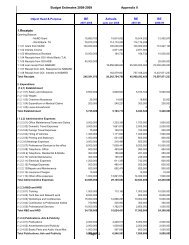
Grameen Sampark Final April 0... - pmgsy
Grameen Sampark Final April 0... - pmgsy
Grameen Sampark Final April 0... - pmgsy
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Block Pavement at Typical Locations<br />
Essentially, there are three important aspects in<br />
detailing. These are: (i) Curves (ii) Intrusions, and (iii)<br />
Changes in alignment<br />
Curves: It is necessary to cut the paving units to fit the<br />
edge restraints. Rectangular blocks of similar or<br />
contrasting colour as an edging have been used to<br />
minimize the visual effects of small errors in block<br />
cutting. To avoid unsightly and potentially weak joints,<br />
it is often preferred to change the laying pattern at the<br />
curves. The curve itself can be installed in Herringbone<br />
bond and yet the pavement can revert to stretcher bond<br />
on the approaches [4 & 5].<br />
Intrusions:<br />
On some pavements, like in city streets,<br />
there could be several intrusions, like, manholes,<br />
drainage gulleys, etc. where coping with these<br />
intrusions with the pavement is desirable. Around<br />
intrusions, it is good practice to lay blocks along both<br />
sides of the intrusion simultaneously so that closure is<br />
made away from the starting workface, rather than<br />
carrying the pavement around the intrusion to return to<br />
the original laying face to avoid accumulation of closing<br />
error [7].<br />
Compaction<br />
For compaction of sand bedding and paving blocks laid<br />
over it, the vibratory plate compactors are used over the<br />
laid paving blocks; at least two passes of the vibratory<br />
plate compactors are needed. Such vibratory<br />
compaction should be continued until the top of each<br />
paving block is in level with the adjacent blocks. It is not<br />
a good practice to leave compaction till the end of the<br />
day, as some blocks may move under construction<br />
traffic, resulting in the widening of joints and corner<br />
contact of blocks, which may cause spalling or cracking<br />
of the blocks. There should not be any delay in the<br />
compaction after paving blocks have been laid. This is<br />
necessary to achieve uniformity of compaction and<br />
retention of the pattern of laying. During compaction of<br />
the blocks laid, some amount of bedding sand may get<br />
filled up into the joints between them; the extent of sand<br />
Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana<br />
getting filled up into the joints will depend on the degree<br />
of compaction of sand, i.e. the force applied by the<br />
compactor. Standard compactors may have a weight of<br />
about 90 kg with plate area of about <strong>0.</strong>3 m2 and apply a<br />
centrifugal force of about 15 kN. On the other hand,<br />
heavy duty compactors may weigh 300-600 kg, with<br />
plate area of about <strong>0.</strong>5-<strong>0.</strong>6 m2 and apply a centrifugal<br />
force of 30-65 kN. Where the bedding sand is required<br />
to be compacted for heavily trafficed pavements, heavyduty<br />
compactors should be used. After compaction by<br />
vibratory plate compactors, some 2 to 6 passes of<br />
vibratory roller (with rubber coated drums or those of<br />
static weight less than 4 tonne and nominal amplitude of<br />
not more than <strong>0.</strong>6 mm) will further help in compaction<br />
of bedding sand and joint filling [7].<br />
Laying and Surface Tolerances<br />
While constructing the block pavement, the surface<br />
toleranes of individual layers may be observed, as<br />
indicated in IRC:SP:63-2004.<br />
Conclusion<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
ICBP technology is gaining importance and is<br />
becoming more popular day-by-day because it is<br />
user friendly and requires less infrastructure in<br />
terms of construction equipment / machineries, as<br />
compared to the conventional flexible and rigid<br />
pavements.<br />
ICBP technology can provide durable and<br />
sustainable road infrastructure where construction<br />
and maintenance of conventional pavements are<br />
not cost effective.<br />
ICBP is much cheaper than the rigid (concrete)<br />
pavement, designed for identical operating<br />
conditions. Compared to the bituminous<br />
pavement for low traffic volume roads and high<br />
strength subgrade, the initial construction cost of<br />
ICBP is likely to be equal to or marginally higher.<br />
For high traffic volume roads and low strength<br />
subgrade, ICBP will be cheaper than the flexible<br />
pavement.<br />
<strong>Grameen</strong> <strong>Sampark</strong> 13