il tumore della prostata. ii. stadiazione - Università degli studi di Pavia
il tumore della prostata. ii. stadiazione - Università degli studi di Pavia
il tumore della prostata. ii. stadiazione - Università degli studi di Pavia
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Università</strong> <strong>degli</strong> Stu<strong>di</strong> <strong>di</strong> <strong>Pavia</strong><br />
AA 2010 - 2011<br />
Corso Integrato <strong>di</strong> Clinica Me<strong>di</strong>ca<br />
Insegnamento <strong>di</strong> Oncologia Me<strong>di</strong>ca<br />
IL TUMORE DELLA PROSTATA. II.<br />
STADIAZIONE<br />
Prof. Alberto Riccar<strong>di</strong>
STAGING METHODS
PROSTATIC CANCER<br />
Clinical staging. I.<br />
* TNM staging system includes categories for<br />
cancers palpable on DRE, those identified solely on<br />
basis of abnormal PSA (T1c), those palpable but<br />
clinically confined to gland (T2) and those extended<br />
outside gland (T3 and T4)
PROSTATIC CANCER<br />
Clinical staging. II.<br />
* DRE alone inaccurate in assessing extent of<br />
<strong>di</strong>sease within gland, capsular invasion, involvement<br />
of seminal vescicles and spread to nodal or more<br />
<strong>di</strong>stant sites;<br />
* assessment refined by imaging <strong>stu<strong>di</strong></strong>es<br />
[ultrasound, computed tomoghraphy (CT), magnetic<br />
resonance imaging (MRI) and bone scan];<br />
- however, no single test accurately pre<strong>di</strong>cts<br />
pathologic stage (organ - confined <strong>di</strong>sease? seminal<br />
vesical involvement? lymph node spread?)
PROSTATIC CANCER<br />
Clinical staging. III. Transrectal ultrasound<br />
* transrectal<br />
ultrasound (TRUS)<br />
most frequently used<br />
→ no consistent<br />
fin<strong>di</strong>ng pre<strong>di</strong>cts PC<br />
with certainty →<br />
primarly used to <strong>di</strong>rect<br />
prostate biopsy
* CT scans lack<br />
sensitivity and<br />
specificity for<br />
extraprostatic<br />
extension and<br />
inferior to MRI in<br />
visualization of<br />
lymph nodes<br />
PROSTATIC CANCER<br />
Clinical staging. IV. CT scan<br />
* CT scan can show abnormal lymph nodes in pelvis<br />
and abdomen, but not sensitive enough to identify<br />
microscopic cancer cells in lymph nodes = CT scans do<br />
not provide reliable enough information about con<strong>di</strong>tion<br />
of prostate or stage of prostate cancer
PROSTATIC CANCER<br />
Clinical staging. V. MRI<br />
* MRI (st<strong>il</strong>l lacking sensitivity and specificity) ↑ lymph<br />
node detection, especially of endorectal co<strong>il</strong>;<br />
[- T1 - weighted images: periprostatic fat and venous<br />
plexus, perivesicular tissues, lymph nodes, and bone<br />
marrow;<br />
- T2 - weighted images: internal architecture of prostate<br />
and seminal vesicles (low signal in most cancers, high<br />
signal in normal peripheral zone)];<br />
- MRI also useful for planning of surgery and ra<strong>di</strong>ation<br />
therapy<br />
= neither TC nor MRI accurately pre<strong>di</strong>cts pathologic<br />
stage at surgery
PROSTATIC CANCER<br />
Clinical staging. VII.<br />
Molecular <strong>di</strong>agnostic (experimental)<br />
* seeks to identify presence of<br />
circulating PC cells using an<br />
assay for PSA based on reverse<br />
transcriptase - polymerase<br />
chain reaction (RT - PCR) in<br />
leukocyte fraction of peripheral<br />
blood or bone marrow;<br />
- test+ in large % of pts with<br />
tumors seemingly confined to<br />
organ (unclear significance)
STAGING
STAGING<br />
* two schemes commonly used to stage PC;<br />
- TNM stage system: most common (by<br />
American Joint Committee on Cancer, AJCC),<br />
evaluating size of tumor, extent of involved<br />
lymph nodes, metastasis and cancer grade;<br />
- Whitmore - Jewett stage: now used less<br />
commonly for research, but often st<strong>il</strong>l used by<br />
clinicians
TNM STAGING
PROSTATIC CANCER<br />
TNM clinical staging<br />
* T categories:<br />
* clinically inapparent, not palpable tumor (T1a<br />
- T1b) or detected from ↑ serum PSA (T1c);<br />
* palpable but clinically confined to gland (T2),<br />
and:<br />
* extended outside gland (T3 and T4);<br />
* N categories: presence or absence of nodal<br />
metastases;<br />
* M categories: presence or absence of <strong>di</strong>stant<br />
metastases
PROSTATIC CANCER<br />
TNM clinical staging
PROSTATIC CANCER<br />
Clinical staging<br />
TNM definitions: T1<br />
* TX: primary tumor cannot be assessed;<br />
* T0: no evidence of primary tumor;<br />
* T1: clinically inapparent tumor not palpable nor<br />
visible by imaging:<br />
T1a: incidental histologic fin<strong>di</strong>ng in ≤ 5% of tissue<br />
resected;<br />
T1b: incidental histologic fin<strong>di</strong>ng in > 5% of tissue<br />
resected;<br />
T1c: identified by needle biopsy due to elevated PSA
* T2: confined within prostate:<br />
- T2a: involving 1 lobe;<br />
- T2b: involving both lobes;<br />
[- note: tumor found in 1 or both lobes by needle<br />
biopsy, but not palpable or visible by imaging,<br />
classified as T1c]<br />
PROSTATIC CANCER<br />
Clinical staging<br />
TNM definitions: T2
PROSTATIC CANCER<br />
Clinical staging<br />
TNM definitions: T3 - T4<br />
* T3: tumor extends through prostatic capsule:<br />
T3a: extracapsular extension (uni- or b<strong>il</strong>ateral);<br />
T3b: tumor invades seminal vesicle(s);<br />
[- note: invasion into prostatic apex or into (but not<br />
beyond) prostatic capsule is not classified as T3, but as<br />
T2];<br />
* T4: tumor fixed to or inva<strong>di</strong>ng adjacent<br />
structures other than seminal vesicles (bladder<br />
neck, external sphincter, rectum, levator muscles<br />
and / or pelvic wall)
LOCAL<br />
STAGING<br />
OF<br />
PROSTATE<br />
CANCER
PROSTATIC CANCER<br />
Clinical staging. TNM definitions: Regional nodes (N)<br />
* = nodes of true pelvis (= nodes below<br />
bifurcation of common <strong>il</strong>iac arteries, inclu<strong>di</strong>ng<br />
pelvic, hypogastric, obturator, <strong>il</strong>iac, periprostatic,<br />
and sacral);<br />
* <strong>di</strong>stant lymph nodes = outside confines of true<br />
pelvis (aortic, common <strong>il</strong>iac, inguinal, superficial<br />
inguinal, supraclavicular, cervical, scalene, and<br />
retroperitoneal nodes) and their involvement =<br />
<strong>di</strong>stant metastases;<br />
* NX: regional lymph nodes cannot be assessed;<br />
* N0: no regional lymph node metastasis;<br />
* N1: metastasis in regional lymph node(s)<br />
[- note: laterality does not affect N classification]
PROSTATIC CANCER<br />
Clinical staging. TNM definitions<br />
Distant metastasis (M)<br />
* MX: <strong>di</strong>stant metastasis cannot be assessed;<br />
* M0: no <strong>di</strong>stant metastasis;<br />
* M1: <strong>di</strong>stant metastasis;<br />
M1a: nonregional lymph node(s);<br />
M1b: bone(s);<br />
M1c: other site(s)
PROSTATIC CANCER<br />
Clinical staging: limits. I.<br />
* limit of TNM system = most PC are now<br />
<strong>di</strong>agnosed as T1c (by needle biopsy, often<br />
because ↑ PSA) or T2 (st<strong>il</strong>l confined within<br />
prostate) <strong>di</strong>sease, lea<strong>di</strong>ng to attempts at refining<br />
pre<strong>di</strong>ction of local <strong>di</strong>sease extent:<br />
- multiplex staging models (based on a<br />
combination of fin<strong>di</strong>ngs of <strong>di</strong>gital examination,<br />
biopsy, Gleason score and baseline PSA);<br />
- models based on no. of cores and % of each<br />
core involved by tumor;<br />
* unproven efficacy at pre<strong>di</strong>cting node<br />
involvement
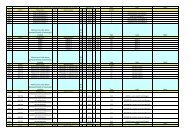
PROSTATIC CANCER<br />
Variables in multiplex staging models
PROSTATIC CANCER<br />
Clinical staging. Differentiation (G)
Stage I<br />
T1a, N0, M0, G1<br />
Stage II<br />
T1a, N0, M0, G 2, 3 - 4<br />
T1b, N0, M0, any G<br />
T1c, N0, M0, any G<br />
T2, N0, M0, any G<br />
PROSTATIC CANCER<br />
AJCC stage groupings<br />
Stage III<br />
T3, N0, M0, any G<br />
Stage IV<br />
T4, N0, M0, any G<br />
any T, N1, M0, any G<br />
any T, any N, M1, any G
PROSTATIC CANCER<br />
AJCC stage groupings
STAGING<br />
WHITEMORE - JEWETT STAGING
PROSTATIC CANCER<br />
Whitemore - Jewett Staging System. Stage A<br />
* stage A = clinically undetectable tumor<br />
confined to prostate gland, as incidental<br />
fin<strong>di</strong>ng at prostatic surgery;<br />
- substage A1: G1 with focal involvement, usually<br />
left untreated;<br />
- substage A2: G2 - G3 or involving multiple foci<br />
in gland
Multicentricity of prostate cancer<br />
whole mount section of prostate showing two <strong>di</strong>stinct foci of<br />
adenocarcinoma <strong>il</strong>lustrating the frequent fin<strong>di</strong>ng of multicentricity
PROSTATIC CANCER<br />
Whitemore - Jewett Staging System. Stages B - C<br />
* stage B = confined to prostate gland:<br />
substage B0: nonpalpable, PSA - detected;<br />
substage B1: single nodule in 1 lobe;<br />
substage B2: more extensive involvement of 1 lobe or<br />
involvement of both lobes<br />
* stage C = clinically localized to periprostatic area<br />
but exten<strong>di</strong>ng through prostatic capsule, with<br />
seminal vesicles possibly involved:<br />
substage C1: clinical extracapsular extension;<br />
substage C2: extracapsular tumor producing bladder<br />
outlet or ureteral obstruction
PROSTATIC CANCER<br />
Whitemore - Jewett Staging System. Stage D<br />
* Stage D = metastatic <strong>di</strong>sease:<br />
substage D0: clinically localized <strong>di</strong>sease (prostate<br />
only) but persistently elevated enzymatic serum<br />
acid phosphatase titers;<br />
substage D1: regional lymph nodes only;<br />
substage D2: metastases to <strong>di</strong>stant lymph nodes,<br />
bone or visceral organs;<br />
substage D3: D2 prostate cancer pts who<br />
relapsed after adequate endocrine therapy
STAGING<br />
COMPARISON BETWEEN TNM AND<br />
WHITEMORE - JEWETT STAGING
CLINICAL STAGES<br />
BY TNM CLASSIFICATION<br />
AND<br />
WHITMORE - JEWETT<br />
STAGING SYSTEM