Negative Temperature Coefficient Thermistors for Temperature ...
Negative Temperature Coefficient Thermistors for Temperature ...
Negative Temperature Coefficient Thermistors for Temperature ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
6 <strong>Thermistors</strong><br />
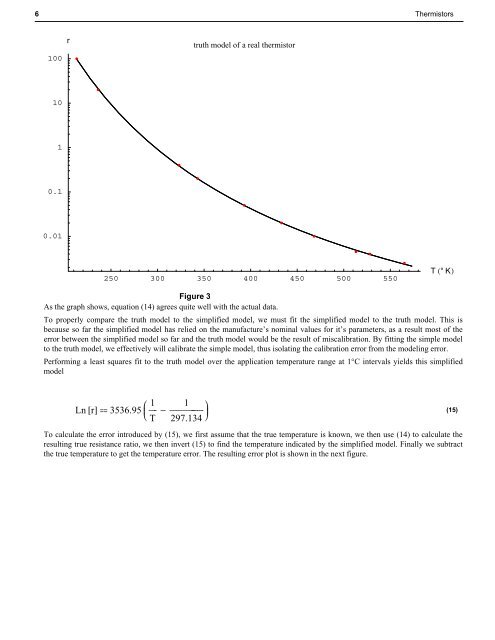
100<br />
10<br />
1<br />
0.1<br />
0.01<br />
r<br />
truth model of a real thermistor<br />
250 300 350 400 450 500 550<br />
Figure 3<br />
As the graph shows, equation (14) agrees quite well with the actual data.<br />
T ° K<br />
To properly compare the truth model to the simplified model, we must fit the simplified model to the truth model. This is<br />
because so far the simplified model has relied on the manufacture’s nominal values <strong>for</strong> it’s parameters, as a result most of the<br />
error between the simplified model so far and the truth model would be the result of miscalibration. By fitting the simple model<br />
to the truth model, we effectively will calibrate the simple model, thus isolating the calibration error from the modeling error.<br />
Per<strong>for</strong>ming a least squares fit to the truth model over the application temperature range at 1°C intervals yields this simplified<br />
model<br />
Ln r 3536.95 <br />
<br />
1 1 <br />
<br />
T 297.134 <br />
To calculate the error introduced by (15), we first assume that the true temperature is known, we then use (14) to calculate the<br />
resulting true resistance ratio, we then invert (15) to find the temperature indicated by the simplified model. Finally we subtract<br />
the true temperature to get the temperature error. The resulting error plot is shown in the next figure.<br />
(15)