Innovation and institutional change: the transition to a sustainable ...
Innovation and institutional change: the transition to a sustainable ...
Innovation and institutional change: the transition to a sustainable ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
214 Chapter 8<br />
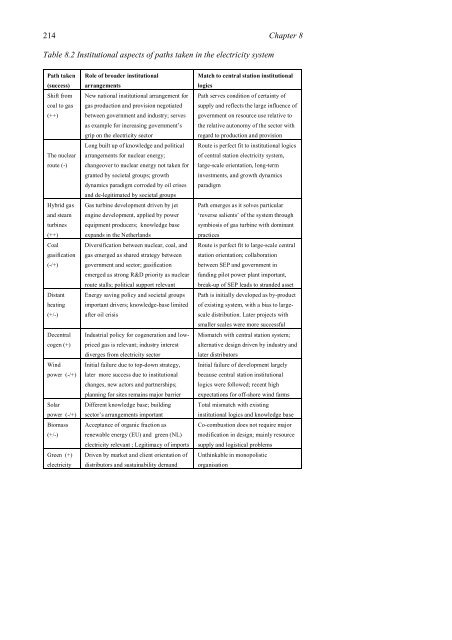
Table 8.2 Institutional aspects of paths taken in <strong>the</strong> electricity system<br />
Path taken<br />
(success)<br />
Shift from<br />
coal <strong>to</strong> gas<br />
(++)<br />
The nuclear<br />
route (-)<br />
Hybrid gas<br />
<strong>and</strong> steam<br />
turbines<br />
(++)<br />
Coal<br />
gasification<br />
(-/+)<br />
Distant<br />
heating<br />
(+/-)<br />
Decentral<br />
cogen (+)<br />
Wind<br />
power (-/+)<br />
Solar<br />
power (-/+)<br />
Biomass<br />
(+/-)<br />
Green (+)<br />
electricity<br />
Role of broader <strong>institutional</strong><br />
arrangements<br />
New national <strong>institutional</strong> arrangement for<br />
gas production <strong>and</strong> provision negotiated<br />
between government <strong>and</strong> industry; serves<br />
as example for increasing government’s<br />
grip on <strong>the</strong> electricity sec<strong>to</strong>r<br />
Long built up of knowledge <strong>and</strong> political<br />
arrangements for nuclear energy;<br />
<strong>change</strong>over <strong>to</strong> nuclear energy not taken for<br />
granted by societal groups; growth<br />
dynamics paradigm corroded by oil crises<br />
<strong>and</strong> de-legitimated by societal groups<br />
Gas turbine development driven by jet<br />
engine development, applied by power<br />
equipment producers; knowledge base<br />
exp<strong>and</strong>s in <strong>the</strong> Ne<strong>the</strong>rl<strong>and</strong>s<br />
Diversification between nuclear, coal, <strong>and</strong><br />
gas emerged as shared strategy between<br />
government <strong>and</strong> sec<strong>to</strong>r; gasification<br />
emerged as strong R&D priority as nuclear<br />
route stalls; political support relevant<br />
Energy saving policy <strong>and</strong> societal groups<br />
important drivers; knowledge-base limited<br />
after oil crisis<br />
Industrial policy for cogeneration <strong>and</strong> low-<br />
priced gas is relevant; industry interest<br />
diverges from electricity sec<strong>to</strong>r<br />
Initial failure due <strong>to</strong> <strong>to</strong>p-down strategy,<br />
later more success due <strong>to</strong> <strong>institutional</strong><br />
<strong>change</strong>s, new ac<strong>to</strong>rs <strong>and</strong> partnerships;<br />
planning for sites remains major barrier<br />
Different knowledge base; building<br />
sec<strong>to</strong>r’s arrangements important<br />
Acceptance of organic fraction as<br />
renewable energy (EU) <strong>and</strong> green (NL)<br />
electricity relevant ; Legitimacy of imports<br />
Driven by market <strong>and</strong> client orientation of<br />
distribu<strong>to</strong>rs <strong>and</strong> sustainability dem<strong>and</strong><br />
Match <strong>to</strong> central station <strong>institutional</strong><br />
logics<br />
Path serves condition of certainty of<br />
supply <strong>and</strong> reflects <strong>the</strong> large influence of<br />
government on resource use relative <strong>to</strong><br />
<strong>the</strong> relative au<strong>to</strong>nomy of <strong>the</strong> sec<strong>to</strong>r with<br />
regard <strong>to</strong> production <strong>and</strong> provision<br />
Route is perfect fit <strong>to</strong> <strong>institutional</strong> logics<br />
of central station electricity system,<br />
large-scale orientation, long-term<br />
investments, <strong>and</strong> growth dynamics<br />
paradigm<br />
Path emerges as it solves particular<br />
‘reverse salients’ of <strong>the</strong> system through<br />
symbiosis of gas turbine with dominant<br />
practices<br />
Route is perfect fit <strong>to</strong> large-scale central<br />
station orientation; collaboration<br />
between SEP <strong>and</strong> government in<br />
funding pilot power plant important,<br />
break-up of SEP leads <strong>to</strong> str<strong>and</strong>ed asset<br />
Path is initially developed as by-product<br />
of existing system, with a bias <strong>to</strong> large-<br />
scale distribution. Later projects with<br />
smaller scales were more successful<br />
Mismatch with central station system;<br />
alternative design driven by industry <strong>and</strong><br />
later distribu<strong>to</strong>rs<br />
Initial failure of development largely<br />
because central station <strong>institutional</strong><br />
logics were followed; recent high<br />
expectations for off-shore wind farms<br />
Total mismatch with existing<br />
<strong>institutional</strong> logics <strong>and</strong> knowledge base<br />
Co-combustion does not require major<br />
modification in design; mainly resource<br />
supply <strong>and</strong> logistical problems<br />
Unthinkable in monopolistic<br />
organisation