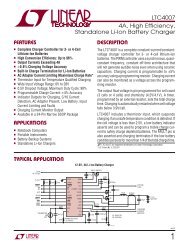
guidance, flight mechanics and trajectory optimization
guidance, flight mechanics and trajectory optimization
guidance, flight mechanics and trajectory optimization
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
p<br />
The kinetic energy of the system is<br />
Thus, Lagranges equations of motion for periods of normal thrusting are seen<br />
to be<br />
where a,, is the acceleration due to the normal thrust. Now substituting<br />
relation for p as a function of time from Equation (2.2) in the second<br />
equation above gives<br />
or<br />
This equation can be considered a first order differential equation in the<br />
variable 4 , i.e.,<br />
But this equation has as a general solution<br />
Equation (2.4) is the solution for the angular rate of the LOS (e ) during<br />
periods of normal thrusting. This equation, however, is not the one employed<br />
to determine the length of time that the normal thrust is to be applied, but<br />
rather the simpler equation which assumes ,d '= 0 is used. The time of normal<br />
thrusting is calculated as<br />
l<br />
That is, if T0 is the threshold<br />
to zero the length of time that<br />
A? ?3<br />
(2.5)<br />
tn = -<br />
an<br />
.<br />
value of t <strong>and</strong> it is desired to drive 8<br />
normal thrusting should be applied is calculated<br />
from (2.5). If the motor used for normal control is actually operated<br />
for this time, 8 will not be driven to zero. Rather, the value that it<br />
33<br />
(2.4)