Full Report - Center for Collaborative Education
Full Report - Center for Collaborative Education
Full Report - Center for Collaborative Education
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
the transfer of large numbers of LEP students from<br />
ELL programs to special education programs not<br />
designed <strong>for</strong> ELLs.<br />
Enrollment in Programs <strong>for</strong><br />
English Language Learners<br />
Boston Public Schools offers several programs <strong>for</strong><br />
English language learners: Sheltered English Immersion<br />
(SEI) (both Language Specific and Multilingual);<br />
Two-Way Bilingual programs; programs <strong>for</strong><br />
Students with Interrupted Formal <strong>Education</strong> (SIFE)<br />
(both Language Specific/HILT-SIFE and Multilingual);<br />
and Transitional Bilingual <strong>Education</strong> programs.<br />
In presenting the enrollment data <strong>for</strong> the ELL<br />
programs, we use SIMS enrollment categories (SEI,<br />
Two-Way Bilingual, and other bilingual programs)<br />
which allow us to show the four-year trends <strong>for</strong><br />
the enrollment in these programs (Table 8). Data<br />
that disaggregate programs further come from<br />
documents and databases of the Office of English<br />
language learners in BPS and are available only <strong>for</strong><br />
SY2009 (Table 9).<br />
Enrollment in Sheltered English Immersion (SEI)<br />
Programs. SEI became the approach of choice <strong>for</strong><br />
educating English language learners in Massachusetts<br />
after the passage of Referendum Question 2 in<br />
2002. It is the ELL program with the largest enrollment<br />
in the district. SEI is a model <strong>for</strong> teaching<br />
English language learners that relies on the use of<br />
simple English in the classroom to impart academic<br />
content, using students’ native language only to<br />
assist students in completing tasks or to answer<br />
questions. BPS offers two types of SEI programs:<br />
Language Specific and Multilingual. SEI<br />
Language-Specific programs are offered to students<br />
whose home language is Spanish, Haitian Creole,<br />
Cape Verdean Creole, Chinese languages, or Vietnamese.<br />
All students in an SEI Language Specific<br />
classroom speak the same language, and a bilin-<br />
gual/bicultural staff fluent in that language is available<br />
to students and their families. In a Multilingual<br />
SEI classroom, students are from various linguistic<br />
backgrounds and staff may or may not speak the<br />
language of the students or of their families.<br />
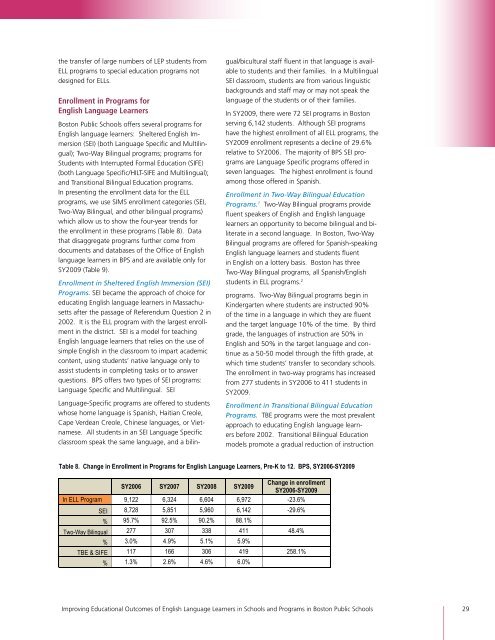
In SY2009, there were 72 SEI programs in Boston<br />
serving 6,142 students. Although SEI programs<br />
have the highest enrollment of all ELL programs, the<br />
SY2009 enrollment represents a decline of 29.6%<br />
relative to SY2006. The majority of BPS SEI programs<br />
are Language Specific programs offered in<br />
seven languages. The highest enrollment is found<br />
among those offered in Spanish.<br />
Enrollment in Two-Way Bilingual <strong>Education</strong><br />
Programs. 1 Two-Way Bilingual programs provide<br />
fluent speakers of English and English language<br />
learners an opportunity to become bilingual and biliterate<br />
in a second language. In Boston, Two-Way<br />
Bilingual programs are offered <strong>for</strong> Spanish-speaking<br />
English language learners and students fluent<br />
in English on a lottery basis. Boston has three<br />
Two-Way Bilingual programs, all Spanish/English<br />
students in ELL programs. 2<br />
programs. Two-Way Bilingual programs begin in<br />
Kindergarten where students are instructed 90%<br />
of the time in a language in which they are fluent<br />
and the target language 10% of the time. By third<br />
grade, the languages of instruction are 50% in<br />
English and 50% in the target language and continue<br />
as a 50-50 model through the fifth grade, at<br />
which time students’ transfer to secondary schools.<br />
The enrollment in two-way programs has increased<br />
from 277 students in SY2006 to 411 students in<br />
SY2009.<br />
Enrollment in Transitional Bilingual <strong>Education</strong><br />
Programs. TBE programs were the most prevalent<br />
approach to educating English language learners<br />
be<strong>for</strong>e 2002. Transitional Bilingual <strong>Education</strong><br />
models promote a gradual reduction of instruction<br />
Table 8. Change in Enrollment in Programs <strong>for</strong> English Language Learners, Pre-K to 12. BPS, SY2006-SY2009<br />
SY2006 SY2007 SY2008 SY2009<br />
Change in enrollment<br />
SY2006-SY2009<br />
In ELL Program 9,122 6,324 6,604 6,972 -23.6%<br />
SEI 8,728 5,851 5,960 6,142 -29.6%<br />
% 95.7% 92.5% 90.2% 88.1%<br />
Two-Way Bilingual 277 307 338 411 48.4%<br />
% 3.0% 4.9% 5.1% 5.9%<br />
TBE & SIFE 117 166 306 419 258.1%<br />
% 1.3% 2.6% 4.6% 6.0%<br />
Improving <strong>Education</strong>al Outcomes of English Language Learners in Schools and Programs in Boston Public Schools 29