Syllabus - GH Raisoni College Of Engineering
Syllabus - GH Raisoni College Of Engineering
Syllabus - GH Raisoni College Of Engineering
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
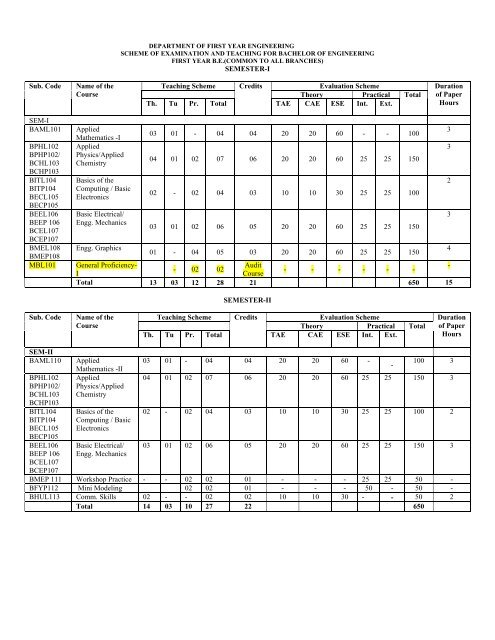
Sub. Code Name of the<br />
Course<br />
SEM-I<br />
BAML101 Applied<br />
BPHL102<br />
BPHP102/<br />
BCHL103<br />
BCHP103<br />
BITL104<br />
BITP104<br />
BECL105<br />
BECP105<br />
BEEL106<br />
BEEP 106<br />
BCEL107<br />
BCEP107<br />
BMEL108<br />
BMEP108<br />
Mathematics -I<br />
Applied<br />
Physics/Applied<br />
Chemistry<br />
Basics of the<br />
Computing / Basic<br />
Electronics<br />
Basic Electrical/<br />
Engg. Mechanics<br />
Engg. Graphics<br />
DEPARTMENT OF FIRST YEAR ENGINEERING<br />
SCHEME OF EXAMINATION AND TEACHING FOR BACHELOR OF ENGINEERING<br />
FIRST YEAR B.E.(COMMON TO ALL BRANCHES)<br />
SEMESTER-I<br />
Teaching Scheme Credits Evaluation Scheme Duration<br />
Theory Practical Total of Paper<br />
Th. Tu Pr. Total TAE CAE ESE Int. Ext.<br />
Hours<br />
03 01 - 04 04 20 20 60 - - 100<br />
04 01 02 07 06 20 20 60 25 25 150<br />
02 - 02 04 03 10 10 30 25 25 100<br />
03 01 02 06 05 20 20 60 25 25 150<br />
01 - 04 05 03 20 20 60 25 25 150<br />
MBL101 General Proficiency-<br />
I<br />
- 02 02<br />
Audit<br />
Course<br />
- - - - - -<br />
-<br />
Total 13 03 12 28 21 650 15<br />
Sub. Code Name of the<br />
Course<br />
SEM-II<br />
BAML110 Applied<br />
BPHL102<br />
BPHP102/<br />
BCHL103<br />
BCHP103<br />
BITL104<br />
BITP104<br />
BECL105<br />
BECP105<br />
BEEL106<br />
BEEP 106<br />
BCEL107<br />
BCEP107<br />
Mathematics -II<br />
Applied<br />
Physics/Applied<br />
Chemistry<br />
Basics of the<br />
Computing / Basic<br />
Electronics<br />
Basic Electrical/<br />
Engg. Mechanics<br />
SEMESTER-II<br />
Teaching Scheme Credits Evaluation Scheme Duration<br />
Theory Practical Total of Paper<br />
Th. Tu Pr. Total TAE CAE ESE Int. Ext.<br />
Hours<br />
03 01 - 04 04 20 20 60 -<br />
-<br />
3<br />
3<br />
2<br />
3<br />
4<br />
100 3<br />
04 01 02 07 06 20 20 60 25 25 150 3<br />
02 - 02 04 03 10 10 30 25 25 100 2<br />
03 01 02 06 05 20 20 60 25 25 150 3<br />
BMEP 111 Workshop Practice - - 02 02 01 - - - 25 25 50 -<br />
BFYP112 Mini Modeling 02 02 01 - - - 50 - 50 -<br />
BHUL113 Comm. Skills 02 - - 02 02 10 10 30 - - 50 2<br />
Total 14 03 10 27 22 650
BAML101 APPLIED MATHEMATICS- I<br />
SEMESTER-I [3L+1T]<br />
Teaching Scheme: Evaluation Scheme: Theory<br />
Lectures: 3 Hrs /Week Teachers Assessment (TAE): 20 Marks<br />
Tutorial: 1 Hr/ Week Class Asses. Exam (CAE) : 20 Marks<br />
Credits: 4 End Semester Exam : 60 Marks<br />
Total: 100 Marks<br />
OBJECTIVE:<br />
To develop mathematical ability of students to comprehend and solve engineering problems.<br />
Differential Calculus [09 Hrs]<br />
Successive differentiation, Taylor’s and Maclaurin’s series for one variable, Indeterminate forms, Curvature and<br />
radius of curvature (excluding Newton’s method), centre of curvature.<br />
Partial Differentiation [06 Hrs]<br />
Partial differentiation, functions of several variables, first and higher order derivatives, Euler’s theorem, chain<br />
rules and total differential coefficient.<br />
Partial Differentiation (Jacobian) [06 Hrs]<br />
Jacobian, Taylor’s and Maclaurin’s series of two variables, maxima and minima of function of two variables,<br />
Lagranges method of undetermined multipliers.<br />
Integral Calculus [08 Hrs]<br />
Beta and Gamma function, Differentiation under integral sign, Tracing of curves (Cartesian and polar curves),<br />
Quadrature, volumes and Surface of solids of revolutions (Cartesian, polar and parametric forms).<br />
Differential Equations [08 Hrs]<br />
First order first degree differential equations, Linear, Reducible to linear and exact differential equations<br />
(excluding the case of integrating factor), Higher order linear differential equations with constant coefficients<br />
upto method of variation of parameters.<br />
Differential Equations (Applications) [08 Hrs]<br />
Cauchy’s and Legendre’s homogeneous differential equations, Simultaneous differential equations, Special<br />
types of differential equations. Application of differential equations to electric circuits, Kinematics and<br />
vibrations (only up to second order).<br />
TEXT BOOK:<br />
Higher <strong>Engineering</strong> Mathematics, RAMANNA,TMG<br />
REFERENCE BOOKS:<br />
1.Higher <strong>Engineering</strong> Mathematics, Grewal B.S, Khanna Publishers, 2004 - Thirty eighth Edition<br />
2.Kreyszig, E.: Advanced Engineeing Mathematics (Eighth Edition); John Wiley & Sons; 2000.<br />
3.Jain, R.K. and Iyengar, S.R.K.; Advanced <strong>Engineering</strong> Mathematics; Narosa Publishers; 2003.<br />
4.Text book of <strong>Engineering</strong> Mathematics : Bali Iyengar (Laxmi Prakashan)<br />
5.Spiegel, M. R.: Advanced Mathematics for Engineers and Scientists ; McGraw-Hill Book Company ; 2000.<br />
6.Applied Mathematics Volume 1: J. N. Wartikar & P. N. Wartikar<br />
7.<strong>Engineering</strong> Mathematics: H. K. Dass, S. Chand, Publication, New Delhi
BAML110 APPLIED MATHEMATICS-II<br />
SEMESTER-II [3L+1T]<br />
Teaching Scheme: Evaluation Scheme: Theory<br />
Lectures: 3 Hrs /Week Teachers Assessment (TAE): 20 Marks<br />
Tutorial: 1 Hr/ Week Class Asses. Exam (CAE) : 20 Marks<br />
Credits: 4 End Semester Exam : 60 Marks<br />
Total: 100 Marks<br />
OBJECTIVE:<br />
To develop mathematical ability of students to comprehend and solve engineering problems.<br />
Multiple Integral [08 Hrs]<br />
Elementary double integrals, change of variables, change of order of integration (Cartesian and polar),<br />
applications to mass, area, volume and center of gravity (Cartesian and polar), elementary triple integrals.<br />
Vector Calculus [07 Hrs]<br />
Scalar triple product, Vector triple product, quadruple product of vectors, differentiation of vectors, Gradient of<br />
scalar point function, Directional derivatives, Divergence and Curl of vector point function, solenoidal motion<br />
and irrotational motion,<br />
Vector Calculus (Integration) [08 Hrs]<br />
Vector integration, line, surface and volume integrals, Stoke’s theorem (without proof), Gauss divergence<br />
theorem, Green’s theorem in plane, Green’s identities and their simple applications.<br />
Infinite sequences and Series. [08 Hrs]<br />
Infinite sequences and series of real and complex numbers, improper integrals, Cauchy criterion, tests of<br />
convergence, absolute and conditional convergence, series of functions, improper integrals depending on a<br />
parameter, uniform convergence, power series, radius of convergence.<br />
Matrices-I [07 Hrs]<br />
Inverse of matrix by adjoint method & its use in solving simultaneous equations. Rank of matrix, consistency of<br />
system of equations, linear dependence, linear & orthogonal transformations, inverse of matrix by partitioning<br />
method<br />
Matrices-II [07 Hrs]<br />
Characteristics equation, eigen values & eigen vectors, reduction to diagonal form, Cayley-Hamilton theorem<br />
(statement & verification), Sylvester’s theorem, association of matrices with linear differential equations of<br />
second order with a constant coefficients.<br />
TEXT BOOK:<br />
Higher <strong>Engineering</strong> Mathematics, RAMANNA,TMG<br />
REFERENCE BOOKS:<br />
1Higher <strong>Engineering</strong> Mathematics, Grewal B.S, Khanna Publishers, 2004 - Thirty eighth Edition<br />
2Kreyszig, E.: Advanced Engineeing Mathematics (Eighth Edition); John Wiley & Sons; 2000.<br />
3Jain, R.K. and Iyengar, S.R.K.; Advanced <strong>Engineering</strong> Mathematics; Narosa Publishers; 2003.<br />
4Text book of <strong>Engineering</strong> Mathematics : Bali Iyengar (Laxmi Prakashan)<br />
5Spiegel, M. R.: Advanced Mathematics for Engineers and Scientists ; McGraw-Hill Book Company ; 2000.<br />
6Applied Mathematics Volume 1: J. N. Wartikar & P. N. Wartikar<br />
7<strong>Engineering</strong> Mathematics: H. K. Dass, S. Chand, Publication, New Delhi
BPHL102 APPLIED PHYSICS<br />
SEMESTER-I & II [4L+1T+2P]<br />
Teaching Scheme: Evaluation Scheme: Theory<br />
Lectures: 4 Hrs /Week Teachers Assessment (TAE): 20 Marks<br />
Tutorial : 1 Hr/ Week Class Asses. Exam (CAE) : 20 Marks<br />
Practical: 2 Hrs /Week End Semester Exam (ESE) : 60 Marks<br />
Credits: 6 Total: 100 Marks<br />
Evaluation Scheme: Practical<br />
Practical Work Exam (PWE): 50 Marks<br />
OBJECTIVE:<br />
Physics is the mother of all engineering subjects. Physics has made tremendous impact on the technological<br />
growth of the world. Teaching physics to engineers is to equip them with understanding of scientific methods to<br />
achieve their higher pursuit.<br />
Quantum Mechanics (12 Hrs)<br />
Compton Effect, Wave – particle duality, de Broglie wavelength, Davisson-Germer experiment; Heisenberg’s<br />
uncertainty principle, Phase velocity, group velocity, Concept of a wave packet; Wave function and its<br />
probability interpretation; Schrödinger’s wave equation; Infinite potential well; Qualitative nature of the wave<br />
function for finite potential well; Tunneling<br />
Semiconductor Physics (12 Hrs)<br />
Qualitative ideas on formation of electron energy bands in solids; Classification of solids into insulators,<br />
semiconductors and conductors; Fermi energy; Intrinsic semiconductors; Energy band diagrams of silicon and<br />
germanium and their comparison with band diagrams of carbon (diamond) and sodium; Extrinsic<br />
semiconductor; Dependence of Fermi energy on temperature and doping concentration(Qualitative analysis);<br />
Current conduction in a semiconductor; Hall effect, p-n junction diode; Diode rectifier equation; Zener diode,<br />
Avalanche and Zener Break Down mechanisms, LED<br />
Lasers (10 Hrs)<br />
Laser characteristics; spontaneous and stimulated emission of radiation; Population inversion; Three and four<br />
level laser schemes, optical resonator, Expressions for coherence length and coherence time, Outline of<br />
construction of Ruby and He-Ne laser, Semiconductor Laser<br />
Wave Optics (08 Hrs)<br />
Interference in thin films of uniform & non-uniform thickness, Anti-reflection coating, Polarization & its type;<br />
Polarization by reflection; Polarization of scattering, Malu’s law, Optic axis, Double refraction in a quartz<br />
prism, Quarter- and Half-wave plates, Production & Detection of Linear, Circular, Elliptical polarizations<br />
Electron Ballistics (12 Hrs)<br />
Motion of charges in uniform electric and magnetic fields; Electron optics: Bethe’s law; Electrostatic and<br />
magneto static focusing; Devices: CRT, CRO and Cyclotron<br />
Advanced Trends in Physics (06 Hrs)<br />
TEXT BOOK:<br />
<strong>Engineering</strong> Physics by Avadhanulu and Kshirsagar, S Chand and Company- Fifth Revised Edition
REFERENCE BOOKS:<br />
1. Fundamentals of Physics, Sixth Edition by David Halliday, Robert Resnick and Jerle Walker; John-<br />
Wiley and Sons.<br />
2. Fundamentals of Physics by David Halliday, Robert Resnick and Jerle Walker; John- Wiley and Sons<br />
2002.<br />
3. Quantum Mechanics by Shief,Tata MCGraw Hill<br />
4. Modern Physics by Baiser, Tata MCGraw Hill<br />
5. Lasers & Non Linear Optics by B B Laud, New Age Publication.<br />
6. Electronic <strong>Engineering</strong> Material and Devices by: John Allison (TMH)<br />
7. Lasers Theory and Application by Avadhanulu, S Chand and Company<br />
BPHP102 Term Work: Any Eight experiments<br />
1. Determination of band gap of a semiconductor.<br />
2. Determination of Activation energy of Thermister.<br />
3. Determination of band gap by Four Probe Method.<br />
4. Determination of Hall coefficient.<br />
5. V-I characteristics of ordinary and Zener diodes.<br />
6. Study of Zener diode as voltage regulator.<br />
7. Determination of e/m by Thomson method.<br />
8. Determination of Wavelength by Newton’s rings.<br />
9. Refractive index of transparent liquid by Newton’s ring.<br />
10. Determination of Thickness of Foil.<br />
11. Use of half-wave and quarter-wave plates to demonstrate idea of polarization.<br />
12. Determination of refractive indices of double image prism.<br />
13. Determination of Brewster’s angle and refractive index for glass surface.<br />
14. To verify Malu’s Cosine square law using for plane polarized light.<br />
15. An experiment based on laser.<br />
16. Determination of Amplitude & Frequency of ac signal by CRO.<br />
17. Determination of phase by dual trace CRO.<br />
18. Open ended experiment.
BCHL103 APPLIED CHEMISTRY<br />
SEMESTER-I & II [4L+1T+2P]<br />
Teaching Scheme: Evaluation Scheme: Theory<br />
Lectures: 4 Hrs /Week Teachers Assessment (TAE): 20 Marks<br />
Tutorial : 1 Hr/ Week Class Asses. Exam (CAE) : 20 Marks<br />
Practical: 2 Hrs /Week End Semester Exam (EAE) : 60 Marks<br />
Credits: 6 Total: 100 Marks<br />
Evaluation Scheme: Practical<br />
Practical work Exam (PWE): 50 Marks<br />
OBJECTIVE:<br />
To develop individuals who are brimming with originality deep learning about chemistry. The program will also<br />
develop ability to solve problems and enables them to understand engineering applications.<br />
Water Technology: - (14 Hrs)<br />
Hardness of water, methods of Softening of water, chemical calculation for softening of water. Boiler troubles<br />
and internal conditioning of boiler feed water, desalination of sea water by membrane process. BIS<br />
Specification for water. Purification of water for domestic uses.<br />
Lubricants: - (08 Hrs)<br />
Introduction, mechanism of lubrication, Types of lubricants, testing of lubricants for i) Viscosity & Viscosity<br />
index, ii) Flash point & Fire point iii) Carbon residue & iv) Cloud & pour point, Criteria for selection of<br />
lubricants for I.C. engines, cutting tools, gears and transformers<br />
A Corrosion Science:- (06 Hrs)<br />
Principles of Corrosion, Galvanic Series, Galvanic Corrosion, Concentration Cell Mechanisms of atmospheric<br />
corrosion and wet corrosion, factors affecting corrosion, Differential aeration theory, Methods of prevention of<br />
corrosion.<br />
Fuel and Combustion calculations: - (14 Hrs)<br />
Calorific value of fuel and its determination, Solid fuels: Ultimate analysis of coal. Liquid fuels- Fractional<br />
distillation, cracking: Fluid bed Catalytic Cracking, Knocking in IC engine and its relation with chemical<br />
structure of fuel. Synthesis of Synthetic petrol, Gaseous fuels –LPG & CNG, Significance of flue gas analysis<br />
and Combustion calculation.<br />
Environmental Chemistry and Battery Technology : - (06 Hrs)<br />
Pollution and its control- Air pollution ,water pollution-BOD and COD- sewage water and its treatment,<br />
Conversion and Storage of Electrochemical Energy:- Batteries- Basic concepts, Classification and types of<br />
batteries (Lead acid battery, Rechargeable battery: Lithium ion, Fuel Cells)<br />
Advances in <strong>Engineering</strong> Chemistry (06 Hrs)<br />
TEXT BOOK:<br />
<strong>Engineering</strong> Chemistry by S. S. Dara, S. Chand & Co Pub. Ltd, Tenth Edition
REFERENCE BOOKS:<br />
1. <strong>Engineering</strong> Chemistry by Jain and Jain<br />
2. Chemistry in <strong>Engineering</strong> and Technology vol .II by J.Rajaram and J.C.Kuriakose<br />
3. Text Book of Engg. Chemistry by Shashi Chawla<br />
4. Chemistry of <strong>Engineering</strong> Material by Leighou<br />
5. <strong>Engineering</strong> Material, Venneth G. Budinski (Prentice – Hall of India).<br />
6. Polymer Science, V. R. Gowarikar (Wiley Eastern Ltd.)<br />
7. Environmental Chemistry, A. K. De (New Age International Publishers).<br />
8. Fundamentals of <strong>Engineering</strong> Chemistry (Theory and Practical ), S. K. Singh (New Age International<br />
Publishers)<br />
BCHP103 Term Work: Any Eight experiments<br />
1. Estimation of Total hardness in water by EDTA.<br />
2. Estimation of calcium hardness in water by EDTA.<br />
3. Estimation of Ni ++ in given sample by complexo metric titration.<br />
4. Estimation type & extent of alkalinity of given water sample by Warder’s method.<br />
5. Estimation of Dissolved oxygen in given water sample.<br />
6. Estimation of Fe ++ , Fe +++ and total iron present in the given alloy.<br />
7. Estimation of amount of Copper by Iodometric titration.<br />
8. Removal of hardness by Ion Exchange resin column<br />
9. Determination of Moisture, Volatile Matter and Ash Content of given coal sample by proximate Analysis.<br />
10. Determination of viscosity of lubricating oil at different temperatures by Redwood Viscometer.<br />
11. Determination of flash point of lubricating oil by Penskey Marten’s / Abels closed –cup apparatus.<br />
12. Determination of Acid value of given lubricating oil.<br />
13. Determination of Saponification number of given lubricating oil.<br />
14. Determine Aniline point of lubricating oil.<br />
15. Determination of Carbon residue of lubricating oil by Conradsons apparatus.<br />
16. Determination of Free Chlorine in Potable Water.<br />
17. Demonstration<br />
a) Determination of COD(Chemical Oxygen Demand) of sample of water<br />
b) Determination of calorific value by Bomb Calorimeter apparatus.<br />
c) Preparation of Phenol Formaldehyde resin<br />
d) Determination of pH.<br />
18. Open ended experiment.<br />
Laboratory Manual:<br />
1. Laboratory Manual on <strong>Engineering</strong> Chemistry by Dr. Sudharani (Dhanpat Rai Publishing Company).<br />
2. Applied Chemistry Theory and Practical O. P. Virmani and A. K. Narula (New Age International<br />
Publishers).<br />
3. A textbook of Experiments and calculation in <strong>Engineering</strong> Chemistry. By Dr. S. S. Dara
BITL104 BASICS OF COMPUTING<br />
SEMESTER-I/II [2L+2P]<br />
Teaching Scheme: Evaluation Scheme: Theory<br />
Lectures: 2 Hrs /Week Teachers Assessment (TAE): 10 Marks<br />
Practical: 2 Hrs /Week Class Asses. Exam (CAE): 10 Marks<br />
Credits: 3 End Semester Exam: 30 Marks<br />
Total: 50 Marks<br />
Evaluation Scheme: Practical<br />
Practical work Exam (PWE): 50 Marks<br />
OBJECTIVE:<br />
To make the student aware about computer fundamentals & enhance the C programming skills of students.<br />
Operating Systems: Introduction, Windows, Linux-Basic command. Computer Networks: Introduction, Peer<br />
to peer connection, LAN, MAN, WAN, Internet, Wireless network.<br />
C Fundamentals: Algorithm, Flowchart, Program development steps, Basic structures of C language, C<br />
tokens. Data types, Declaration of variables. Assigning values, Arithmetic, Relational and logical operators.<br />
Increment and Decrement operators. Control operators, Expressions, Evaluation. I/O operations, If and<br />
SWITCH statements. WHILE, DO-WHILE and FOR Statements. Programming Examples under linux.<br />
Arrays, string & structure<br />
One and Two Dimensional Arrays, Initialization, String variables, Declaration, Reading, Writing, String<br />
handling functions, User defined functions, Variables and storage classes. Recursion, Preprocessor, Structure<br />
definition. Initializing, Assigning values, Passing of structure as arguments, Unions, Programming Examples.<br />
Pointers & File management<br />
Declaration and initializing pointers, Pointer based expressions, Arrays, Strings. FtmGt.iol1s and structures, C<br />
program examples, File management in C, Opening and closing, I/0 operations on files. Programming<br />
Examples.<br />
Enumerated Data types & Functions<br />
Enumerated data types, Renaming data types with typedef( ), Type casting, Bit wise operators. and bit<br />
manipulation. pointer to pointer, Pointers to functions, Functions Returning pointers, Functions with variable<br />
number of arguments, Dynamic memory aliocation. Programming Examples.<br />
TEXT BOOK:<br />
Programming in ANSI C by E. Balguruswami- Tata-Mcgraw Hill- Third Edition<br />
REFERENCE BOOKS:<br />
1. UNIX & shell Programming, Yeshavant Kanetkar, BPB Publication.<br />
2. Introduction to Unix & Shell Programming, M.G. Venkateshmurthy , Pearson Education.<br />
1. Unix Systems V.4 Concepts & Application , Das , Tata Mcgraw Hill<br />
2. Computer fundamentals & programming in C ,Oxford Press, Pradip Dey, Manas Ghosh<br />
3. The C Programming Language by Kerningham amd et.al.<br />
4. LET US C by Y. C. Kanetkar<br />
BITP104 Term Work: Any Eight experiments
1) To study File structure, commands of Linux & features of Linux operating system.<br />
2) To study Directory structure & commands of Linux operating system.<br />
3) To study user connections & communication channels.<br />
4) Write a program to solve a quadratic equation.<br />
5) Write a program to prepare pay bill for the employees of a company.<br />
6) Write a program to print the Fibonacci series for any number of terms.<br />
7) Write a program to delete any element from any array.<br />
8) Write a program to copy the value of one string variable to another variable.<br />
9) Write a program to check whether any given word is a palindrome or not.<br />
10) A company maintains the record of their employees as: Name, designation, Details of the pay like<br />
Gross pay, Provident Fund deductions, Professional tax and the Net pay. Keep the details of the pay<br />
within a separate structure<br />
11) Accept ten names and print the given names in opposite order using array of pointers.<br />
12) A program to search data from any array.<br />
13) Open ended experiment.
BECL105 BASIC ELECTRONICS<br />
SEMESTER-I/II [2L+2P]<br />
Teaching Scheme: Evaluation Scheme: Theory<br />
Lectures: 2 Hrs /Week Teachers Assessment (TAE): 10 Marks<br />
Practical: 2 Hrs /Week Class Asses. Exam (CAE): 10 Marks<br />
Credits: 3 End Semester Exam: 30 Marks<br />
Total: 50 Marks<br />
Evaluation Scheme: Practical<br />
Practical work Exam (PWE): 50 Marks<br />
OBJECTIVE:<br />
To teach basic principals of few electronic devices and their applications.<br />
Bipolar Junction Transistor and its applications (12 Hours)<br />
Transistor action, BJT configurations: CE, CC, CB with normal biasing, DC load line, Single stage CE<br />
transistor as amplifier, I/P and O/P impedance, Practical amplifier biasing, RC coupled single stage Amplifier,<br />
frequency response and bandwidth, BJT as a switch<br />
Digital Electronics Fundamentals (12 Hours)<br />
Boolean Algebra, Boolean Identities, Logic Problems, Binary, Gray, Octal, Hex & ASCII codes, Gates and their<br />
truth tables, D Morgan’s Laws, Sum of products & Product of Sums. Logic families: TTL, ECL, CMOS etc,<br />
Properties of logic gates, Arithmetic Circuits-Adders, Subtractors, (Half & Full), Simplification of sum of<br />
products and products of sum, Implementation of expressions with universal gates, Karnaugh Map, Solution to<br />
problems using K-Maps Properties, Quine Macklousky method<br />
Combinational circuit design (12 Hours)<br />
Fast adders (carry look ahead, parallel adder), Sequential circuits, Flip flops, registers, counters, Multiplexers,<br />
Demultiplexers, encoder, decoder, comparators<br />
Advanced Trends in Basics of Electronics<br />
TEXT BOOKS:<br />
1. Electronics Devices and Circuit Theory, Robert Boylstad & Louis Nashel sky, PHI Pub. - Tenth Edition<br />
2. Digital Electronics by R P Jain (McGraw Hill)- Fourth Edition<br />
REFERENCE BOOKS:<br />
1. Electronics Principles: Malvino, PHI.<br />
2. Devices & Circuits: Allen Mottershed, PHI.<br />
3. Electronics Devices And Circuits By-Millman And Halkies<br />
4. Digital Logic and Computer Design: Morris Mano (PHI)<br />
5. Digital Electronic Principles- Malvino PHI<br />
6. Digital Integrated Electronics by Taub H. (McGraw Hill)<br />
7. Digital Circuits & Microprocessors by Taub H. (McGraw Hill)<br />
8. Digital Communication Lee S C (Wiley)
BECP105 Term Work: Any Eight experiments<br />
1) Study of Transistor in CB & CE mode<br />
2) CE transistor as amplifier Study of various logic gates<br />
3) Study of various gates<br />
4) Implementation of expressions with universal gates<br />
5) Study of Half adder & Full adder<br />
6) Study of fast adders<br />
7) Design of JK Flip flops using SR Flipflop<br />
8) Design of T flip flop using JK Flip flops<br />
9) Design of D flip flop using JK Flip flops<br />
10) Design of Multiplexers<br />
11) Design of Demultiplexers<br />
12) Design of Decade counter<br />
13) Study of Register types<br />
14) Study of Encoder<br />
15) Study of Decoder<br />
16) Study of Comparators<br />
17) Open ended experiment.
BEEL106 BASIC ELECTRICAL<br />
SEMESTER-I & II [3L+1T+2P]<br />
Teaching Scheme: Evaluation Scheme: Theory<br />
Lectures: 3 Hrs /Week Teachers Assessment (TAE): 20 Marks<br />
Tutorial : 1 Hr/ Week Class Asses. Exam (CAE) : 20 Marks<br />
Practical: 2 Hrs /Week End Semester Exam (ESE) : 60 Marks<br />
Credits: 5 Total: 100 Marks<br />
Evaluation Scheme: Practical<br />
Practical Work Exam (PWE): 50 Marks<br />
OBJECTIVE:<br />
This Subject Introduces Basic Concept/Component used in Electrical Systems, Behavior of this components<br />
when subjected to different circuits (AC/DC) is also taught. This lays down foundation to learn further in higher<br />
semester subjects and to understand the applications.<br />
Electric Circuits (08 Hrs )<br />
Circuits Elements(R, L, C), Kirchhoffs Laws, Superposition Theorem , Voltage source, (definition,<br />
characteristics of practical source, equivalent current source) Star-Delta transformation. Magnetic circuits :<br />
Flux, mmf, reluctance, analogous electric circuits, simple calculations for composite magnetic circuits.<br />
A. C. Circuits (09 Hrs)<br />
Periodic functions, average & rms values, Steady state behaviors with sinusoidal excitation, phasor<br />
representation, reactances and impedance, series and parallel A.C. circuits, resonance, power in A.C.circuits,<br />
power factor, Principle of generation of single phase & Three phase voltages. Power in balanced three phase A.<br />
C. systems.<br />
Electrical Measurements (08 Hrs)<br />
Deflecting, controlling and damping mechanisms. Ammeters and voltmeters of permanent magnet moving coil<br />
type, electrodynamometer type, Wattmeter, Induction type single phase, Extension of Instrument range.<br />
Single Phase Transformers (10 Hrs)<br />
Introduction, Basic principles, construction phasor diagram for transformer under no load, Transformer on load,<br />
Balance of mmf on two sides, Phasor diagram, Equivalent circuit, Losses, Efficiency, Regulation, Open-circuit<br />
& short-circuit tests.<br />
D.C.Machines (08 Hrs)<br />
Introduction, construction, EMF and Torque equation, classification, self-excitation of d. c. shunt generators,<br />
EMF, voltage, current relations in generator and motor, Characteristics, starting and speed control of d. c.<br />
motors.<br />
Introduction to AC Motors (07 Hrs)<br />
Construction, rotating field, synchronous speed, Rotor current, torque and slip, Principle of Single phase<br />
Capacitor Start motor, Universal motor.<br />
TEXT BOOK:<br />
A Textbook of Basic Electrical <strong>Engineering</strong> by S.B. Bodkhe, N.M.Deskar, Professional Pub. House Pvt. Ltd.<br />
REFERENCE BOOKS:<br />
1. Introduction to Electrical <strong>Engineering</strong> by Naidu, Kamakshaiah, Tata McGraw Hill.<br />
2. Basic Electrical <strong>Engineering</strong> by H. Cotton.
3. A Textbook of Electrical <strong>Engineering</strong> Electrical <strong>Engineering</strong> Vol. I & II by B.L.Theraja, S. Chand & Co.<br />
4. Laboratory courses in Electrical Engg, S G Tarnekar, P K Kharbanda, S B Bodkhe, S D Naik, Chand & Co.<br />
5. Electric Machinery by Nagrath, Kothari, Tata McGraw Hill.<br />
BEEP106 TERM WORK: Any Eight experiments<br />
LIST OF EXPERIMENT<br />
1. Introduction to Basic Electrical <strong>Engineering</strong> Laboratory/Equipment/Meters<br />
2. To Verify Superposition Theorem.<br />
3. To Determine Resistance and Inductance of Choke Coil.<br />
4. To Plot B-H Curve of Magnetic Material.<br />
5. To Plot Phasor Diagram of R-L-C Series Circuit.<br />
6. To Study Resonance in R-L-C Series Circuit.<br />
7. To Study resonance in Parallel circuit.<br />
8. To Study improvement of Power Factor by Capacitor.<br />
9. To Find Efficiency and Regulation <strong>Of</strong> Single Phase Transformer By O/C & S/C Test.<br />
10. Verification of Line Voltage and Phase Voltage in Three Phase Star Connected Balanced Load.<br />
11. To Observe Reversal of Three Phase Induction Motor.<br />
12. Speed Control of Dc Shunt Motor.<br />
13. Open ended experiment.
BCEL107 ENGINEERING MECHANICS<br />
SEMESTER-I & II [3L+1T+2P]<br />
Teaching Scheme: Evaluation Scheme: Theory<br />
Lectures: 3 Hrs /Week Teachers Assessment (TAE): 20 Marks<br />
Tutorial : 1 Hr/ Week Class Asses. Exam (CAE) : 20 Marks<br />
Practical: 2 Hrs /Week End Semester Exam (ESE) : 60 Marks<br />
Credits: 5 Total: 100 Marks<br />
Evaluation Scheme: Practical<br />
Practical Work Exam (PWE): 50<br />
OBJECTIVE:<br />
The purpose of mechanics is to explain and predict physical phenomena and thus to lay the foundations for<br />
engineering applications.<br />
Fundamentals of Statics: 01 Hr<br />
Definition of mechanics, Body, Rigid Body, Scalar quantities, Vector quantities, Representation of vector,<br />
Fundamental Units, Derived Units, Particle, Mass, Weight, Fundamental principles of mechanics, Newton’s law<br />
of universal gravitation.<br />
Equivalent Force System (2-D): 04 Hrs<br />
Concept of Force, Unit Newton force, System of force, Principle of transmissibility of force, Resolution and<br />
composition of coplanar force system, Resultant, Equilibrant, Law of parallelogram of force, Triangle law,<br />
Polygon law, Moment of force, Varignon’s theorem, Couple and it’s properties, Reduction of system of forces<br />
into a force couple system. Numericals on equivalent force involving co-planer force systems acting on body,<br />
Numericals on reduction of system of forces into a force couple system.<br />
Equilibrium of Two Dimensional Force System` 02 Hrs<br />
Force System :<br />
Concept of equilibrium, Principles of equilibrium, Equations of Equilibrium, Lami’s theorem, Numericals on<br />
equilibrium involving co-planer force systems acting on body.<br />
Equilibrium of Two Dimensional Force System: 06 Hrs<br />
Beam:<br />
Beam, Simply Supported Beam, Overhanging Beam, Beam reaction, Types of load acting over beam i.e.<br />
Concentrated load, Uniformly distributed load (UDL), Uniformly varying load (UVL), Types of support i.e.<br />
Simple support, Hinge support, Roller Support, Numericals on reaction of beam subjected to combination of<br />
loads.<br />
Analysis of Truss :<br />
Perfect Frame, Imperfect frame, Deficient frame, Redundent frame, Assumptions made in analysis of truss,<br />
Method of joints, Method of sections, Numericals on forces in the members of a truss.<br />
Spatial Force System (Three Dimensional Force System ) : 08 Hrs<br />
Component of force in a space, Resultant of spatial force system, Force multiplier, Cartesian form of<br />
representation of vector, Unit vector, Position vector, Displacement Vector, Scalar product or Dot product,<br />
Vector product or Cross product, Length of common perpendicular between two non intersecting vectors,
Shortest distance, Moment of force about point, Moment of force about axis, Moment arm of force about point,<br />
Moment arm of force about axis, Resultant moment, Couple<br />
Friction: 03 Hrs<br />
Definition of friction, Types of friction, Angle of repose, Coulombs laws of dry friction, Analysis of rigid<br />
bodies on rough inclined surfaces<br />
Properties of Areas: 04 Hrs<br />
Centroid of plane areas, Moment of Inertia of composite lamina, Radius of gyration, Second moment of area,<br />
Product of inertia, Parallel axis theorem, Perpendicular axis theorem, Polar moment of inertia, Moment of<br />
inertia & product of inertia about new axes, Principal moment of inertia and principal axis direction by<br />
analytical method only<br />
Virtual Work: 03 Hrs<br />
Virtual Displacement, Definition of virtual work, Principles of virtual work, Virtual work method applied to<br />
beams, frames & mechanisms.<br />
Kinematics: 03 Hrs<br />
Motion curves, Rectangular components of acceleration, Normal & tangential components of acceleration<br />
Kinetics: 03 Hrs<br />
Kinetics of rectilinear and circular motion of a particle acted upon by a constant and variable force system.<br />
D’Alembert’s principle, Concept of dynamic equilibrium, Rectilinear motion of interconnected bodies /<br />
particles. (Limited to two interconnected bodies).<br />
Impulse and Momentum: 03 Hrs<br />
Linear impulse, Linear momentum, Momentum equation for a particle and a system of particles, Direct central<br />
impact, Coefficient of restitution.<br />
Simple Stress & Strain: 05 Hrs<br />
Elasticity, Elastic body, Plastic body, Rigid body, Perfectly elastic body, Partially elastic body, Axial loading.<br />
Stress, Strain, Tensile stress & strain, Compressive Stress & Strain, Elastic limit, Hook’s law, Stress strain<br />
curve, Working stress, Allowable ( safe ) stress, Factor of safety, Principle of superposition, Numerical on bar<br />
of different sections with uniform materials, Natural deformation, Thermal stress & strain in homogeneous bars.<br />
TEXT BOOK:<br />
<strong>Engineering</strong> Mechanics: F. L. Singer, Harper Publication- Third Edition<br />
REFERENCE BOOKS:<br />
1. Vector Mechanics for Engineers : Beer & Johnston, Tata McGraw Hill Company.<br />
2. <strong>Engineering</strong> Mechanics ( Statics ) e - Book. : Timoshenko & Young<br />
3. <strong>Engineering</strong> Mechanics : Iriving K. Shames, Pearson Education Asia Pvt. Ltd.
4. <strong>Engineering</strong> Mechanics : I.C. Haung<br />
5. <strong>Engineering</strong> Mechanics : Hibbler, Prentice Hall;10th edition (September 19, 2003)<br />
6. <strong>Engineering</strong> Mechanics (Statics): Mokashi, Tata McGraw Hill Pvt. Ltd.<br />
7. <strong>Engineering</strong> Mechanics ( Dynamics): Mokashi, Tata McGraw Hill Pvt. Ltd.<br />
8. <strong>Engineering</strong> Mechanics : Basudeb Bhattacharyya (Oxford Publication)<br />
BCEP107 TERM WORK: Any Eight experiments<br />
LIST OF EXPERIMENTS: Any eight from the list<br />
1) Familiarity (study) of simple lifting machines.<br />
2) Determination of reactions at the supports of simply supported beam.<br />
3) Determination of forces in the members of jib crane.<br />
4) Determination of coefficient of friction of inclined planes<br />
5) Determination of coefficient of coil friction.<br />
6) Determination of forces in the members of a shear leg apparatus.<br />
7) Determination of velocity ratio, law of machine for “Simple Screw Jack”.<br />
8) Determination of velocity ratio, law of machine for “Differential Axle and Wheel”.<br />
9) Determination of velocity ratio, law of machine for “Single Purchase Crab Winch” or “Double Purchase<br />
Crab Winch”.<br />
10) Determination of mass moment of inertia of flywheel.<br />
11) Determination of ‘g’ by compound pendulum.<br />
12) Verification of Newton’s second law of motion by Fletcher’s trolley.<br />
13) Study of gear trains.<br />
14) Open ended experiment.<br />
GRAPHICAL SOLUTIONS:<br />
Minimum two graphical solutions (On Half Imperial Drawing Sheet)<br />
• Verification of law of parallelogram of force & verification of law of polygon of forces. (One numerical<br />
on each ).<br />
• Resultant of force system :<br />
Graphical solution to non-concurrent force system & parallel force system.<br />
(One numerical on each)<br />
• Equilibrium of force system :<br />
Determination of beam reaction & determination of forces in the members of a truss. (One numerical on<br />
each).<br />
• Determination of principal moment of inertia and principal axis direction by “Mohr’s Circle Method”.<br />
(Two numericals)
BMEL108 ENGINEERING GRAPHICS<br />
SEMESTER - I [1L+ 4P]<br />
Teaching Scheme: Evaluation Scheme: Theory<br />
Lectures: 1 Hrs /Week Teachers Assessment (TAE): 20 Marks<br />
Tutorial: Nil Class Asses. Exam (CAE): 20 Marks<br />
Practical: 4 Hrs /Week End Semester Exam: 60 Marks<br />
Credits: 3 Total: 100 Marks<br />
Evaluation Scheme: Practical<br />
Practical Internal: 25Marks<br />
Practical External: 25Marks<br />
OBJECTIVE:<br />
Computerized drafting is an upcoming technology and provides accurate and easily modifiable graphics entities,<br />
easy data storage and retrieval facility and enhances students’ creativity, imagination skill and drafting skills to<br />
communicate design ideas<br />
Introduction ( 2 Hrs)<br />
Use of various drawing instruments, lines, lettering and ISI standards for drafting. Simple geometrical<br />
construction .<br />
Definition of scale, Representative fraction, construction of various scales such as Plain, Diagonal,<br />
Comparative, Vernier, and Scale of Chords. Introduction to basic <strong>Engineering</strong> curves (conic sections )<br />
Theory of Projections ( 2Hrs)<br />
Theory, techniques, first and third angle projections, multi view drawing from pictorial views.) and view in<br />
orthographic projections. Projection of points. Projection of straight lines inclined to both reference plane.<br />
Projection of Planes ( 2Hrs)<br />
Projection of plane figures such as triangle, quadrilateral, regular polygons circle, Plane inclined to both<br />
reference plane. Auxiliary planes and view: Auxiliary vertical plane and Auxiliary inclined plane. True shapes<br />
of plane figures.<br />
Projection of Solids ( 3 Hrs)<br />
Projections of solids such as Prisms, pyramids, cone, cylinder with varying position of axes with ground line.<br />
Sections of solids (3 Hrs)<br />
Section of solid such as Prisms, pyramids, cone, cylinder and introduction to development of surfaces.<br />
Orthographic Projection (2 Hrs)<br />
Conversion of pictorial view of solid to orthographic views.<br />
TEXT BOOK:<br />
<strong>Engineering</strong> Drawing with an Introduction to Auto CAD, Dhanajay A. Jhole, Tata Mc Graw Hills<br />
Publishing company Ltd, Second Edition<br />
REFERENCE BOOKS:<br />
1. A text book of <strong>Engineering</strong> Drawing by N. D. Bhatt & V. M. Panchal, Charotar Publisher, 2007.<br />
2. A text book of <strong>Engineering</strong> Drawing by R. K. Dhawan / P. J. Shah<br />
3. <strong>Engineering</strong> Graphics by Phakatkar, Nirali Publications
BMEP108: TERM WORK <strong>Engineering</strong> Graphics<br />
Unit Learning Objectives Topics to be covered<br />
1<br />
Introduction to software<br />
“Intelli CAD – Professional<br />
6.6”<br />
2 Theory of Projections<br />
3 Spatial geometry<br />
4<br />
Geometrical solids and<br />
sections<br />
Basic commands 8<br />
Theory, techniques, first and third angle<br />
projections, multi view drawing from pictorial<br />
views. Theory of isometric, construction of<br />
isometric from orthographic<br />
Projection of points; lines, true lengths,<br />
inclinations; planes<br />
Construction of right, regular, oblique solids. 12<br />
Practical<br />
classes<br />
Term Work: Student should submit hard copy of the above work based on the above practical topics.<br />
TEXT BOOK:<br />
Engg. Graphics with Auto CAD, D. M. Kulkarni, A. P. Rastogi, A. K. Sarkar, Apmyimate PHI Learning<br />
Private Ltd., New Delhi- Revised Edition<br />
REFERENCE BOOKS:<br />
1. N. D. Bhatt & V. M. Panchal., <strong>Engineering</strong> drawing, Charotar publisher, 2007.<br />
2. A text book of <strong>Engineering</strong> Drawing by R. K. Dhawan / P. J. Shah<br />
3. <strong>Engineering</strong> Graphics by Phakatkar, Nirali Publications<br />
24<br />
12
BMEP 111 WORKSHOP PRACTICE<br />
SEMESTER -II [2P]<br />
Teaching Scheme: Evaluation Scheme: Practical<br />
Practical: 2 Hrs /Week Practical work Exam (PWE): 50 Marks<br />
Credits: 01<br />
OBJECTIVE:<br />
Topics to be studied or demonstrated during practical-Names, uses and setting of hand tools for Black smithy,<br />
Fitting, Carpentry and Welding. Students can do the work related to Mini-Modeling in following workshops:-<br />
Mechanical<br />
Mechanical Workshop:-Welding: Work related to gas welding, arc welding equipments.<br />
Black smithy: Work of the smithy tools and the process.<br />
Fitting: Use of tools of fitting and the processes involved in fitting.<br />
Carpentry: Applications of different carpentry tools and the carpentry processes.<br />
Electrical<br />
Electrical Workshop:- Work related to electromagnet, wind power generation, Twilight system, earthling<br />
system.<br />
Basic Electrical Lab: Work related to Ohms Law<br />
Electronics<br />
Electronics Workshop:-Electronics Workshop Lab; By using PCBs students can prepare Smart Sensors,<br />
Smart Gadgets like wireless communication, display, voice operating system.<br />
Electronic Circuits & Devises Lab: Various Electronics circuits can be prepared and tested on Bread Board in<br />
EDC Lab like Regulator, Oscillators, Power supplies, Transistors based amplifier. Embedded System Lab:<br />
Project like temperature control traffic light control, Memory circuits can be prepared in this lab.<br />
Computer<br />
Computers workshop:- Multimedia lab: Where tools like Flash Develop, Game Factory and Game Marker<br />
are available for Designing games.<br />
IT Software Lab: For graphic programming, Physical Modeling of musical instruments, Image Processing,<br />
Web Designing.<br />
Computer Lab:- Kits are available for projects based on Embedded System and Smart Environment.<br />
*It is mandatory for the students to use above workshop for preparing their Mini Model.<br />
TEXT BOOK:<br />
Course in Workshop Technology Volume-I, B. S. Raghuwanshi, Laxmi Publication-Revised Edition
BFYP112 MINI MODELING<br />
SEMESTER -II [2P]<br />
Teaching Scheme: Evaluation Scheme: Practical<br />
Practical: 2 Hrs /Week Practical Work Exam (PWE): 50 Marks<br />
Credits: 01<br />
OBJECTIVE:<br />
Different themes will be selected by the students in the First semester depending on their interests and abilities.<br />
Later, they have to give the detailed topic and prepare working model in Second Semester.<br />
Evaluation Scheme of Mini-Modeling:-<br />
Model Working /<br />
Not Working<br />
Creative /<br />
Innovative<br />
Knowledge of concept/<br />
Explanation (Viva)<br />
Aesthetic<br />
Total<br />
(10 Marks) (15 Marks) (15 Marks) (10 Marks) (50 Marks)
MBL101 GENERAL PROFICIENCY<br />
SEMESTER-I [2P]<br />
Teaching Scheme:<br />
Practical: 2 Hrs /Week<br />
Audit course<br />
OBJECTIVE:<br />
To analyze the potential of the students through Self Analysis, building up their Self Esteem, helping them to<br />
set up their Goals through Goal Setting, developing a healthy and positive Attitude. The GP training also<br />
focused on Change management and Time management as well. Grooming and etiquette were an integral part<br />
of the teaching.<br />
Orientation: Face to face with future- Need & Importance of soft skills in the career of <strong>Engineering</strong> graduate<br />
Change Management: Different aspects of change in life & how to incorporate positive change in one’s life as<br />
per environment<br />
Attitude Development: Programming one’s mind for positive results<br />
Self Esteem: Understanding and changing self image for betterment<br />
Self Analysis: Significance & Techniques of SWOT<br />
Goal Setting: To set & pursue well defined objectives for one’s life<br />
Time Management: Understanding value of time & managing it-List time savers & time wasters<br />
Dress & Appearance: Significance & application of Occasion wise dressing. Understanding & improving self<br />
appearance<br />
Manners & etiquettes: Dinning & Social etiquettes<br />
Introduction to Aptitude & Vocabulary Building<br />
REFERENCE BOOKS:<br />
1. Unlimited Power by Anthony Robbins<br />
2. Awaken the giant within you by Anthony Robbins<br />
3. Success Never Ends, Failure is Never Final by Robert Schuller<br />
4. How to read a person like a book by Oscar Bruce<br />
5. Body Language by Allen Pease
BHUL113 COMMUNICATION SKILLS<br />
SEMESTER-II [2L]<br />
Teaching Scheme:<br />
Lectures: 2Hrs /Week<br />
Credits: 02<br />
OBJECTIVE:<br />
Improving communication and language speaking abilities, enhance power of expression, vocabulary and<br />
personality development<br />
Types of Communication: Verbal- Spoken communication – Language lab<br />
Written communication- Upward & Down Communication<br />
Para lingual – Toll, Voice, Rolling, Accent, Pronunciation,<br />
Pause, Repetition<br />
Non-Verbal- Body language<br />
Introduction to Effective Public speaking & Orientation: Debate, Group discussion, extempore etc.<br />
Vocabulary Building: Building new words from combination of basic roots in latin, roman, greek etc.<br />
TEXT BOOK:<br />
Technical Communication by Dr. Minakshi Raman and Sangeeta Sharma<br />
REFERENCE BOOKS:<br />
1. How to read better and faster by Norman Lewis<br />
2. Thirty days to more power vocabulary by Wilfred Funk and Norman Lewis