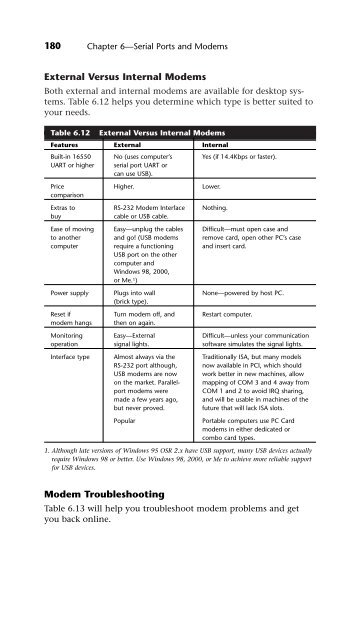
180 Chapter 6—Serial Ports and Modems External Versus Internal Modems Both external and internal modems are available for desktop systems. Table 6.12 helps you determine which type is better suited to your needs. Table 6.12 External Versus Internal Modems Features External Internal Built-in 16550 No (uses computer’s Yes (if 14.4Kbps or faster). UART or higher serial port UART or can use USB). Price comparison Higher. Lower. Extras to RS-232 Modem Interface Nothing. buy cable or USB cable. Ease of moving Easy—unplug the cables Difficult—must open case and to another and go! (USB modems remove card, open other PC’s case computer require a functioning USB port on the other computer and Windows 98, 2000, or Me. and insert card. 1) Power supply Plugs into wall (brick type). None—powered by host PC. Reset if Turn modem off, and Restart computer. modem hangs then on again. Monitoring Easy—External Difficult—unless your communication operation signal lights. software simulates the signal lights. Interface type Almost always via the Traditionally ISA, but many models RS-232 port although, now available in PCI, which should USB modems are now work better in new machines, allow on the market. Parallel- mapping of COM 3 and 4 away from port modems were COM 1 and 2 to avoid IRQ sharing, made a few years ago, and will be usable in machines of the but never proved. future that will lack ISA slots. Popular Portable computers use PC Card modems in either dedicated or combo card types. 1. Although late versions of Windows 95 OSR 2.x have USB support, many USB devices actually require Windows 98 or better. Use Windows 98, 2000, or Me to achieve more reliable support for USB devices. Modem Troubleshooting Table 6.13 will help you troubleshoot modem problems and get you back online.
Table 6.13 Modem Troubleshooting (All Types) Modems 181 Modem Type Problem Solution Any Modem fails to dial. Check line and phone jacks on modem. Line jack—modem to telco service. Phone jack—modem to telephone receiver. If you’ve reversed these cables, you’ll get no dial tone. Check the cable for cuts or breaks. If the cable looks bad, replace it. Make sure your modem has been properly configured by your OS. With Windows 9x, use the Modems icon in Control Panel to view and test your modem configuration. From the General tab, click the Diagnostics tab, click your modem on the serial port it’s installed on, and then click More Info. This sends test signals to your modem. A properly working modem responds with information about the port and the modem. External Modem fails to dial. Make sure the RS-232 modem cable is running from the modem to a working serial port on your computer and that it is switched on. Signal lights on the front of the modem can be used to determine if the modem is on and if it is responding to dialing commands. Make sure a USB modem is plugged tightly into a USB port. If it is connected to an external hub, verify that the hub is connected to your system. PCMCIA/PCCard Modem fails to dial. Make sure it is fully plugged into the PCMCIA/PC Card slot. With Windows 9x/Me, you should see a small PCMCIA/PC card icon on the toolbar. Double-click it to view the cards that are currently connected. If your modem is properly attached, it should be visible. Otherwise, remove it, reinsert it into the PCMCIA/PC card slot, and see if the computer detects it. Check dongle used to attach modem PCMCIA/PC card modems to jack; carry a spare. If your dongle doesn’t have a connector to a standard phone line, use a line coupler to attach the short dongle cable to a longer standard RJ-11 cable for easier use. Carry at least a 10 RJ-11 phone cable with you for easier use in hotel rooms.
- Page 147 and 148: How FDISK and the Operating System
- Page 149 and 150: How FDISK and the Operating System
- Page 151 and 152: Now, the operating system can use t
- Page 153 and 154: The command switches are explained
- Page 155 and 156: MS-DOS Command-Line Access to CD-RO
- Page 157 and 158: • Make sure the drive shows up as
- Page 159: Troubleshooting Optical Drives 141
- Page 162 and 163: 144 Chapter 5—Floppy, Removable,
- Page 164 and 165: 146 Chapter 5—Floppy, Removable,
- Page 166 and 167: 148 Chapter 5—Floppy, Removable,
- Page 168 and 169: 150 Chapter 5—Floppy, Removable,
- Page 170 and 171: 152 Chapter 5—Floppy, Removable,
- Page 172 and 173: 154 Chapter 5—Floppy, Removable,
- Page 174 and 175: 156 • OnStream’s ADR (Advanced
- Page 176 and 177: 158 Chapter 5—Floppy, Removable,
- Page 178 and 179: 160 Table 5.13 High-Performance Tap
- Page 180 and 181: 162 Chapter 5—Floppy, Removable,
- Page 182 and 183: 164 Chapter 5—Floppy, Removable,
- Page 184 and 185: 166 Chapter 6—Serial Ports and Mo
- Page 186 and 187: 168 Table 6.2 25-Pin (PC, XT, and P
- Page 188 and 189: 170 Table 6.4 Overview of UART Chip
- Page 190 and 191: 172 Chapter 6—Serial Ports and Mo
- Page 192 and 193: 174 Chapter 6—Serial Ports and Mo
- Page 194 and 195: 176 Chapter 6—Serial Ports and Mo
- Page 196 and 197: 178 Chapter 6—Serial Ports and Mo
- Page 200 and 201: 182 Chapter 6—Serial Ports and Mo
- Page 202 and 203: 184 Chapter 6—Serial Ports and Mo
- Page 204 and 205: 186 Chapter 6—Serial Ports and Mo
- Page 206 and 207: 188 (These settings require changes
- Page 208 and 209: 190 Chapter 7—Parallel Ports, Pri
- Page 210 and 211: 192 Building a Parallel Loopback Pl
- Page 212 and 213: 194 Chapter 7—Parallel Ports, Pri
- Page 214 and 215: 196 Chapter 7—Parallel Ports, Pri
- Page 216 and 217: 198 Chapter 7—Parallel Ports, Pri
- Page 218 and 219: 200 Chapter 7—Parallel Ports, Pri
- Page 220 and 221: 202 Chapter 7—Parallel Ports, Pri
- Page 222: 204 Chapter 7—Parallel Ports, Pri
180<br />
Chapter 6—Serial Ports and Modems<br />
External Versus Internal Modems<br />
Both external and internal modems are available for desktop systems.<br />
Table 6.12 helps you determine which type is better suited to<br />
your needs.<br />
Table 6.12 External Versus Internal Modems<br />
Features External Internal<br />
Built-in 16550 No (uses computer’s Yes (if 14.4Kbps or faster).<br />
UART or higher serial port UART or<br />
can use USB).<br />
Price<br />
comparison<br />
Higher. Lower.<br />
Extras to RS-232 Modem Interface Nothing.<br />
buy cable or USB cable.<br />
Ease of moving Easy—unplug the cables Difficult—must open case and<br />
to another and go! (USB modems remove card, open other PC’s case<br />
computer require a functioning<br />
USB port on the other<br />
computer and<br />
Windows 98, 2000,<br />
or Me.<br />
and insert card.<br />
1)<br />
Power supply Plugs into wall<br />
(brick type).<br />
None—powered by host PC.<br />
Reset if Turn modem off, and Restart computer.<br />
modem hangs then on again.<br />
Monitoring Easy—External Difficult—unless your communication<br />
operation signal lights. software simulates the signal lights.<br />
Interface type Almost always via the Traditionally ISA, but many models<br />
RS-232 port although, now available in PCI, which should<br />
USB modems are now work better in new machines, allow<br />
on the market. Parallel- mapping of COM 3 and 4 away from<br />
port modems were COM 1 and 2 to avoid IRQ sharing,<br />
made a few years ago, and will be usable in machines of the<br />
but never proved. future that will lack ISA slots.<br />
Popular Portable computers use PC Card<br />
modems in either dedicated or<br />
combo card types.<br />
1. Although late versions of Windows 95 OSR 2.x have USB support, many USB devices actually<br />
require Windows 98 or better. Use Windows 98, 2000, or Me to achieve more reliable support<br />
for USB devices.<br />
Modem Troubleshooting<br />
Table 6.13 will help you troubleshoot modem problems and get<br />
you back online.