A systematic review of the effectiveness of adalimumab
A systematic review of the effectiveness of adalimumab
A systematic review of the effectiveness of adalimumab
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
88<br />
Health economics<br />
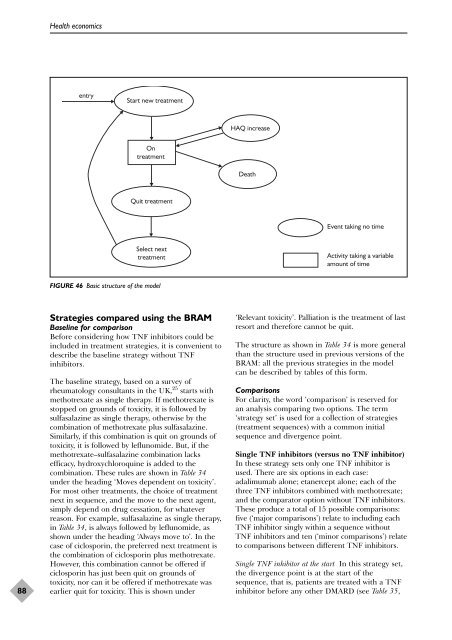
entry<br />
Start new treatment<br />
On<br />
treatment<br />
Quit treatment<br />
Select next<br />
treatment<br />
FIGURE 46 Basic structure <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> model<br />
Strategies compared using <strong>the</strong> BRAM<br />
Baseline for comparison<br />
Before considering how TNF inhibitors could be<br />
included in treatment strategies, it is convenient to<br />
describe <strong>the</strong> baseline strategy without TNF<br />
inhibitors.<br />
The baseline strategy, based on a survey <strong>of</strong><br />
rheumatology consultants in <strong>the</strong> UK, 25 starts with<br />
methotrexate as single <strong>the</strong>rapy. If methotrexate is<br />
stopped on grounds <strong>of</strong> toxicity, it is followed by<br />
sulfasalazine as single <strong>the</strong>rapy, o<strong>the</strong>rwise by <strong>the</strong><br />
combination <strong>of</strong> methotrexate plus sulfasalazine.<br />
Similarly, if this combination is quit on grounds <strong>of</strong><br />
toxicity, it is followed by leflunomide. But, if <strong>the</strong><br />
methotrexate–sulfasalazine combination lacks<br />
efficacy, hydroxychloroquine is added to <strong>the</strong><br />
combination. These rules are shown in Table 34<br />
under <strong>the</strong> heading ‘Moves dependent on toxicity’.<br />
For most o<strong>the</strong>r treatments, <strong>the</strong> choice <strong>of</strong> treatment<br />
next in sequence, and <strong>the</strong> move to <strong>the</strong> next agent,<br />
simply depend on drug cessation, for whatever<br />
reason. For example, sulfasalazine as single <strong>the</strong>rapy,<br />
in Table 34, is always followed by leflunomide, as<br />
shown under <strong>the</strong> heading ‘Always move to’. In <strong>the</strong><br />
case <strong>of</strong> ciclosporin, <strong>the</strong> preferred next treatment is<br />
<strong>the</strong> combination <strong>of</strong> ciclosporin plus methotrexate.<br />
However, this combination cannot be <strong>of</strong>fered if<br />
ciclosporin has just been quit on grounds <strong>of</strong><br />
toxicity, nor can it be <strong>of</strong>fered if methotrexate was<br />
earlier quit for toxicity. This is shown under<br />
HAQ increase<br />
Death<br />
Event taking no time<br />
Activity taking a variable<br />
amount <strong>of</strong> time<br />
‘Relevant toxicity’. Palliation is <strong>the</strong> treatment <strong>of</strong> last<br />
resort and <strong>the</strong>refore cannot be quit.<br />
The structure as shown in Table 34 is more general<br />
than <strong>the</strong> structure used in previous versions <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong><br />
BRAM: all <strong>the</strong> previous strategies in <strong>the</strong> model<br />
can be described by tables <strong>of</strong> this form.<br />
Comparisons<br />
For clarity, <strong>the</strong> word ‘comparison’ is reserved for<br />
an analysis comparing two options. The term<br />
‘strategy set’ is used for a collection <strong>of</strong> strategies<br />
(treatment sequences) with a common initial<br />
sequence and divergence point.<br />
Single TNF inhibitors (versus no TNF inhibitor)<br />
In <strong>the</strong>se strategy sets only one TNF inhibitor is<br />
used. There are six options in each case:<br />
<strong>adalimumab</strong> alone; etanercept alone; each <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong><br />
three TNF inhibitors combined with methotrexate;<br />
and <strong>the</strong> comparator option without TNF inhibitors.<br />
These produce a total <strong>of</strong> 15 possible comparisons:<br />
five (‘major comparisons’) relate to including each<br />
TNF inhibitor singly within a sequence without<br />
TNF inhibitors and ten (‘minor comparisons’) relate<br />
to comparisons between different TNF inhibitors.<br />
Single TNF inhibitor at <strong>the</strong> start In this strategy set,<br />
<strong>the</strong> divergence point is at <strong>the</strong> start <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong><br />
sequence, that is, patients are treated with a TNF<br />
inhibitor before any o<strong>the</strong>r DMARD (see Table 35,