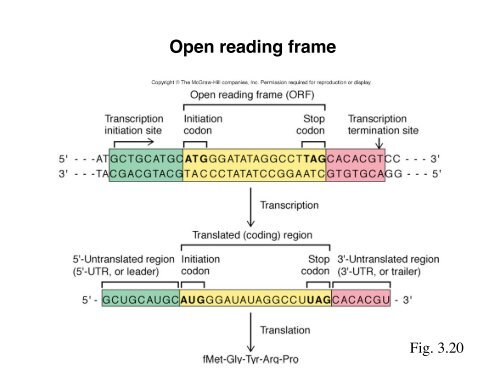
Open reading frame
Open reading frame
Open reading frame
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Open</strong> <strong>reading</strong> <strong>frame</strong><br />
Fig. 3.20
The translation cycle<br />
Fig. 3.19
Polysomes:<br />
Individual mRNAs<br />
engaged in<br />
translation with<br />
multiple ribosomes.<br />
Polysomes<br />
Fig. 19.26
tRNAs in translation<br />
Fig. 3.17
tRNAs mediate incorporation of amino<br />
acids into protein<br />
Charged tRNA<br />
Incorporation of radioactive<br />
amino acid ( 14 C-Leucine)<br />
onto tRNA was followed.<br />
Protein<br />
Charged tRNA<br />
Incorporation of<br />
Fig. 19.28<br />
14C- Leucine from charged tRNA<br />
into protein was followed<br />
over time.
The tRNA, not the amino acid, reads the codon<br />
(reduces Cysteine<br />
to Alanine)<br />
Fig. 19.34
tRNAs contain numerous modified nucleotides<br />
Fig. 19.29
tRNA structure<br />
Fig. 19.31
Two classes of tRNA synthetases charge tRNAs<br />
Fig. 19.37
The tRNA charging reaction<br />
Fig. 17.2
The tRNA anticodon is a key determinant<br />
for tRNA charging<br />
CAU<br />
The effect of mutations in the<br />
tRNA-Met anticodon loop on<br />
methionine charging was<br />
tested. (CAU = wild-type).
The ribosome<br />
Which reactions<br />
take place in<br />
which subunits?<br />
Fig. 3.16
Proteins in the small ribosomal subunit<br />
Fig. 19.10
The dependence<br />
of S12 on other<br />
proteins for<br />
incorporation<br />
into 16S rRNA is<br />
followed.<br />
Complexes are<br />
separated in<br />
sucrose<br />
gradients. 14Clabeled<br />
S12 is<br />
shown in red.<br />
16S rRNA<br />
14 C-S12<br />
Assembly of proteins onto the small rRNA<br />
Incorporated<br />
16S rRNA<br />
Unincorporated<br />
Heavy Light<br />
+<br />
14 C-<br />
S12<br />
S4,S7,S8,<br />
S16,S20<br />
16S rRNA<br />
S4, S8,<br />
S16,S17<br />
14 C-<br />
S12<br />
16S rRNA<br />
14 C-<br />
S12<br />
All proteins,<br />
except S12<br />
Fig. 19.11
Assembly pathway derived from<br />
experiments in Fig. 19.11<br />
Fig. 19.12
Crystal structure of the small<br />
ribosomal subunit<br />
Protein: Purple<br />
rRNA: Grey<br />
Fig. 19.14
Crystal structure of the large<br />
ribosomal subunit<br />
Transition state analog<br />
(Marks the catalytic site<br />
of the ribosome)<br />
Protein: Yellow<br />
rRNA: Grey<br />
Fig. 19.22
Peptidyl transferase transition state analog<br />
Transition state<br />
Transition state analog<br />
Fig. 19.21
Distance from peptidyl transferase center to<br />
closest proteins<br />
Fig. 19.23
tRNA-pep<br />
Fig. 19.24<br />
Mechanism of peptidyl transfer<br />
23S rRNA<br />
nucleotide<br />
tRNA-aa<br />
tRNA-pep<br />
Early model (2000) -<br />
later proven wrong Newer model (2005).<br />
tRNA-aa
The polypeptide exit tunnel<br />
Fig. 19.25
Crystal structure of the ribosome<br />
with tRNAs and mRNA<br />
Fig. 19.7
The mRNA produce a 45 o kink to<br />
accommodate the tRNAs<br />
Fig. 19.8