Part 1: General - Computer Security Resource Center - National ...
Part 1: General - Computer Security Resource Center - National ...
Part 1: General - Computer Security Resource Center - National ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
2<br />
Pre-Operational<br />
Phase<br />
3<br />
7<br />
1<br />
4<br />
Operational<br />
Phase<br />
6<br />
Post-Operational<br />
Phase<br />
Destroyed<br />
Phase<br />
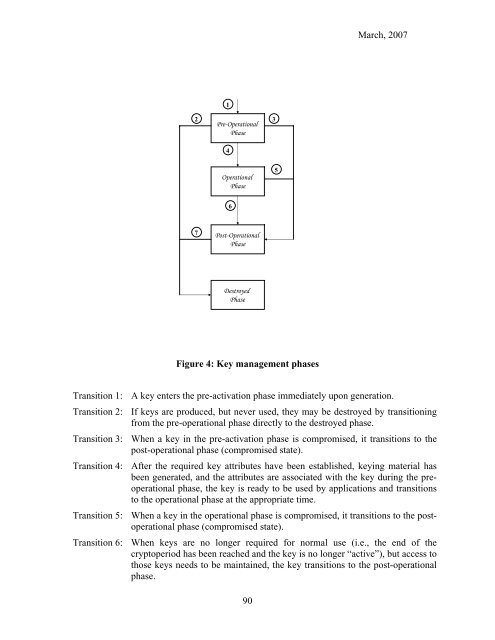
Figure 4: Key management phases<br />
5<br />
March, 2007<br />
Transition 1: A key enters the pre-activation phase immediately upon generation.<br />
Transition 2: If keys are produced, but never used, they may be destroyed by transitioning<br />
from the pre-operational phase directly to the destroyed phase.<br />
Transition 3: When a key in the pre-activation phase is compromised, it transitions to the<br />
post-operational phase (compromised state).<br />
Transition 4: After the required key attributes have been established, keying material has<br />
been generated, and the attributes are associated with the key during the preoperational<br />
phase, the key is ready to be used by applications and transitions<br />
to the operational phase at the appropriate time.<br />
Transition 5: When a key in the operational phase is compromised, it transitions to the postoperational<br />
phase (compromised state).<br />
Transition 6: When keys are no longer required for normal use (i.e., the end of the<br />
cryptoperiod has been reached and the key is no longer “active”), but access to<br />
those keys needs to be maintained, the key transitions to the post-operational<br />
phase.<br />
90