A systematic review of the effectiveness of adalimumab
A systematic review of the effectiveness of adalimumab
A systematic review of the effectiveness of adalimumab
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
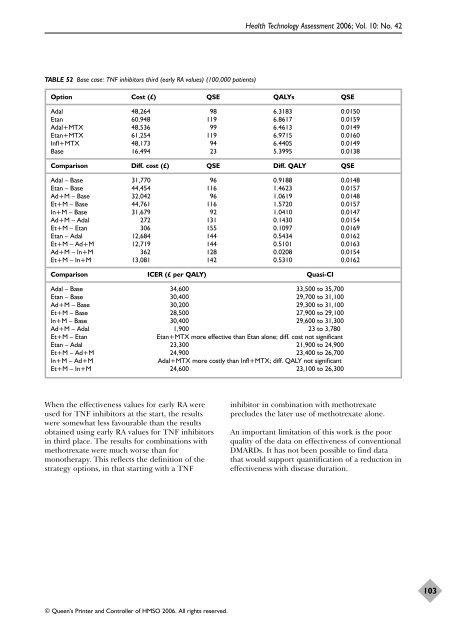
TABLE 52 Base case: TNF inhibitors third (early RA values) (100,000 patients)<br />
© Queen’s Printer and Controller <strong>of</strong> HMSO 2006. All rights reserved.<br />
Health Technology Assessment 2006; Vol. 10: No. 42<br />
Option Cost (£) QSE QALYs QSE<br />
Adal 48,264 98 6.3183 0.0150<br />
Etan 60,948 119 6.8617 0.0159<br />
Adal+MTX 48,536 99 6.4613 0.0149<br />
Etan+MTX 61,254 119 6.9715 0.0160<br />
Infl+MTX 48,173 94 6.4405 0.0149<br />
Base 16,494 23 5.3995 0.0138<br />
Comparison Diff. cost (£) QSE Diff. QALY QSE<br />
Adal – Base 31,770 96 0.9188 0.0148<br />
Etan – Base 44,454 116 1.4623 0.0157<br />
Ad+M – Base 32,042 96 1.0619 0.0148<br />
Et+M – Base 44,761 116 1.5720 0.0157<br />
In+M – Base 31,679 92 1.0410 0.0147<br />
Ad+M – Adal 272 131 0.1430 0.0154<br />
Et+M – Etan 306 155 0.1097 0.0169<br />
Etan – Adal 12,684 144 0.5434 0.0162<br />
Et+M – Ad+M 12,719 144 0.5101 0.0163<br />
Ad+M – In+M 362 128 0.0208 0.0154<br />
Et+M – In+M 13,081 142 0.5310 0.0162<br />
Comparison ICER (£ per QALY) Quasi-CI<br />
Adal – Base 34,600 33,500 to 35,700<br />
Etan – Base 30,400 29,700 to 31,100<br />
Ad+M – Base 30,200 29,300 to 31,100<br />
Et+M – Base 28,500 27,900 to 29,100<br />
In+M – Base 30,400 29,600 to 31,300<br />
Ad+M – Adal 1,900 23 to 3,780<br />
Et+M – Etan Etan+MTX more effective than Etan alone; diff. cost not significant<br />
Etan – Adal 23,300 21,900 to 24,900<br />
Et+M – Ad+M 24,900 23,400 to 26,700<br />
In+M – Ad+M Adal+MTX more costly than Infl+MTX; diff. QALY not significant<br />
Et+M – In+M 24,600 23,100 to 26,300<br />
When <strong>the</strong> <strong>effectiveness</strong> values for early RA were<br />
used for TNF inhibitors at <strong>the</strong> start, <strong>the</strong> results<br />
were somewhat less favourable than <strong>the</strong> results<br />
obtained using early RA values for TNF inhibitors<br />
in third place. The results for combinations with<br />
methotrexate were much worse than for<br />
mono<strong>the</strong>rapy. This reflects <strong>the</strong> definition <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong><br />
strategy options, in that starting with a TNF<br />
inhibitor in combination with methotrexate<br />
precludes <strong>the</strong> later use <strong>of</strong> methotrexate alone.<br />
An important limitation <strong>of</strong> this work is <strong>the</strong> poor<br />
quality <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> data on <strong>effectiveness</strong> <strong>of</strong> conventional<br />
DMARDs. It has not been possible to find data<br />
that would support quantification <strong>of</strong> a reduction in<br />
<strong>effectiveness</strong> with disease duration.<br />
103