You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
700 Chapter <strong>13</strong> Optical Storage<br />
time intervals (usually refered to as 3T) and the maximum spacing between 1s is 11 time intervals<br />
(11T).<br />
Because some of the EFM codes start and end with a 1 or more than five 0s, three additional bits<br />
called merge bits are added between each 14-bit EFM value written to the disc. The merge bits usually<br />
are 0s but might contain a 1 if necessary to break a long string of adjacent 0s formed by the adjacent<br />
14-bit EFM values. In addition to the now 17-bits created for each byte (EFM plus merge bits), a 24-bit<br />
sync word (plus 3 more merge bits) is added to the beginning of each frame. This results in a total of<br />
588 bits (73.5 bytes) actually being stored on the disc for each frame. Multiply this for 98 frames per<br />
sector and you have 7,203 bytes actually being stored on the disc to represent each sector. A 74minute<br />
disc, therefore, really has something like 2.4GB of actual data being written, which after being<br />
fully decoded and stripped of error correcting codes and other information, results in about 682MB<br />
(650MiB) of actual user data.<br />
The calculations for EFM encoded frames and sectors are shown in Table <strong>13</strong>.4.<br />
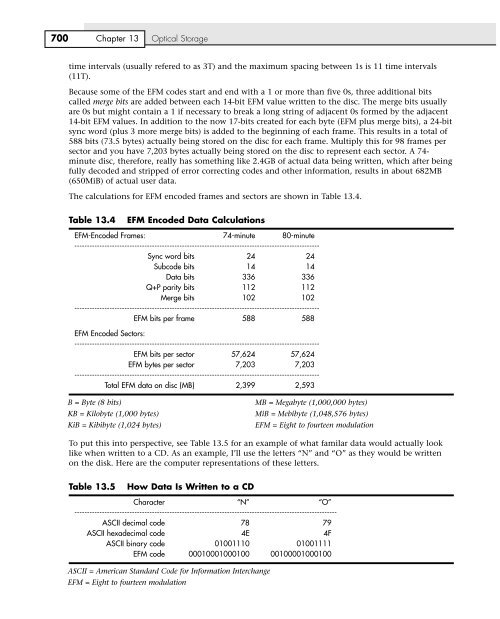
Table <strong>13</strong>.4 EFM Encoded Data Calculations<br />
EFM-Encoded Frames: 74-minute 80-minute<br />
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------<br />
Sync word bits 24 24<br />
Subcode bits 14 14<br />
Data bits 336 336<br />
Q+P parity bits 112 112<br />
Merge bits 102 102<br />
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------<br />
EFM bits per frame 588 588<br />
EFM Encoded Sectors:<br />
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------<br />
EFM bits per sector 57,624 57,624<br />
EFM bytes per sector 7,203 7,203<br />
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------<br />
Total EFM data on disc (MB) 2,399 2,593<br />
B = Byte (8 bits) MB = Megabyte (1,000,000 bytes)<br />
KB = Kilobyte (1,000 bytes) MiB = Mebibyte (1,048,576 bytes)<br />
KiB = Kibibyte (1,024 bytes) EFM = Eight to fourteen modulation<br />
To put this into perspective, see Table <strong>13</strong>.5 for an example of what familar data would actually look<br />
like when written to a CD. As an example, I’ll use the letters “N” and “O” as they would be written<br />
on the disk. Here are the computer representations of these letters.<br />
Table <strong>13</strong>.5 How Data Is Written to a CD<br />
Character “N” “O”<br />
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------<br />
ASCII decimal code 78 79<br />
ASCII hexadecimal code 4E 4F<br />
ASCII binary code 01001110 01001111<br />
EFM code 00010001000100 00100001000100<br />
ASCII = American Standard Code for Information Interchange<br />
EFM = Eight to fourteen modulation