Biology 48 - Human Physiology Lecture 5 Cellular Respiration ...
Biology 48 - Human Physiology Lecture 5 Cellular Respiration ...
Biology 48 - Human Physiology Lecture 5 Cellular Respiration ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
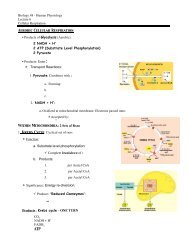
Steps in Glycolysis:<br />
1. Glucose “Activation”<br />
<br />
Glucose → 2 (Pyruvate) or Pyruvic Acid<br />
Activated <strong>Cellular</strong> Glucose: “Locked” within cell by :<br />
Phosphate obtained from :<br />
Result:Fructose1,6 Diphosphate<br />
Glycolysis: Requires INITIAL energy investment of :<br />
of :<br />
2. Production of :<br />
C6H12O6+ 2ATP→ 2 (C3H4O3) + 4ATP<br />
For every glucose molecule:<br />
3. Production of :<br />
4 ATP produced<br />
- 2 ATP invested<br />
C 6H 12O 6 + 2ATP→ 2 (C 3H 4O 3) + 4ATP<br />
C 6H 12O 6 → 2 ( C 3H 4O 3 )<br />
4 missing hydrogen atoms ?<br />
C = 6 C (3x2) =<br />
H = 12 H (4x2) =<br />
O = 6 O (3x2) =<br />
Question: What happened to the electrons ? What molecules might be holding them ?