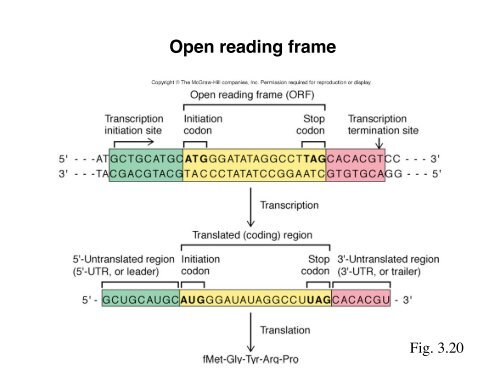
Open reading frame
Open reading frame
Open reading frame
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>Open</strong> <strong>reading</strong> <strong>frame</strong><br />
Fig. 3.20
The translation cycle<br />
Fig. 3.19
Polysomes:<br />
Individual mRNAs<br />
engaged in<br />
translation with<br />
multiple ribosomes.<br />
Polysomes<br />
Fig. 19.26
tRNAs in translation<br />
Fig. 3.17
tRNAs mediate incorporation of amino<br />
acids into protein<br />
Charged tRNA<br />
Incorporation of radioactive<br />
amino acid ( 14 C-Leucine)<br />
onto tRNA was followed.<br />
Protein<br />
Charged tRNA<br />
Incorporation of<br />
Fig. 19.28<br />
14C- Leucine from charged tRNA<br />
into protein was followed<br />
over time.
The tRNA, not the amino acid, reads the codon<br />
(reduces Cysteine<br />
to Alanine)<br />
Fig. 19.34
tRNAs contain numerous modified nucleotides<br />
Fig. 19.29
tRNA structure<br />
Fig. 19.31
Two classes of tRNA synthetases charge tRNAs<br />
Fig. 19.37
The tRNA charging reaction<br />
Fig. 17.2
The tRNA anticodon is a key determinant<br />
for tRNA charging<br />
CAU<br />
The effect of mutations in the<br />
tRNA-Met anticodon loop on<br />
methionine charging was<br />
tested. (CAU = wild-type).
The ribosome<br />
Which reactions<br />
take place in<br />
which subunits?<br />
Fig. 3.16
Proteins in the small ribosomal subunit<br />
Fig. 19.10
The dependence<br />
of S12 on other<br />
proteins for<br />
incorporation<br />
into 16S rRNA is<br />
followed.<br />
Complexes are<br />
separated in<br />
sucrose<br />
gradients. 14Clabeled<br />
S12 is<br />
shown in red.<br />
16S rRNA<br />
14 C-S12<br />
Assembly of proteins onto the small rRNA<br />
Incorporated<br />
16S rRNA<br />
Unincorporated<br />
Heavy Light<br />
+<br />
14 C-<br />
S12<br />
S4,S7,S8,<br />
S16,S20<br />
16S rRNA<br />
S4, S8,<br />
S16,S17<br />
14 C-<br />
S12<br />
16S rRNA<br />
14 C-<br />
S12<br />
All proteins,<br />
except S12<br />
Fig. 19.11
Assembly pathway derived from<br />
experiments in Fig. 19.11<br />
Fig. 19.12
Crystal structure of the small<br />
ribosomal subunit<br />
Protein: Purple<br />
rRNA: Grey<br />
Fig. 19.14
Crystal structure of the large<br />
ribosomal subunit<br />
Transition state analog<br />
(Marks the catalytic site<br />
of the ribosome)<br />
Protein: Yellow<br />
rRNA: Grey<br />
Fig. 19.22
Peptidyl transferase transition state analog<br />
Transition state<br />
Transition state analog<br />
Fig. 19.21
Distance from peptidyl transferase center to<br />
closest proteins<br />
Fig. 19.23
tRNA-pep<br />
Fig. 19.24<br />
Mechanism of peptidyl transfer<br />
23S rRNA<br />
nucleotide<br />
tRNA-aa<br />
tRNA-pep<br />
Early model (2000) -<br />
later proven wrong Newer model (2005).<br />
tRNA-aa
The polypeptide exit tunnel<br />
Fig. 19.25
Crystal structure of the ribosome<br />
with tRNAs and mRNA<br />
Fig. 19.7
The mRNA produce a 45 o kink to<br />
accommodate the tRNAs<br />
Fig. 19.8