Vellakovil City Development Plan - Municipal
Vellakovil City Development Plan - Municipal
Vellakovil City Development Plan - Municipal
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Submitted to<br />
CITY DEVELOPMENT PLAN<br />
The Commissionerate of <strong>Municipal</strong> M nicipal<br />
Administration<br />
6th Floor, Ezhilagam Annex Building<br />
Chepauk, Chennai – 600 005<br />
VELLAKOIL MUNICIPALITY<br />
Final Report p<br />
August 2009<br />
Submitted by<br />
SMEC (India) (I di ) Pvt. P t Ltd. Ltd<br />
No. 11/6, 18th East Street,<br />
Thiruvanmiyur<br />
Chennai – 600 041
CITY DEVELOPMENT PLAN<br />
VELLAKOIL MUNICIPALITY<br />
Final Report<br />
December 2009<br />
Submitted to Submitted by<br />
The Commissonerate of <strong>Municipal</strong> Administration SMEC (India)Pvt. Ltd<br />
6 th Floor, Ezhilagam Anex Building No.11/6,18 th East Street,<br />
Chepauk, Chennai‐600 005 Thiruvanmiyur,<br />
Chennai‐600 041
Final Report <strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity<br />
CITY DEVELOPMENT PLAN - VELLAKOIL MUNICIPALITY<br />
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY<br />
1. CITY DEVELOPMENT PLAN – CONTEXT and CONTENT<br />
The Commissioner of <strong>Municipal</strong> Administration (CMA), Government of Tamil Nadu, under the Third Tamil<br />
Nadu Urban <strong>Development</strong> Programme (TNUDP III) has taken effective steps to assist the Urban Local<br />
Bodies (ULBs) in the State, particularly the Grade III municipalities to strengthen and improve the financial<br />
position for effective capital investment management and service delivery to the public. These ULBs spread<br />
over the State, are service centres to the surrounding rural areas, offering marketing, physical and social<br />
infrastructure facilities. These centres have potential for future growth, and therefore, it is essential to<br />
formulate a <strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> (CDP) for these urban centres and immediate implementation of reforms<br />
in these ULBs for better management. In this regard, the CMA has appointed SMEC India Pvt. Ltd as<br />
Consultants for preparing a comprehensive <strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> (CDP) for four of the Grade III <strong>Municipal</strong><br />
Towns in the Thanjavur region.<br />
2. SWOT and VISION<br />
Vellakoil, a Grade III <strong>Municipal</strong>ity in Tiruppur district is located at a distance of 48 km, east of Coimbatore<br />
and 60km, south of Erode town. The area of the town is 64.75 sq.km and the population is 34,438 as per<br />
census 2001. The latitude and longitude of this town are 8º36’’41’’N and 78º3 ‘’30’’E respectively. It is well<br />
connected by road to the surrounding urban centres.<br />
Vellakoil municipality is a prominent commercial center for agro products like oil, vanaspathy and textiles.<br />
The town and its surroundings has high concentration of power loom & handloom weaving, textile<br />
processing units, rice milling, edible oil expelling units, paper products and basic metal products industries<br />
etc.<br />
The <strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> is a tool which adapts a participative approach to planning, and implementing<br />
projects as stakeholder workshops; involving users, elected councillors, line agencies, private organizations,<br />
NGOs and CBOs. Some of the core issues which emerged during interaction with stakeholders include<br />
provision of adequate and quality water supply to all the residents of the city, improvement in solid waste<br />
management and sewerage systems in the town (both currently impacting the physical environment in a<br />
negative manner), rejuvenation of water bodies, and road improvement and improving the financial and<br />
technical capacity of the municipal body.<br />
A town level SWOT analysis, with reference to its regional context has been done based on feedback from<br />
stakeholder workshops and analysis of the status of various sectors of the city.<br />
SWOT Analysis for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity<br />
STRENGTH WEAKNESS<br />
Access to Erode, a major node for textile, Crippling Environmental pollution to odais & agricultural<br />
leather & agriculture, timber based industries hinterland<br />
Good connectivity with nearby Urban centres Absence of recreational facilities<br />
Nh-67 bisecting the town Need to expedite infrastructure improvements<br />
Perennial source of water from River Cauvery Inadequate social infrastructure facilities<br />
High Urban literacy rate at 75% Extensive <strong>Municipal</strong> area – Increased demand for<br />
Fertile agricultural hinterland<br />
penetration of <strong>Municipal</strong> services<br />
Excellent industrial base of textile, bricks, agro<br />
Absence of rail connectivity<br />
based timber & leather<br />
OPPORTUNITIES THREATS<br />
Availability of land for future development Rising land and labour costs<br />
Co-operative mindset of community. Increased Environmental regulations & falling margins<br />
Access to Higher Educational Institutions Low skill, low technology manufacturing units<br />
Opposition to leather based industries /brick industries<br />
Source : Feedback from stakeholders meeting and analysis.
Final Report <strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity<br />
The town of Vellakoil is visualized as “An clean and green town; economically self sustaining, with<br />
access to physical and social infrastructure”.<br />
Supporting this vision is a set of development objectives, defined along various sectors of infrastructure. It<br />
covers the current status, issues in the sector, likely future demand, strategies for improvement and<br />
identified projects to meet these objectives. The sectors covered in the CDP for Vellakoil include water<br />
supply, sewerage and sanitation, solid waste management, storm water drains, street lights, slum<br />
improvement and other remunerative and social projects.<br />
3. CITY INVESTMENT PLAN<br />
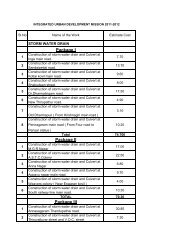
The summary of sector-wise investment requirements and prioritisation is given in the following table. The<br />
total investment required would be over Rs. 9018.42 lakhs.<br />
Capital Investment Needs for Vellakoil<br />
S.N Physical Infrastructure facilities Amount<br />
( in lakhs)<br />
1 Water Supply 1199.12<br />
2 Sewerage System 3300.00<br />
3 Storm Water Drains 300.00<br />
4 Solid Waste management 800.00<br />
5 Roads 2043.00<br />
7 Bus Shelter 10.00<br />
8 Street Lights 182.00<br />
9 Slum Improvement 709.00<br />
10 Parks and Play Fields 20.00<br />
11 Market 150.00<br />
12 Public Convenience 35.00<br />
13 Burial Ground 100.00<br />
14 E-Governance 16.00<br />
15 Urban Greenery 10.00<br />
16 Other Projects 100.00<br />
17 Updation of Database on GIS Platform 4000<br />
18 Property Mapping 4.30<br />
Total 9018.42<br />
4. FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE OF VELLAKOIL MUNICIPALITY<br />
The summary of the financial status of Vellakoil municipality is as follows:<br />
• In the case of Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity, it is observed that the <strong>Municipal</strong>ity has shown net deficit in all<br />
the 5 years. Prior to depreciation, the <strong>Municipal</strong>ity has shown surplus in 4 out of the last 5 years<br />
except 2006-07. Thus the <strong>Municipal</strong>ity has earned cash surplus in 4 years.<br />
• The average current collection efficiency of the municipality is very good as compared as to other<br />
municipalities in the district in case of all the sources of income and is around 95% - 100%. The<br />
arrears collection performance in respect of Property Tax and Other Income needs to be improved.<br />
• The broad financial analysis of the Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity finances reveal that the <strong>Municipal</strong>ity has to<br />
gradually increase its own sources of income and collection efficiency for servicing the additional<br />
borrowings in the future.<br />
• The <strong>Municipal</strong>ity’s borrowings are high at Rs. 236 lakhs compared to its income. This may result<br />
high debt service in future years. So the <strong>Municipal</strong>ity’s capacity to borrow further funds depends on<br />
its capacity to increase its revenues.<br />
To summarise, the overall income pattern of <strong>Vellakovil</strong> <strong>Municipal</strong>ity indicates both positive and negative<br />
features. The positive trends are on the income side, where the <strong>Municipal</strong>ity has higher growth rate and<br />
good collection performance.
Final Report <strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity<br />
5. PROPOSED REFORMS IN URBAN MANAGEMENT<br />
In the Final Report a detailed action plan and implementation schedule to aid the effective execution of the<br />
business plan would be furnished. Achieving the set objectives would require a high degree of commitment<br />
from the municipality and active support of the council and the state government.<br />
• The municipality will be expected to adopt measures to improve property tax base, ensure<br />
operational efficiency in street lighting and water supply, computerisation of <strong>Municipal</strong> functions,<br />
introduce charges for SWM, timely auditing and online publishing of account statements , asset<br />
management plan , capacity building initiatives in the engineering, health and accounts sections.<br />
• The <strong>Municipal</strong> council may assume charge of increase in water charges, removal of public<br />
fountains, privatisation initiatives, and premobilisation of deposits, parking / advertisement<br />
regularisation plan and execution of property mapping exercise. The council would also be required<br />
to include charges for SWM (non-domestic) and regularise unauthorised layouts.<br />
• The expectations from the State Government are fast track litigation for disputed properties,<br />
enacting Community Participation law, facilitating private participation in investments, ensuring<br />
transparency in accounting and creating public awareness on the roles and responsibilities of the<br />
citizens.<br />
6. ESTIMATION OF INVESTMENT CAPACITY<br />
The borrowing and investment capacities of the town are arrived considering the revenue income<br />
and expenditure under the sustainable scenario, after implementation of the mandatory reforms<br />
proposed in this report.<br />
The investment capacity for the sustainable scenario can be summed up as below:<br />
Summary of Borrowing and Investment Capacity<br />
Description Scenario I Scenario II Scenario III<br />
Borrowing Capacity Rs. 373.26lacs Rs. 744.13 lacs Rs. 937.48 lacs<br />
Investment Capacity Rs. 1493.02 lacs Rs. 4134.08 lacs Rs. 5208.24 lacs<br />
Investment Requirement - Rs. 9018.12 lacs Rs. 9018.12 lacs<br />
Sustainable investment capacity % - IC / IR - 46% 57.75%<br />
Scenario I - Estimation of Investment Capacity on as is where basis<br />
Scenario II - Estimation of Investment Capacity with Projects & Growth Rate of 7.5% for Devolution Funds<br />
Scenario III - Estimation of Investment Capacity with Projects & Growth Rate of 10% for Devolution Funds.<br />
7. INFERENCE<br />
The investment capacity of Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity on ‘As is Where Basis’ works out to Rs. 1493<br />
lacs.<br />
The investment capacity of Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity works to 46% in case of Scenario II (Growth<br />
Rate of Devolution Funds assumed @ 7.5% p.a.) and 58% in case of Scenario III (Growth<br />
Rate of Devolution Funds assumed @ 10% p.a.).<br />
In value terms the investment capacity works out to Rs. 4135 lacs under Scenario II and Rs.<br />
5210 lacs under Scenario III.<br />
It may be observed that the investment capacity has improved with the introduction of new<br />
projects as compared to ‘As is Where Basis’ scenario. The same is on account of the fact that<br />
the <strong>Municipal</strong>ity has large number of commercial and industrial assessments, which are<br />
presently untapped on account of water and sewerage connections.<br />
Thus it can be inferred that the investment capacity of the <strong>Municipal</strong>ity is around 46% of the<br />
total investment requirement.
Final Report <strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity<br />
Based on the above, it can be inferred that the <strong>Municipal</strong>ity can take up only the small projects,<br />
where the funding is mostly by way of Grants as given below :<br />
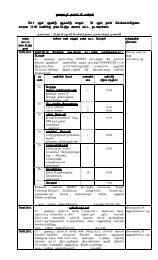
S.No. Particulars Total Priority Funding By<br />
A Physical Infrastructure Facilities L : G : O<br />
I Water Supply<br />
a) Improvements to Water Supply 1199.20 A 0:90:10<br />
II Sewerage & Sanitation<br />
a) New Underground Sewerage Scheme 3300.00 A 37:35;28<br />
Total 4499.20<br />
The above two projects can be taken up by the <strong>Municipal</strong>ity as there are large number of<br />
commercial and industrial assessments and on stand alone basis these projects are viable at<br />
the funding pattern given above.<br />
Besides the above, the following other small projects can be taken up, where the funding<br />
pattern is mainly by way of grants and deposit mobilization :<br />
Priority projects suggested under CDP<br />
S.No. Particulars Total Priority Funding By<br />
A Physical Infrastructure Facilities L : G : O<br />
I Strom Water Drains<br />
a) Construction of new drains and providing mesh covers 300.00 A 0:90:10<br />
II Bus Shelter<br />
a) Construction of New Bus Shelter 10.00 A 100% Grant<br />
III Street Lights<br />
a) High mast lights at Old & New Bus Stand 14.00 A 100% Grant<br />
b) Retrofitting and energy saving devices 23.00 A ESCO<br />
c) Central Median lights at main roads for 3Km 45.00 A 0:90:10<br />
B Social Infrastructure Facilities<br />
I Slum Improvements<br />
a) Improvement to Slums 709.00 B 100% Grant<br />
II Market<br />
a) Construction of Daily Market 75.00 A 100% ULB<br />
b) Construction of Weekly Market 75.00 A 100% ULB<br />
C Other Projects<br />
I Remunerative Projects<br />
a) Commercial Building (G+2) at Erode Road near 50.00 A 100% ULB<br />
Bus Stand<br />
II E-Governance<br />
a) E-Governance 16.00 A 100% Grant<br />
b) Updation of Database on GIS 40.00 C 0:90:10<br />
c) Property Mapping 4.30 A 100% ULB<br />
Total 1361.30<br />
As regards other projects with large financial cost, the <strong>Municipal</strong>ity would require more support<br />
from the Government towards both capital cost and operation & maintenance expenses. Thus<br />
it would be possible to take up those projects if more support is provided by the Government<br />
and by improving own sources of income.
Abbreviation and Acronyms<br />
ANM : Auxiliary Nurse Midwife<br />
AMT : Anna Marumalarchi Thittam<br />
BOT : Build, Operate and Transfer<br />
BPL : Below Poverty Line<br />
BSUP : Basic Services for Urban Poor<br />
CAA : Constitution Amendment Act<br />
CAGR : Compounded Annual Growth Rate<br />
CC : Cement Concrete<br />
CCP : <strong>City</strong> Corporate <strong>Plan</strong><br />
CBED : Community Based Energy <strong>Development</strong><br />
CDP : <strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong><br />
CETP : Common Effluent Treatment <strong>Plan</strong>t<br />
CFC : Central Finance Commission<br />
CIP : Capital Investment <strong>Plan</strong><br />
CPHEEO : Central Public Health & Environmental Engineering Organization<br />
CPM : Consultative Process Meeting<br />
D&O : Dangerous and Offensive Trade<br />
DFR : Draft Final Report<br />
DPR : Detailed Project Report:<br />
EAR : Environmental Assessment Report<br />
ECR : East Coast Road<br />
ESF : Environmental and Social Framework<br />
ETRP : Emergency Tsunami Reconstruction Project<br />
FY : Financial Year<br />
FOP : Financial Operating <strong>Plan</strong><br />
GLR : Ground Level Reservoir<br />
G.S.T Road : Grand South Trunk Road<br />
Gm : Grams<br />
GoTN : Government of Tamil Nadu<br />
Ha : Hectares<br />
HP : Horse Power<br />
HSC : House Service Connection<br />
IHSDP : Integrated Housing & Slum <strong>Development</strong> Programme<br />
IPT : Intermediate Public Transport<br />
ISP : Integrated Sanitation program<br />
IUDP : Integrated Urban <strong>Development</strong> Project<br />
JNNURM : Jawaharlal Nehru National Urban Renewal Mission<br />
Kg : Kilogram<br />
Km : Kilometer<br />
LAP : Local Assistance Programme
LCS : Low Cost Sanitation<br />
Ll : Lakh Litres<br />
LPA : Local <strong>Plan</strong>ning Area<br />
Lpcd : Liters Per Capital per day<br />
M : Metres<br />
MIAM : <strong>Municipal</strong> Infrastructure Asset Management<br />
ML : Million Litres<br />
MLD : Million Litres per day<br />
MSW : <strong>Municipal</strong> Solid Waste<br />
NGO : Non Governmental Organisation<br />
NH : National Highway<br />
Nos : Numbers<br />
OHT : Over Head Tank<br />
O&M : Operation and Maintenance<br />
PAP : Project Affected Persons<br />
PHC : Primary Health Center<br />
PPI : Pulse Polio Immunization<br />
PPP : Public Private Partnership<br />
PWD : Public Works Department<br />
SFC : State Finance Commission<br />
SH : State Highway<br />
SHG : Self Help Group<br />
Sq.km : Square Kilometers<br />
SST : Summer Storage Tank<br />
STP : Sewage Treatment <strong>Plan</strong>t<br />
SWM : Solid Waste Management<br />
TEAP : Tsunami Emergency Assistance Project<br />
TNEB : Tamil Nadu Electricity Board<br />
TNRDC : Tamil Nadu Road <strong>Development</strong> Corporation<br />
TNSCB : Tamil Nadu Slum Clearance Board<br />
TNUDP : Tamil Nadu Urban <strong>Development</strong> Project<br />
TNUIFSL : Tamil Nadu Urban Infrastructure Financial Service Limited<br />
TPD : Tonnes Per Day<br />
TUFIDCO : Tamil Nadu Urban Finance and Infrastructure <strong>Development</strong> Corporation<br />
TWAD : Tamil Nadu Water Supply and Drainage Board<br />
UA : Urban Area<br />
UGD : Under Ground Drainage<br />
UIDSSMT : Urban Infrastructure <strong>Development</strong> Scheme for Small & Medium Towns<br />
ULB : Urban Local Body<br />
VAMBAY : Valmiki Ambedkar Awas Yojana<br />
WBM : Water Bound Macadem<br />
WSP : Waste Stabilization Pond<br />
WTP : Water Treatment <strong>Plan</strong>t
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY<br />
COUNCIL RESOLUTION<br />
ABBREVIATIONS AND ACRONYMS<br />
CONTENT<br />
1 CONTEXT, CONCEPT AND CONTENTS OF CITY DEVELOPMENT PLAN<br />
1.1 Context of the Study 1<br />
1.2 Objectives 1<br />
1.3 Revice Meeting for Dtaft Final Reports 1<br />
2 TOWN PROFILE, PHYSICAL PLANNING AND GROWTH MANAGEMENT 4<br />
2.1 Regional Setting 4<br />
2.2 Physical Features 4<br />
2.3 Climate and Rainfall 4<br />
2.4 History of the <strong>Municipal</strong>ity 4<br />
2.5 Demographic Features 4<br />
2.5.1 Population and its Growth 4<br />
2.5.2 Population projection 6<br />
2.5.3 Sex ration and literacy 7<br />
2.6 Occupational Pattern 7<br />
2.7 Physical <strong>Plan</strong>ning and growth management issues 8<br />
2.8 Growth Management issues and solution initiatives 8<br />
3 VISION AND STRATEGIES FOR ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT 9<br />
3.1 Stakeholders workshop and Vision statement 9<br />
3.2 SWOT Analysis 9<br />
3.3 Vision for Vellakoil Town 9<br />
3.4 Strategies for Economic <strong>Development</strong> 10<br />
3.5 Urban Infrastructure 11<br />
3.5.1 Sector wise Vision 11<br />
3.6 Performance and Demand Assessment 12<br />
3.7 Strategies for Poverty Reduction and Slum Upgradation 14<br />
4 ORGANISATIONAL STRUCTURE 15<br />
4.1 Elected Body 15<br />
Executive Wing 15<br />
4.2.1 General Administration 15<br />
4.2.2 Engineering Department 16<br />
4.2.3 Accounts Department 16<br />
4.2.4 Public Health Department 16<br />
4.2.5 Town <strong>Plan</strong>ning Department 16<br />
4.3 Staff Strength Position and vacancy position 16<br />
4.4 Issues in Human Resource 18<br />
4.5 Organisation Management 18<br />
5 INFRASTRUCTURE STATUS AND NEEDS ASSESSMENT 19<br />
5.1 Physical Infrastructure 19<br />
5.1.1 Water Supply 19<br />
5.1.2 Sewerage 21<br />
5.1.3 Storm Water Drains 21<br />
5.1.4 Improvement to water bodies 22<br />
5.1.5 Soild Waste Management 23<br />
5.1.6 Roads 25<br />
5.1.7 Bus Stand 27<br />
5.1.8 Bus Shelter 27<br />
5.1.9 Street Lights 27
5.2 Social Infrastructure 29<br />
5.2.1 Slum Improvement 29<br />
5.2.2 Parks and Play fields 30<br />
5.2.3 Market 31<br />
5.2.4 Public Convenience 31<br />
5.2.5 Slaughter House 31<br />
5.2.6 Burial Ground 31<br />
5.2.7 E-Governance 32<br />
5.2.8 Urban Greenary 32<br />
5.3 Other Projects 32<br />
5.3.1 Updation of Database On GIS Platform 32<br />
5.4 Proposals to be implemented by other Agencies 33<br />
5.5 Capital Investment <strong>Plan</strong> 34<br />
6 REFORMS AND ACTION PLAN FOR PROJECT IMPLEMENTATION 36<br />
6.1 Present Scenario in Urban Reforms 36<br />
6.2 Proposed Interventions at state level 37<br />
6.3 Proposed Interventions at <strong>Municipal</strong> level 38<br />
6.3.1 Reforms In Resource Mobilisation 39<br />
6.3.2 Privatisation Initiatives 42<br />
6.3.3 Energy and Resource efficiency 44<br />
6.3.4 Computerisation and E-governance 45<br />
6.3.5 Accounts and auditing 46<br />
6.3.6 Institutional Management 46<br />
6.3.7 Reforms in <strong>Municipal</strong> Service Delivery 51<br />
7 ASSETS MANAGEMENT 52<br />
7.1 Activities of Asset Management <strong>Plan</strong> (AMP) 52<br />
7.2 Priority asset management options 53<br />
7.3 Land Assets 54<br />
7.4 Management Options for land assets 55<br />
7.5 Proposed New Assets 55<br />
8 FINANCIAL OPERATING PLAN 57<br />
8.1 Capital Investment <strong>Plan</strong> 57<br />
8.2 Other Projects and on going projects 59<br />
8.3 Means of Finance 60<br />
8.4 Financial Sustainability 65<br />
8.5 Basic Assumptions for Projections 65<br />
8.5.1 Income 66<br />
8.5.2 Expenditure 71<br />
8.5.3 Collections 72<br />
8.5.4 Annuity Factor 73<br />
8.6 Project Cash Flows and FOP Results 73<br />
8.7 Impact of Potential Improvements 81<br />
8.8 Estimation of Investment Capacity 81<br />
8.9 Key Indicators 83<br />
8.10 Inference 83<br />
9 PUBLIC CONSULTATION PROCESS 86
TABLES<br />
2.1 Population and growth 4<br />
2.2 Comparative statement of projected population 7<br />
2.3 Occupational Pattern - 2001 7<br />
3.1 SWOT Analysis 9<br />
3.2 Sector wise vision for the key Infrastructure 11<br />
3.3 Performance Indicators for key <strong>Municipal</strong> Services 12<br />
3.4 Demand for <strong>Municipal</strong> Services 13<br />
4.1 Staff Strength 17<br />
4.2 Additional Staff Required 18<br />
5.1 Details of OHTs 20<br />
5.2 Water Tariff-Deposit Details 20<br />
5.3 Demand & Supply in Water Supply - Projection 20<br />
5.4 Storm water Drains - proposals 22<br />
5.5 Solid Waste management – Proposals* 25<br />
5.6 Category of roads 26<br />
5.7 Road improvement - Proposals 26<br />
5.8 Existing street lights and energy consumption 27<br />
5.9 Street lights - Proposals 28<br />
5.10 Location of Existing Slum Areas 29<br />
5.11 Details of Existing Slum Areas 29<br />
5.12 Slum - Proposals 30<br />
5.13 Market - proposals 31<br />
5.14 Proposals to be implemented by other Agencies 33<br />
5.15 Capital Investment Programme 34<br />
6.1 Road map – Environmental Improvement 39<br />
6.2 Road Map - Improving revenue from own sources 40<br />
6.3 Road Map Improving revenue from user charges 41<br />
6.4 Road Map for Formation of new sustainable revenue bases 42<br />
6.5 Road Map for Privatization initiatives 44<br />
6.6 Road Map for Energy and Resource efficiency 45<br />
6.7 Road map for Computerization and E-Governance 46<br />
6.8 Technical Assistance for Elected representatives 47<br />
6.9 Technical Assistance for ULB staff 48<br />
6.10 Road map for Accounts & auditing and Institutional Management 49<br />
6.11 Road Map For Implementation Of All Projects 50<br />
6.12 Reform Agenda - <strong>Municipal</strong> Service Delivery 51<br />
7.1 Priority <strong>Municipal</strong> Assets – Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity 53<br />
7.2 Proposed Use – Land Asset 54<br />
7.3 New Assets for the year - 2010 to 2015 55<br />
8.1 Projects to be executed by the <strong>Municipal</strong>ity 57<br />
8.2 Projects to be executed by Other Agencies 59<br />
8.3 Projects under Implementation by the <strong>Municipal</strong>ity 59<br />
8.4 Multi Year Investment <strong>Plan</strong> and Means of Finance 60<br />
8.5 Consolidated Means of Finance 65<br />
8.6 Ratio of Property tax 66<br />
8.7 Water supply Charges - Existing 67<br />
8.8 House Service Connections - Percentage 68<br />
8.9 Sewage Charges 68<br />
8.10 Increase in Tariff - Sewage Charges 69<br />
8.11 Increase in Deposit - Sewage Charges 69<br />
8.12 Assumptions - Increase in Expenditure 71<br />
8.13 Assumptions – O&M 71<br />
8.14 Assumptions – Provision of doubtful debts 72<br />
8.15 Assumptions – Property tax collection 72<br />
8.16 Assumptions – Profession tax 72<br />
8.17 Assumptions – Other Non Tax Income 72<br />
8.18 Assumptions – Water Charges 72<br />
8.19 Assumptions – Drainage Charges 73<br />
8.20 Terms of Loan Funding for Proposed Investments 73
8.21 Consolidated Income & Expenditure for next 20 years (up to FY 2028-29) 74<br />
8.22 Consolidated Balance Sheet for next 20 years (up to FY 2028 – 29) 76<br />
8.23 Summary of Borrowing and Investment Capacity - Scenario I 82<br />
8.24 Summary of Borrowing and Investment Capacity - Scenario II 82<br />
8.25 Summary of Borrowing and Investment Capacity - Scenario III 83<br />
8.26 Key Indicators 83<br />
8.27 Priority Projects suggested under CDP 84<br />
8.27a Priority Projects suggested under CDP through Grants and Deposits 84<br />
9.1 Major issues and solution initiatives 87<br />
9.2 Minutes of the consultative process meeting 87<br />
FIGURES<br />
2.1 Occupational Pattern of Vellakoil -2001 7<br />
4.1 Status of <strong>Municipal</strong> Staff Strength 17<br />
4.2 Organisational structure of Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity 17<br />
5.1 Functional Elements of a <strong>Municipal</strong> Solid Waste Management System 24<br />
MAPS<br />
2.1 Regional setting of the Town 5<br />
2.2 Town Map - Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity 6<br />
1 Minutes of Meeting<br />
2 Population Projection<br />
3 Finance Working Sheets<br />
4 Urban Indicators<br />
ANNEXURES
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
1.1 CONTEXT OF THE STUDY<br />
CONTEXT, CONCEPT AND CONTENTS OF CITY DEVELOPMENT PLAN<br />
The Commissioner of <strong>Municipal</strong> Administration (CMA), Government of Tamil Nadu, under the<br />
Third Tamil Nadu Urban <strong>Development</strong> Programme (TNUDP III) has taken effective steps to<br />
assist the Urban Local Bodies (ULBs) in the State, particularly the Grade III municipalities to<br />
strengthen and improve the financial position for effective capital investment management, and<br />
service delivery to the public. These ULBs spread over the State, are service centres to the<br />
surrounding rural areas, offering marketing, physical and social infrastructure facilities. These<br />
centres have a good potential for future growth, and therefore, it is essential to formulate a <strong>City</strong><br />
<strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> (CDP) for these urban centres and immediate implementation of reforms in<br />
these ULBs for better management. The CMA has begun the process of capacity building in<br />
these ULBs to enhance their performance. In this regard, the CMA has appointed Consultants for<br />
preparing comprehensive <strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> (CDP) for each of the Grade III <strong>Municipal</strong><br />
Towns.<br />
1.2 OBJECTIVES<br />
The objectives of the study include:<br />
• Defining the directions of growth of the town, and up gradation of services relevant to<br />
economic activities and development.<br />
• Examination of the need for the projects identified by the Urban Local Bodies, and<br />
assessment of the demand in terms of gaps either as deficiency or as excess.<br />
• Studying the status of essential urban infrastructural services and outlining broadly the<br />
needs.<br />
• Defining specific rehabilitation and capital improvement needs of infrastructural facilities<br />
and services in all parts of the urban areas including slums.<br />
• Analysis of improvement techniques and methods to enhance the local bodies’ resource<br />
positions and improve the management system that would sustain the proposed<br />
rehabilitation programmes.<br />
• Identification of reforms required in administration and service delivery system of the<br />
urban local body.<br />
• Studying improvements / changes required in the ULB setup to improve the O&M of<br />
assets.<br />
• Identifying measures to address overall growth measures including service needs in a<br />
sustainable mode.<br />
1.3 REVIEW MEETING FOR DRAFT FINAL REPORTS<br />
On the review of the Final reports (Stage-IV) held at the RDMA office, Tiruppur on 10.11.09 for<br />
the towns of Kasipalayam, Surampatti, Veerappanchatram, Periyasemur and Vellakoil<br />
<strong>Municipal</strong>ities, the Review Committee indicated certain remarks in the minutes of the meeting,<br />
and the Consultant’s updations are presented below:<br />
1<br />
1
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
The consultants were asked to:<br />
S.N Points raised in the minutes of meeting<br />
Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity<br />
Reply / Remarks<br />
1. The cost and funding pattern for water supply improvement scheme<br />
has to be revised to Rs.1199.12 lakhs (Grant – Rs.852.35 lakhs,<br />
TUFIDCO Loan –Rs.300 lakhs and ULB contribution – Rs.46.77<br />
lakhs). The O&M cost to be revised to Rs.49 lakhs.<br />
Since done. Refer chapter 5, section 5.1.2<br />
2. Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity has been annexed to Tiruppur District and the<br />
same needs to be updated in the report.<br />
3. The Proposed cost for the construction of commercial building near<br />
Bus stand has to be revised to Rs.100 lakhs.<br />
2<br />
Since updated.<br />
4. The Weekly Market has to be given as Weekly Market/Shandy. Since done.<br />
Common Points<br />
1. The proposed years under CIP need to changed to 2010-11 to 2014-<br />
15 or as Years 1 to 5.<br />
Since done. The revised cost has been given under chapter 5, section 5.3<br />
Since done.
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
Road map for <strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong><br />
The Table given below presents the stages and contents under each stage of the presentation of the CDP.<br />
Stage I<br />
Inception Report<br />
Town reconnaissance and<br />
Data collection.<br />
Modules :<br />
- Strategic vision<br />
- <strong>Development</strong> objectives<br />
- Methodology<br />
Stage II<br />
Interim Report<br />
Consultations and Analysis<br />
Modules :<br />
- Demand assessment<br />
- <strong>Municipal</strong> Fiscal status<br />
- Investment needs<br />
- Stake holder consultation<br />
3<br />
Stage III<br />
Draft Final Report<br />
Finalisation of<br />
Capital Investment Programme<br />
(CIP)<br />
Modules :<br />
- Strategic plan<br />
- Capital Investment<br />
Need(CIN)<br />
-Priority Asset management<br />
Stage IV<br />
Final Report<br />
FOP and Adoption by Council<br />
Modules:<br />
- FOP<br />
- Draft MOA<br />
- Policy interventions<br />
- Technical Assistance<br />
Present stage
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
2.1 REGIONAL SETTING<br />
TOWN PROFILE, PHYSICAL PLANNING AND GROWTH MANAGEMENT<br />
Vellakoil, a Grade III <strong>Municipal</strong>ity in Tiruppur district is located at a distance of 48 km, east of<br />
Coimbatore and 60km, south of Erode town. The area of the town is 64.75 sq.km and the<br />
population is 34,438 as per census 2001. The latitude and longitude of this town are 8º36’’41’’N<br />
and 78º3 ‘’30’’E respectively. It is well connected by road to the surrounding urban centres.<br />
Vellakoil municipality is a prominent commercial center for oil and vanaspathy. The regional<br />
setting of the town and the town map is shown in Map 2.1 and 2.2.<br />
2.2 PHYSICAL FEATURES<br />
Vellakoil is situated on Coimbatore – Thiruchirapalli NH-67. The major arterials from the town are<br />
the Thiruchirapalli – Coimbatore road running west to east, Erode – Tharapuram road & Moolanur<br />
road. The general gradient of the town slopes from North to South. The major soil found in this<br />
region is Black soil. The ground water table varies from 50m to 200m.<br />
2.3 CLIMATE AND RAINFALL<br />
The town and the surrounding region have a sub- tropical climate with temperatures varying from<br />
28 to 36ºC. Rainfall is intermittent, irregular and usually heavy during the southwest monsoon. The<br />
average annual rainfall ranges between 700-800 mm.<br />
2.4 HISTORY OF THE MUNICIPALITY<br />
Vellakoil was constituted as village panchayat during 1938 , upgraded to town panchayat in 1977<br />
and as Third Grade municipality in 2004. There are 21 wards in the <strong>Municipal</strong>ity.<br />
2.5 DEMOGRAPHIC FEATURES<br />
2.5.1 Population and its Growth<br />
Vellakoil population has grown in the past decade. As per the 2001 census, the town registered a<br />
population of 34438. The population growth rate of the town is19.3% during the period 1991-<br />
2001.<br />
Table 2.1 Population and growth.<br />
Year Population of Vellakoil Growth rate<br />
1991 28,878 -<br />
2001 34,438 19.3<br />
Source: Census of India.<br />
4<br />
2
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
Map 2.1 Regional setting of the Town<br />
5
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
PACHAPALAYAM<br />
VILLAGE<br />
TO KOVAI<br />
UTTHAMAPALAYAM VILLAGE<br />
TO DHARAPURAM<br />
1<br />
VELAGOUNDANPALAYAM<br />
KADAIYARAN VALASU<br />
PACHAGOUNDANVALASU<br />
THANEER<br />
PANTHAL<br />
LACHAMANAICKANPATTI<br />
VILLAGE<br />
21<br />
VAIYAPURI NAGAR 4<br />
KALLANKATTU<br />
VALASU<br />
KUTTAKATTUPUDUR<br />
SEERANGAGOUNDANVALASU<br />
SIVANATHAPURAM<br />
CHERAN NAGAR<br />
POTHIYAKADU<br />
14<br />
AGALARAIPALAYAMPUDUR<br />
2<br />
UPPUPALAYAM<br />
T.C.ROAD<br />
20<br />
L.K.C NAGAR<br />
METTUPALAYAM VILLAGE<br />
THIRUMANGALAM<br />
ARIYANDIPALAYAM<br />
K.P.C NAGAR<br />
K.P.C NAGAR<br />
19 18<br />
KAMARAJAPURAM<br />
ANNA NAGAR<br />
17<br />
16<br />
PUDUKADU<br />
DHARAPURAM ROAD<br />
15<br />
GANAPATHYPALAYAM<br />
THIRUVALLUVAR NAGAR<br />
KUMARAVALASU<br />
GANDHI NAGAR<br />
5<br />
6<br />
7<br />
RAJIV NAGAR<br />
SIVANATHAPURAM<br />
THEETHAMPALAYAM<br />
13<br />
NACHIYAPPA GOUNDAN<br />
VALASU<br />
SALAVAIYALLAR COLONY<br />
M.G.R.NAGAR<br />
3<br />
ARIVOLI NAGAR<br />
D.R . NAGAR<br />
THEETHAMPALAYAM<br />
SEMMANDAMPALAYAM ROAD<br />
KATCHERI<br />
VALASU<br />
6<br />
TO ERODE<br />
INDRA GANDHI NAGAR<br />
8<br />
10<br />
11<br />
ARUN CRUSHER<br />
MULANUR ROAD<br />
9<br />
SEMMANDAMPALAYAM<br />
KALIMOOPANPATTI<br />
ORAMPUPALAYAM<br />
MULAIYAMPOONDI VILLAGE<br />
MUTHU NAGAR<br />
TO TRICHY<br />
12<br />
KARATTUPALAYAM<br />
NACHIPALAYAM<br />
SENAPATHYPALAYAM<br />
VILLAGE<br />
PULLACHELIPALAYAM<br />
SUBRAMANIYAGOUNDANVALASU<br />
TO<br />
MULANUR<br />
MADAMEDU<br />
MANJAANGADU<br />
MOOTHANAICKAN VALSU<br />
Map 2.2 Town Map – Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity<br />
2.5.2 Population projection<br />
Based on the growth rate for the past two decades, the future population of the town has been<br />
projected using various methods and are tabulated as below:<br />
1. Arithmetical Increase Method<br />
2. Geometric Increase Method<br />
3. Incremental Increase Method<br />
4. Method of least square<br />
N<br />
NW<br />
W<br />
SW<br />
S<br />
NE<br />
SE<br />
E
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
Table 2.2 Comparative statement of projected population<br />
Sl. no. Method<br />
Projected Population for Vellakoil<br />
2010 2025 2040<br />
1 Arithmetical Increase 52208 72516 92823<br />
2 Geometrical increase 51620 81873 112132<br />
3 Incremental Increase 53348 94325 156681<br />
4 Method of Least Squares 49605 67605 85605<br />
Source: Analysis and calculations<br />
After a detailed analysis and comparison of each method, Geometrical increase method is found<br />
to be suitable and the population projections are based on the same. The details are given in<br />
Annexure-2. Therefore, the projected population for Vellakoil town is:<br />
1. Base year 2010 - 52,702<br />
2. Intermediate year 2025 - 88,836<br />
3. Ultimate year 2040 - 1,46,349<br />
2.5.3 Sex ratio and literacy<br />
The sex ratio in the town is 964 and the literacy rate is 75% higher than the national average of<br />
59.5%.<br />
2.6 OCCUPATIONAL PATTERN<br />
The work force participation of the town is 19,737 in 2001.As per the census 2001; more than<br />
80% of the work force is involved in the tertiary sector. The sector wise distribution of the work<br />
force is depicted in the table below:<br />
Table 2.3 Occupational Pattern, 2001<br />
Category of Workers<br />
Total<br />
% to<br />
Population<br />
% to Total work<br />
force<br />
Total workers 19,737 57 -<br />
Primary sector 1,526 4 8<br />
Secondary sector 1,252 4 6<br />
Tertiary sector 16,959 49 86<br />
Non-workers<br />
Source: Census of India 2001.<br />
14,701 43 -<br />
Fig: 2.1 Occupational pattern of Vellakoil -2001<br />
7
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
2.7 PHYSICAL PLANNING AND GROWTH MANAGEMENT ISSUES<br />
The existing developmental issues and future potential are addressed below:<br />
The major arterials connecting the town to the surrounding urban centres are:<br />
• Coimbatore – Thiruchirapalli National Highway<br />
• Erode – Tharapuram road<br />
• Moolanur road<br />
The Coimbatore – Thiruchirapalli road is one of the major road, running west to east connecting the<br />
town to major urban centres. The town has no railway connectivity. The nearest railway stations<br />
are in Erode, Karur and Tiruppur. The nearest Airports are at Coimbatore (88km) & Trichy (117km)<br />
The Major industrial activities in the town are hand loom and power loom, spinning mills, oil mills<br />
and brick manufacturing. Vellakoil is one of the major marketing centers for sunflower oil.<br />
Land use Pattern<br />
The land use pattern for Vellakoil is followed by the major activity areas in the Town. Commercial<br />
areas are mainly located along the major roads such as Erode road, Coimbatore Road, Trichy<br />
Road are radiates out from the centre of the town where the bus stand is located.<br />
The major developments are seen on the north along Erode road and on the west along<br />
Coimbatore Road, south along Moolanur and Tharapuram Road and east along Karur and Trichy<br />
road. More than 50 % of the land in the town constitutes undeveloped area comprising of lands<br />
under agricultural, unused vacant lands and waste lands.<br />
a. Residential<br />
Residential development has almost spread over the entire municipal area. The density varies from<br />
high to low from the centre of the town.<br />
b. Commercial and Industrial<br />
The main commercial areas are located along the major road network. Weekly Market is located<br />
near the bus stand in about 3 acres of land. The oil extracting industries and power loom/handloom<br />
industries are sporadically distributed in the town.<br />
2.8 GROWTH MANAGEMENT ISSUES AND SOLUTION INITIATIVES<br />
Need to strengthen <strong>Municipal</strong> Revenue base<br />
• Low levels of revenue generation of <strong>Municipal</strong>ity leading to poor service delivery. The<br />
reforms to be under taken by the urban local body will be addressed in detail in the list of<br />
Reform Agenda suggested in the CDP.<br />
Need for guided development for a sustained economic growth<br />
• The town has vast land for future development. But at present the industrial developments<br />
are sporadically distributed over the town. There is mixed land use in the town area causing<br />
congestion and unsafe environmental conditions.<br />
• Thus, there is an immediate need for Master <strong>Plan</strong> and Detailed <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong>s for<br />
sustained economic growth and safe environment to live in.<br />
Need for Railway connectivity<br />
• Discontinued Railway connectivity directly affecting the town’s economy.<br />
Need land for future development<br />
• Inadequate municipal owned vacant land for implementing social, physical infrastructure<br />
facilities and remunerative developments.<br />
8
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
VISION AND STRATEGIES FOR ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT<br />
3.1 STAKEHOLDERS WORKSHOP AND VISION STATEMENT<br />
The <strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> is a tool which adapts a participative approach in planning and<br />
implementing projects involving users, elected councilors, line agencies, private organizations,<br />
NGOs and CBOs. In this process, residents of various sections of the communities in the town were<br />
enquired into at random during reconnaissance survey and visits to all the sites of the projects<br />
identified by the <strong>Municipal</strong>ity and also otherwise suggested by the elders.<br />
The broad purpose of public participation is to involve the stakeholders in the development plan for<br />
the city. The Vision Statement has been firmed up based on the feed backs received from the stake<br />
holders and expert survey of the municipal services for the perspective year of 2030.The analysis<br />
and findings of the study are based on secondary data collected from respective departments and<br />
during the course of the study, data gaps if any were supplemented through primary survey. A<br />
detailed analysis to find out the existing status of each admissible sector, cross-referring the norms<br />
and standards, demand and gaps based on present and future service requirements is done. A<br />
SWOT analysis was done based on the data collected on the resources and consultation with the<br />
stake holders in the following section. Accordingly, interventions are suggested.<br />
3.2 SWOT ANALYSIS<br />
Table 3.1 SWOT Analysis<br />
STRENGTH WEAKNESS<br />
Access to Erode, a major node for textile, leather &<br />
agriculture, timber based industries<br />
Crippling Environmental pollution to odais & agricultural<br />
hinterland<br />
Good connectivity with nearby Urban centres Absence of recreational facilities<br />
Nh-67 bisecting the town Need to expedite infrastructure improvements<br />
Perennial source of water from River Cauvery Inadequate social infrastructure facilities<br />
High Urban literacy rate at 75% Extensive <strong>Municipal</strong> area – Increased demand for<br />
Fertile agricultural hinterland<br />
penetration of <strong>Municipal</strong> services<br />
Excellent industrial base of textile, bricks, agro<br />
Absence of rail connectivity<br />
based timber & leather<br />
OPPORTUNITIES THREATS<br />
Availability of land for future development Rising land and labour costs<br />
Co-operative mindset of community. Increased Environmental regulations & falling margins<br />
Access to Higher Educational Institutions Low skill, low technology manufacturing units<br />
Opposition to leather based industries /brick industries<br />
Source: Feedback from stakeholders meeting and analysis.<br />
3.3. VISION FOR VELLAKOIL TOWN<br />
<strong>Vellakovil</strong> town is a major commercial centre for agro products and textiles. Based on the feed backs<br />
from stakeholder workshops and analysis of the town the vision statement for the town of<br />
VELLAKOIL is framed as<br />
9<br />
3
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
“An clean and green town; economically self sustaining, with access to physical and social<br />
infrastructure”.<br />
3.4 STRATEGIES FOR ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT<br />
The district has high concentration of power loom & handloom weaving, textile processing units, rice<br />
milling, edible oil expelling units, paper products and basic metal products industries etc.<br />
1. Benefit from the proximity to Erode and Tiruppur to generate further employment<br />
opportunities and economic development.<br />
Vellakoil is strategically located between Erode and Tiruppur, on the National Highway to Trichy<br />
.Thus there is a scope for further development of knitwear and readymade garments, especially for<br />
export oriented units. Provision of marketing centers, adequate housing, basic infrastructure<br />
facilities, medical, educational and recreational facilities would enhance overall growth of the town.<br />
2. Build on the industrial base to create further scope for development.<br />
a. Establishment of industrial estates<br />
b. <strong>Development</strong> of food processing industries<br />
c. Establishment of industrial parks and SEZs<br />
d. Guidance through research and training institutes<br />
e. Implementing <strong>Development</strong> centers and schemes for industrial and social<br />
development<br />
a. Establishment of industrial estates<br />
There are 5 industrial estates in this district promoted by official agencies namely SIDCO<br />
Industrial Estate- Erode, SIDCO Industrial Estate -Dharapuram, SIDCO Industrial Estate -Nanjai<br />
Uthukuli, TAHDCO Industrial Estate -Perundurai, Perundurai Industrial Estate.The proposed<br />
Industrial estates in the region are SIDCO Industrial Estate -Rasathivalasu, SIDCO Industrial<br />
Estate Vadamugam -Kangayampalayam, SIDCO Industrial Estate -Chennimalai.<br />
As the SIPCOT Industrial Growth centre is at Perundurai providing all the necessary<br />
infrastructure facilities. There is a good scope for setting up industries like Textile Processing,<br />
Leather, Chemical, Engineering, Electrical & Electronics Industries.<br />
The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs gave its approval to the implementation of the<br />
Comprehensive Power loom Cluster <strong>Development</strong> Scheme at Erode (Tamil Nadu) as a Central<br />
Sector <strong>Plan</strong> Scheme with a budget provision of Rs.70 crore. The implementation of the Scheme<br />
will benefit the weavers in developing / diversifying new designs and products, their skill upgradation,<br />
up-gradation of their looms, providing a suitable workplace, market support etc. to<br />
improve their earnings and socio-economic conditions.<br />
b. <strong>Development</strong> of Food Processing Industries<br />
There is ample scope for development of Food Processing Industries in the district. Availability of<br />
technology and training is a problem for the aspiring entrepreneurs. Hence there is need for<br />
10
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
Food Technology & Training centre under the guidance of CFTRI, Mysore, in this district is<br />
recommended by the Industrial Potential Survey Report- Erode 2001 – 2002.<br />
c. Establishment of Industrial parks and SEZs<br />
Establishment of Garment Park in the region will support the industrial activity as Tiruppur is near<br />
to the town. Establishing Special Economic Zones (SEZs) for textile and agro products in the<br />
region will enhance the economy of the region.<br />
d. Implementing<br />
development<br />
<strong>Development</strong> centers and schemes for industrial and social<br />
To develop handloom sector both Central & State Government are implementing various<br />
schemes through the office of the Assistant Director (Handloom & Textiles) at Erode. The<br />
schemes are<br />
• Handloom <strong>Development</strong> Centre<br />
• Project Package Scheme<br />
• Help Package Scheme<br />
• Housing scheme for weavers<br />
• Export Package scheme<br />
To increase the productivity of power loom, the Government has introduced the Technology<br />
Upgratation Fund Scheme (TUFS) for undertaking modernization of textile industry. Utilisation of<br />
this fund will meet the requirement of power loom textile industry. By implementing export<br />
package scheme and help package schemes, the edible oil units may be further encouraged in<br />
production and marketing.<br />
3.5 URBAN INFRASTRUCTURE<br />
Infrastructure provision is perceived to have a significant impact on health, reducing incidence of<br />
illnesses which are related to an unhygienic living environment. Thus, infrastructure plays an<br />
inevitable role in the economic development and social well being of the town.<br />
3.5.1 Sector wise Vision<br />
The sector wise vision for the key infrastructure services are as given in the table below:<br />
Table 3.2 Sector wise vision for the key Infrastructure<br />
S.n Sector Vision statement<br />
1 Water Supply To check wastage and pilferage of water<br />
To generzate more revenue for efficient operation & maintenance of the<br />
system and to supplement the capital works, in order to render the delivery<br />
of the service self sustaining over a period of time.<br />
2 Sewerage and<br />
sanitation<br />
To provide coverage of the sewerage facilities or LCS measures for slum<br />
areas.<br />
To maintain high level of environmental hygiene generally in the town and<br />
particularly the cleanliness of the water bodies<br />
11
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
3 Storm water drainage<br />
and improvement to<br />
water bodies<br />
4 Solid Waste<br />
management<br />
To improve condition of storm water drains to handle run off water and<br />
prevent water stagnation.<br />
Rejuvenate water bodies and improve recharge of ground water.<br />
To provide Rain Water Harvesting to improve the quality and quantity of<br />
Ground water.<br />
To provide a litter free town for the healthy living of the public.<br />
To minimize the O&M expenditure of SWM<br />
To involve private organizations to the extent possible<br />
5 Roads and Streets To provide safe, comfortable and speedy circulation network for the<br />
residents and traffic<br />
To relieve congestion by adopting a traffic management plan<br />
To channelise by-passable traffic through arteries outside the town limit.<br />
6 Street lighting To provide sufficient illumination to the town, for safety of the people and to<br />
adequately cope with the requirements of traffic.<br />
To optimize the use of electricity by adapting energy efficient technology<br />
7 Educational<br />
Institutions<br />
To Provide comfortable conducive physical infrastructure and sound<br />
environment for the learning process<br />
8 Medicare To make quality preventive and curative care available and<br />
accessible to the Public.<br />
To support people for healthy living and environment.<br />
3.6 PERFORMANCE AND DEMAND ASSESSMENT<br />
To assess the indicators of performance in each sector of infrastructure, the existing levels of key<br />
<strong>Municipal</strong> services is benchmarked against their norms and standards to arrive at performance<br />
assessment index .The norms and standards are based on SFC recommendation, <strong>Plan</strong>ning<br />
Commission recommendation, UDPFI guidelines, CPHEEO manual, best practices etc.<br />
The demand assessment for projects is arrived from the Stake holder consultative meetings,<br />
discussions with officials, field visits and service analysis. The improvement needs proposed are<br />
based on the demand and performance assessments with reference to short term and long term<br />
proposals for each sector.<br />
The Performance assessment index for the existing status against the norms and standards for<br />
water supply, sewerage, drainage, solid waste, street lighting and social facilities are illustrated in<br />
the table below:<br />
Table: 3.3 Performance Indicators for key <strong>Municipal</strong> Services<br />
Sl<br />
No<br />
Service Indicators Unit Normative<br />
Standard<br />
Performance of Key Water Supply Service Indicators<br />
1 Daily per capita supply lpcd 135 70<br />
2 Roads covered with distribution network Percent >100 96<br />
3 Storage Capacity with respect to supply Percent 33 45<br />
4 Property tax assessments covered by service connections Percent 85 27<br />
5 Proportion of non – domestic service connections Percent >5.00 2.5<br />
Performance of Key Sewerage and Sanitation Service Indicators<br />
6 Roads covered by UGD network Percent 100 -<br />
7 Sewage contribution lpcd 100 -<br />
9 Assessment having access to UGD facility Percent 85 -<br />
12<br />
Current<br />
Status
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
10 Population covered by UGD Percent 85 -<br />
Performance of Key Storm water Drainage Service Indicators<br />
11 Road length covered with storm water drainage Percent 130 11<br />
Performance of Key Solid Waste Management Service Indicators<br />
12 Estimated waste generation Grams<br />
capita/ day<br />
/ 400 300<br />
13 Waste collected as per the estimate of ULB (w.r.t. waste Percent<br />
generation)<br />
100 85<br />
Performance of Key Road Service indicators<br />
14 Road density Km/sq.km 10-15 2.7<br />
15 Per capita road length meters 1.75 3.5<br />
16 Proportion of surfaced roads Percent 100 67<br />
Performance of Key Street Lighting Service indicators<br />
17 Spacing between lamp posts meters 30 87<br />
18 Proportion of fluorescent lamps (tube lights) w.r.t. total fixtures Percent ≥80 89<br />
19 Proportion of high power fixtures w.r.t. total fixtures Percent ≤20 11<br />
Performance of Key indicators for Slums<br />
20 Proportion of slum population to total city population Percent 100% to road length<br />
Under Ground Sewerage System<br />
km 77.43 85.99 122.81 168.20<br />
Network coverage @ 100% to road length km 77.43 85.99 122.81 168.20<br />
Storm Water Drains<br />
Requirement @ 130% to road length km 101 112 160 219<br />
Solid Waste Management<br />
Waste generation at 300 gms TPD 15.49 17.20 28.66 39.25<br />
Compost yard area requirement @ 1 acre per 10000 pop Acres 5 6 8 11<br />
Roads<br />
Road requirement with benchmark @ 1.5 to 2 m per capita<br />
road length km 77.43 85.99 122.81 168.20<br />
Street Lights<br />
Requirement @ 30 m gap between street lights Nos 2581 2866 4094 5607<br />
Parks and Open spaces<br />
Requirement @1.0 to 1.2 hectare per 1000 population Acres 127.5 141.59 202.23 276.97<br />
Community Hall and Library<br />
Requirement @ 1 per 15000 population (2000 sq.m) Nos 3 4 5 7<br />
Source: Analysis and calculations<br />
13
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
The chapters that follow propose projects needed to ensure efficient delivery of the services.<br />
3.7 STRATEGIES FOR POVERTY REDUCTION AND SLUM UPGRADATION<br />
Towards Building Successful Slum-Upgrading Strategies<br />
• Youth groups can be very effective.<br />
Youth SHGs can be encouraged and made active participants in developmental activities.<br />
Unlike Women SHGs, which are formed originally for social empowerment, Youth SHGs can<br />
aim at both economic empowerment and social empowerment as the primary focus. The<br />
focus can be on skill training for increasing their employability and promotion of economic<br />
activities.<br />
Group formation:<br />
The SHGs can be formed with unemployed youth in the age group of 18 to 35 years. Each<br />
group may comprise 10 to 20 members drawn from the below poverty line population.<br />
Youth SHGs can be beneficial in the following ways<br />
• To engage the communities in development activities through a dialogue with the active<br />
participation of the youth (men and women) with a sense of commitment and integrity<br />
• To equip the youth by building their skills, capacity and capability in managing<br />
development, so that, they can help build the capacity of the citizens to manage the affairs of<br />
the community on their own.<br />
• Infrastructure provision<br />
Infrastructure provision brings indirect social and economic development, particularly for<br />
women. Improved infrastructure reduces women’s work burden and gives them more time,<br />
increased space allows for more home-based economic activity, and lighting and better road<br />
coverage increase mobility and security at night. Infrastructure provision is perceived to have<br />
a significant impact on health, reducing incidence of illnesses which are related to an<br />
unhygienic living environment.<br />
• Community halls are valuable for project work as well as for private and public social<br />
activities, however, halls are prone to capture and maintenance can be a problem. They can<br />
also be used as location for health camps, balwadis (pre-schools), vocational training and<br />
neighborhood committee meetings. They can be used by the community for a variety of<br />
occasion such as religious ceremonies, marriages, political meetings etc. conflicts over use<br />
and maintenance are common, and control over the hall give some individuals power in the<br />
community.<br />
• Balwadis (pre-schools) and Schools<br />
Both these institutions benefit poor and working families, especially working mothers. If<br />
timings of balwadis are appropriate, then they have a positive effect on the lives of working<br />
women, freeing them of childcare and giving more time to women to do paid as well as nonpaid<br />
work.<br />
• Medical facilities<br />
Frequent illnesses and consequent break from work is a major factor that costs the time and<br />
money of the low income group. The availability and accessibility to medical facilities as<br />
necessary needs to be addressed as a priority issue.<br />
14
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final report TNUDP III<br />
ORGANISATIONAL STRUCTURE<br />
The organisational structure of the Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity generally consists of administrative and<br />
executive wings.<br />
4.1 ELECTED BODY<br />
The <strong>Municipal</strong> Council, the political wing of the Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity consists of 21 elected<br />
councilors. Each Councilor represents one electoral ward. The Councilors in turn elect the Chairman<br />
as head of the <strong>Municipal</strong> Council.<br />
Administrative wing<br />
The administrative wing gives overall guidance to the municipal functions through set of committees.<br />
Three committees have been formed namely, Appointment Committee, Contract Committee and<br />
Taxation and Appeal committee consisting of the Chairman, the <strong>Municipal</strong> Commissioner and<br />
elected Councilors as members. Appointment Committee is a statutory committee, and the<br />
Chairman of the <strong>Municipal</strong>ity is also the Chairman of the committee. The Committee is responsible<br />
for making appointments for posts which fall under the purview of the Appointing Committee.<br />
Contract Committee is another statutory committee and quotation of works is finalized by the<br />
Contract Committee. The Taxation Appeal Committee is responsible for hearing of appeals of the<br />
tax items.<br />
4.2 EXECUTIVE WING<br />
The executive wing is responsible for the <strong>Municipal</strong> operations and maintenance. The Executive<br />
Officer is the administrative head of the executive wing and is supported mainly by 5 department<br />
heads in the <strong>Municipal</strong> operation and maintenance. The organization structure of the <strong>Municipal</strong>ity<br />
comprises of 5 functional departments namely,<br />
1. General Administration<br />
2. Engineering and Water Supply Department<br />
3. Accounts Department<br />
4. Public Health Department, and<br />
5. Town <strong>Plan</strong>ning Department<br />
4.2.1 General Administration<br />
Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity is a Grade Three <strong>Municipal</strong>ity. The Manager is the head of Administration, next<br />
to the Commissioner in the section of General Administration, and he is responsible for general<br />
supervision and administration of the Office. All establishment matters are dealt by the General<br />
Administration Section.<br />
Manager<br />
Manager is the Head of General Section. His duty includes general supervision of the ministerial<br />
staff, and maintenance of discipline in the office premises, ' and to sign receipts for all remittances<br />
made in the <strong>Municipal</strong> Treasury to acknowledge registered tapals, Money orders etc on behalf of the<br />
Commissioner. The Manager is the custodian of the cash collected by daily-checking of Chitta and<br />
15<br />
4
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final report TNUDP III<br />
Cash and Petty cash, payment advance etc, and for the administration report by way of Annual<br />
Inspection of the office, checking of Personal Registers of all staff and subsidiary registers in respect<br />
of all the sections. All papers are routed through the Manager to the commissioner except the<br />
Engineering section and the Health section.<br />
All matters relating, to the Establishment including public health, maintenance of Increment &<br />
Punishment registers, maintenance of service registers, register of Probationers; maintenance of<br />
temporary and permanent post sanction register, Pension & Gratuity for all Establishment Audit<br />
Register, issue of Office order, common office order book, maintenance of stock file, maintenance of<br />
personal register & audit objection register etc are looked up by the Manager.<br />
4.2.2 Engineering Department<br />
The <strong>Municipal</strong> Engineer is the over-all in-charge of Engineering Section. The <strong>Municipal</strong> Engineer is<br />
controlling the Overseer, Work Inspector, and Road Mazdoor, Water works Superintendent,<br />
Wiremen, Helper and Fitter working in the section. The <strong>Municipal</strong> Engineer looks after the<br />
maintenance of roads, street lights, road laying, and construction of building, drainage, maintenance<br />
of parks, head works and municipal vehicles. The other subordinate officers are assisting the<br />
Engineer to look after the above works.<br />
4.2.3 Accounts Department<br />
The Account Section is included in the General Section. The Accountant is the Head of the Wing<br />
controlling financial matters. It involves preparation of Budget and looks after the Accrual based<br />
Accounting System.<br />
4.2.4 Public Health Department<br />
Sanitary Officer is the overall in-charge of the Health Section. He looks after conservancy, sweeping<br />
streets, maintenance of drainage, controlling of epidemic diseases, ensuring of license to D&O<br />
trades, Birth and Death Registration and issuing of certificate to birth and death registration.<br />
Sanitary Inspector, Sanitary Supervisor and Sanitary Workers are assisting the Sanitary Officer. The<br />
Sanitary Officer is held responsible for the solid waste management. Pulse Polio Immunization<br />
camps are conducted every year under the section.<br />
4.2.5 Town <strong>Plan</strong>ning Department<br />
Town <strong>Plan</strong>ning Officer/Inspector is over all in-charge of the section. He looks after the work of<br />
preparation of Master <strong>Plan</strong>, Detailed <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> and maintains the land use registers as per<br />
the approved zoning uses. He is also responsible for licensing of plan approved, booking of<br />
unauthorized construction, approval of lay out plans with in the town limit, controlling and removing<br />
the encroachment in the town. The Town <strong>Plan</strong>ning Inspector helps in planning the future<br />
development of the town and allied works.<br />
4.3 STAFF STRENGTH POSITION AND VACANCY POSITION<br />
As of now, there is 136 vacancies in the 177 sanctioned strength of the <strong>Municipal</strong> office. The<br />
vacancies are mostly under the Sanitation section.<br />
16
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final report TNUDP III<br />
S.<br />
No<br />
Name of the<br />
department<br />
Table 4.1 Staff Strength<br />
Sanctioned<br />
strength<br />
17<br />
Working<br />
strength<br />
No. of post<br />
Vacant<br />
1 General Section 7 7 -<br />
2 Engineering Section 9 8 1<br />
3 Public Health Section 28 28 -<br />
Total 44 43 1<br />
Source: Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity, 2008.<br />
Engineering<br />
staff<br />
Fig 4.1 Status of <strong>Municipal</strong> Staff Strength<br />
Vellakoil MUNIC IPALITY<br />
EXECUTIVE BODY ELECTED BODY<br />
Wa ter<br />
Supply<br />
Dra ins<br />
Roa ds<br />
Streetlights<br />
Ex ecu tiv e Off icer Chairman<br />
P ublic<br />
Healt h staff<br />
Solid waste,<br />
Drai nage,<br />
Birth &<br />
Dea th<br />
Registration<br />
Administra tion<br />
/Re ven ue St aff<br />
Off ice<br />
Ad m in istr at i<br />
on Accounts<br />
Ta x<br />
Colle ctio n<br />
Fig 4.2 Organisational structure of Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity<br />
V ice Ch air m an an d<br />
war d Co un cilo rs<br />
Project<br />
Approva ls
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final report TNUDP III<br />
4.4 ISSUES IN HUMAN RESOURCE<br />
Out of the Sanctioned posts of 44, in all sections of the <strong>Municipal</strong>ity, 1 post is vacant. Considering<br />
the present and proposed quantum of work in the municipality, the vacant posts in Engineering<br />
Section, Public Health Section need to be filled up expediously.<br />
In view Privatization of Solid Waste Management and Maintenance of street lights through ESCO/<br />
Private agency, implementation of proposed improvements in infrastructure, the various sections of<br />
the municipality need to be strengthened with the following personnel:<br />
Table 4.2 Additional Staff Required<br />
S No Name of the Post Section No. of Personnel<br />
1 Accounts officer General 1<br />
2 Data Entry Operator General 1<br />
3 Revenue Inspector General 1<br />
4 <strong>Municipal</strong> Engineer Engineering 1<br />
5 Supervisors Engineering 1<br />
6 Overseers Engineering 1<br />
7 Public health Engineer Public Health 1<br />
8 Town <strong>Plan</strong>ning Officer Town <strong>Plan</strong>ning 1<br />
Total 8<br />
Source: Analysis and discussions with <strong>Municipal</strong> officials<br />
Besides appointing the additional staff, the existing staff in the Administrative, Engineering, Public<br />
Health, and Town <strong>Plan</strong>ning sections of the municipality needs to be given training in their respective<br />
field periodically towards capacity building to take up new assignments.<br />
4.5 ORGANIZATION MANAGEMENT<br />
As may be seen from various sections of the report particularly relating to service deliveries, there<br />
are gaps of various sizes which result in a shortage in the delivery system. This could be over come<br />
by certain specific options:<br />
In most of the service sections of the <strong>Municipal</strong>ity, there are only a few vacancies which could be<br />
filled up. A totally satisfactory system delivery of the services would require an efficient personnel<br />
management system.<br />
• The organization and delivery mechanism in some of the important personnel intensive<br />
service sectors have to be modernized. To mention the important few relate to solid waste<br />
management, where large number of workers and staff are involved, could be privatized.<br />
Scientific solid waste management need to be assigned to NGOs, voluntary organizations or<br />
even the respective resident associations in the various colonies. This is a remunerative<br />
venture as is proved in many places.<br />
• Privatizing the repair and maintenance of water supply, collection of taxes and fees and<br />
maintenance of public assets particularly sanitary and public health units is a well known<br />
option. This also could be taken up as joint venture between urban local body and private<br />
sector.<br />
18
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
5.1 PHYSICAL INFRASTRUCTURE<br />
5.1.1 WATER SUPPLY<br />
INFRASTRUCTURE STATUS AND NEEDS ASSESSMENT<br />
i) Existing Status<br />
a. Source and headworks:<br />
Vellakoil municipality is provided with water supply from River Amaravathy and from the Muthur-<br />
Kangeyam CWSS with River Cauvery as source. Since the flow in River Amaravathy is nonperennial,<br />
water supply from this source is not dependable.<br />
Indicators for Water supply<br />
Population (Census 2001) 34,438<br />
Present population 49,500<br />
Total area of the town 64.75 sq.km<br />
Total no. of wards 21<br />
Source<br />
Water supplied 30 Ll<br />
Length of distribution system 168 km<br />
Rate of supply 70 lpcd<br />
Storage<br />
No. of OHTs and total capacity 6 and 13.50 Ll<br />
Frequency of supply Once in 4 days, for 3 hrs<br />
Distribution<br />
No. of open wells 56<br />
No. of Hand pumps 136<br />
No. of power pumps 76<br />
No. of public fountains 471<br />
Total no. of service connections 4012<br />
Domestic connections 3910<br />
Commercial 57<br />
Industrial 45<br />
Muthur-Kangeyam Combined Water Supply Scheme<br />
The Muthur-Kangeyam CWSS covers 994 rural habitations, 2 municipalities and 7 town<br />
panchayats. The water requirement for Vellakoil municipality is being pumped from Metukadai<br />
sump. The present level of supply from Amaravathi scheme and Muthur-Kangeyam CWSS is 0.5<br />
and 2.5 MLD respectively. Due to the rate of increase in population, the Muthur-Kangayam<br />
CWSS is inadequate to meet the water demand.<br />
Formulating a new scheme for additional requirement of Vellakoil municipality, Kangayam Town<br />
Panchayat, omitted rural habitations and enhancing supply to 994 rural beneficiaries will cause<br />
overlapping and duplication of pipeline for the entire project area. Hence it is proposed to de-link<br />
Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity and Kangayam Town Panchayat from the existing scheme and a separate<br />
CWSS is prepared for Vellakoil municipality and Kangayam Town Panchayat.<br />
19<br />
5
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
b. Service Reservoirs<br />
There are totally 6 over head tanks in the town. The details of the Over head tanks are shown in<br />
Table 5.1.<br />
Table 5.1 Details of OHTs<br />
S.No Location of OHT Capacity (Lakh litres)<br />
1 Salavaiyalar colony 1.00<br />
2 Natesan nagar 4.00<br />
3 Uppupalayam 3.50<br />
4 <strong>Municipal</strong> office 2.00<br />
5 Theethampalayam 1.50<br />
6 Sivananthapuram 1.50<br />
Total 13.50<br />
Source: Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity<br />
c. Distribution system<br />
The total length of the existing distribution system is 168 km against a total length of roads<br />
174.50 km.<br />
d. Water Tariff<br />
The monthly tariff and deposits collected for water supply is as follows:<br />
Table No. 5.2: Water Tariff-Deposit Details<br />
Type of connection Deposit amount (in Rs) Flat rate /month (in Rs)<br />
Domestic 3000.00 65.00<br />
Commercial 6000.00 115.00<br />
Industrial 6000.00 105.00<br />
Source: Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity<br />
ii) Water Supply Demand<br />
The population of the town is projected for the intermediate and ultimate years. The projected<br />
water demand is given in table 5.3<br />
Year Population<br />
Table 5.3 Demand & Supply in Water Supply - Projection<br />
Supply in<br />
MLD<br />
Demand @ 135<br />
lpcd<br />
20<br />
Gap in<br />
MLD<br />
Floating<br />
population<br />
2001 34438 3.0 4.65 1.65 - -<br />
2010 51620 3.0 6.96 3.96 10000 0.20<br />
2025 81873 3.0 11.05 8.05 13000 0.26<br />
2040 112132 3.0 15.14 12.14 17000 0.34<br />
Source: <strong>Municipal</strong> records, Analysis and calculation<br />
Floating population<br />
demand at 20 lpcd<br />
The present floating population is taken as 10000. The annual increase of 2% is taken for<br />
calculating the projection. The per capita supply of 20 lpcd is proposed for floating population.<br />
The demand of water supply for the above period is calculated at 135 lpcd.<br />
iii) Demand Assessment<br />
The water supply improvement scheme has been prepared by TWAD Board which is awaiting<br />
fund release from Government of India. The issues in water supply are identified and remedial
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
measures have been suggested. The water supply demand calculated by the TWAD Board for<br />
the intermediate population (2024) is 6.1 MLD and Ultimate year (2039) is 7.32 MLD.<br />
The town is experiencing high population growth as the town has a high potential for industrial<br />
growth. Therefore, the total demand of water supply calculated for intermediate period is 8.31<br />
MLD and ultimate period is 12.48 MLD.<br />
The present storage capacity of the service reservoirs is of 13.5 Ll. Therefore the storage<br />
requirement will be 12.48/3 = 4.16 MLD < 1.35 MLD (existing). Hence, additional storage of 1.42<br />
ML is required for intermediate period and 2.81 ML, required for the ultimate period.<br />
iv) Proposals<br />
The source proposed for this project is River Cauvery near Kodumudi. The proposed head works<br />
will be located just on the upstream of the existing headworks of Muthur-Kangeyam CWSS. It is<br />
proposed to draw 6.11 MLD for the intermediate stage and 7.32 MLD for the ultimate stage for<br />
Vellakoil alone.<br />
The salient features of the proposal are the head works, pump sets, raw water pumping main,<br />
treatment plant, clear water reservoir, clear water pump sets, pump house, Booster station,<br />
Laying of distribution system (feeder mains only) for 23 km and Construction of 4 OHTs at<br />
Melagoundanpalayam colony (1Ll), Muthur road (5Ll), Sivanathapuram (3 Ll) and Pudur road (2<br />
Ll). The per capita cost for this project is Rs.2926.00 and the cost per 1000 liters is Rs.8.05<br />
(schedule of rates 2007-08 + 10% price escalation).<br />
The installation cost of the water supply improvement scheme is Rs.1199.12 lakhs. The Annual<br />
Maintenance cost is Rs.49.00 lakhs.<br />
5.1.2 SEWERAGE<br />
i) Existing Status<br />
The town does not have an Under Ground Sewerage System. Disposal of the sewage is<br />
normally by way of individual facilities and the sullage is through the open drains. The main mode<br />
of individual disposal in the town is through septic tanks, low cost sanitation units and through<br />
public / community toilets.<br />
ii) Demand Assessment<br />
In order to improve the sanitation in the town, Under Ground Sewerage System is necessary with<br />
treatment facilities at terminal points.<br />
iii) Proposals<br />
The field survey for UGSS has been done by TWAD Board. Identification STP site is in progress.<br />
The total estimated cost of the proposed Under Ground Sewerage System for Vellakoil<br />
municipality is Rs.3300.00 lakhs. The Operation and Maintenance cost will be is Rs. 82.00<br />
lakhs.<br />
5.1.3 STORM WATER DRAINS<br />
i) Existing Status<br />
Vellakoil municipality has provided open storm water drains for a length of 19 km. The total<br />
length of the existing road length in the town is about 174.50 km. The percentage coverage of<br />
storm water drains is about 11%.<br />
21
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
At present, storm water drains carry the sullage and rain water which is ultimately let into the<br />
PAP channel (Parampikulam Aazhiyar Program) and Kurukampalayam Pirivu (proposed STP<br />
site) without any treatment. This imposes health and environmental hazard to the natural water<br />
system and needs to be addressed through a proper treatment and disposal facilities.<br />
ii) Issues<br />
The main issues persisting in the town due to the absence of a storm water drainage system are<br />
summarized as follows:-<br />
• Open drains creating unhygienic conditions<br />
• Absence of Under Ground Drainage System in the town<br />
• Water stagnation in low lying areas during rainy season<br />
iii) Demand Assessment<br />
The residential areas of the town are provided with open drains. The town area is 64.75 sq.km<br />
and about 75% of land are undeveloped, agricultural lands or barren lands. The storm water is<br />
carried by the natural drain network in these areas emptying into the channels.<br />
Absence of UGSS and storm water drains in the residential areas of the town are the major<br />
causes of land and water pollution. This situation degrades the environment by emanation of foul<br />
smell and unhealthy conditions due to stagnation at a number of points.<br />
iv) Proposals<br />
Proposals by consultants<br />
To develop a Comprehensive Drainage Master <strong>Plan</strong> channelizing the runoff along the<br />
natural contours so as to cover the entire town and implement in phases.<br />
Measures to be taken to improve, upgrade and clean the existing natural and man made<br />
storm water drains to the required functional level with the involvement of local<br />
community to ensure sustainable operation<br />
Provision of new drains in newly developing areas<br />
Table 5.4 Storm water Drains - proposals<br />
S.No Description Capital Investment<br />
in lakhs<br />
1 Preparation of Comprehensive Drainage Master <strong>Plan</strong> 3.00<br />
2 Provision of new drains including newly developing area (15 km) 240.00<br />
3 Rejuvenation of entire existing drain network (19 km) 57.00<br />
Total 300.00<br />
Annual O & M 4.50<br />
Source: Analysis and discussions with municipal officials<br />
Therefore, the total investment required for the improvement of storm water drains (short term) is<br />
Rs.300.00 lakhs. The rest of the road length will be covered in the long term plan.<br />
5.1.4 IMPROVEMENT TO WATER BODIES<br />
i) Existing Status<br />
There is no water body in the town maintained by the municipality. The PAP channel is the<br />
manmade channel maintained by the PWD.<br />
22
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
5.1.5 SOLID WASTE MANAGEMENT<br />
i) Existing status<br />
Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity generates 14 MT of solid waste. Out of 21 wards, 8 wards in the town are<br />
privatized (SHG) for solid waste collection. The solid waste generated in the town is collected<br />
and segregated at source and dumped in the compost yard (3.50 acres) at<br />
Soriyankinathupalayam. An income of Rs.1000 per annum is generated through selling of the<br />
segregated recyclable waste. The details on solid waste management are given below:<br />
Total waste generation per day - 14 MT<br />
Frequency of collection - daily<br />
Collection efficiency - 85% (12 MT)<br />
Collection points - 40<br />
Push cart - 49<br />
Tri cycle - 5<br />
Tipper Lorries - 2<br />
Tractor - 1<br />
Power tillers - 2<br />
ii) Issues<br />
• Absence of scientific waste management and disposal<br />
• Inadequate sanitary workers and supervisors – of the 159 sanctioned sanitary workers,<br />
only 24 workers are available.<br />
• The existing compost yard is not provided with adequate infrastructure facilities<br />
• Easy access and availability of open lands has led to negligent dumping and unsanitary<br />
conditions.<br />
iii) Demand Assessment<br />
Currently, 14 MT of solid waste is generated with a per capita waste generation of 300 grams per<br />
day. In future years assuming the per capita generation of solid waste in the town at 400 gm/day,<br />
there will be corresponding addition of 30% to 40% in solid waste generation. Solid Waste<br />
Management is one of the principal sectors of expenditure in Urban Local Bodies. Hence, there<br />
is a need for scientific management of solid waste to cope with future demand.<br />
Of the <strong>Municipal</strong> waste in Tamil Nadu, 40 - 60% of the waste is biodegradable. Of this, on<br />
conversion, nearly 30% by weight forms the manure. Incidentally, the manure generated from<br />
<strong>Municipal</strong> waste is found to be richer in NPK values compared to the one available in the market.<br />
This has resulted in producing better yield of agricultural products both in quantity and quality.<br />
iv) Proposals<br />
The improvements proposed towards solid waste management are as follows.<br />
Integrated Solid Waste Management is the application of suitable techniques, technologies and<br />
management programs covering all types of solid wastes from all sources to achieve the twin<br />
objectives of waste reduction and effective management of waste still produced after waste<br />
reduction. <strong>Municipal</strong> solid waste management involves the application of Integrated Solid Waste<br />
Management to <strong>Municipal</strong> waste.<br />
23
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
The activities associated with the management of municipal solid wastes from the point of<br />
generation to final disposal can be grouped into the six functional elements:<br />
a. Waste generation<br />
b. Waste handling and sorting, storing<br />
c. Collection<br />
d. Sorting, processing and transformation<br />
e. Transfer and transport<br />
f. Disposal<br />
The inter-relationship between the functional elements is given in Fig 5.1<br />
Fig 5.1 Functional Elements of a <strong>Municipal</strong> Solid Waste Management System<br />
The objective of solid waste management is to reduce the quantity of solid waste disposed into<br />
land by recovery of materials and energy form the waste. This in turn results in lesser<br />
requirement of raw material and energy as inputs for technological processes.<br />
1. The municipality must focus on revenue enhancement by privatizing of waste<br />
management of the following components:<br />
a. Primary collection<br />
b. Transfer to collection points<br />
c. Transfer to compost yard<br />
d. Segregation of waste and option of<br />
i. Selling scraps/recyclable waste.<br />
ii. Treatment of biodegradable waste<br />
iii. Transfer to identified regional land fill sites<br />
e. Compost yard management and sale of manure.<br />
2. The management of biodegradable waste as a revenue generating activity may involve,<br />
24
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
production of manure from composting. Wind rows composting is an established<br />
technology for dealing with bio degradable waste, which is the suggested option for this<br />
<strong>Municipal</strong>ity. The necessary infrastructure is given in the proposals.<br />
3. Conducting IEC campaigns to facilitate effective waste segregation at source and proper<br />
disposal.<br />
4. Implementing collection of conservancy fee for primary collection of waste and levy on<br />
commercial and industrial establishments.<br />
5. Involvement of voluntary agencies, SHGs in the various components of solid waste<br />
management on BOT, BOOT basis.<br />
6. Need to organize the rag pickers into waste-management associations/groups under the<br />
supervision of the urban local body and the relevant residents’ associations or market<br />
associations.<br />
The CDP proposals based on analysis, discussion with <strong>Municipal</strong> officials and norms is given in<br />
the table below:<br />
Table 5.5 Solid Waste management – Proposals*<br />
Sl.<br />
No Project details<br />
Small vehicle with containers for door to door collection @ 160 litres capacity<br />
Cost in lakhs<br />
1 (220 Nos) 25.00<br />
2 Dumper placer vehicle (2 nos) 15.00<br />
3 Purchase of land for additional Compost yard (2.50 acres)<br />
Improvements for existing and new compost yard - with one side compound<br />
wall, segregation sheds, internal roads and machineries for preparation of<br />
250.00<br />
4 compost 200.00<br />
5 Proportionate cost for regional land fill site 300.00<br />
6 IEC activities 10.00<br />
Total 800.00<br />
Annual Operation and Maintenance cost 6.25<br />
Source: Analysis and calculations<br />
Therefore, the total investment required for improvement in Solid Waste Management is<br />
Rs.800.00.00 lakhs.<br />
*-No rational decisions on municipal solid wastes system are possible until data of composition<br />
and quantity of solid waste are available. The method and capacity of storage, the correct type of<br />
collection vehicle, the optimum size of crew and the frequency of collection depend mainly on<br />
volume and density of wastes. Climate also has some influence.<br />
5.1.6 ROADS<br />
i) Existing status<br />
The major roads connecting the town to the surrounding urban centers are:<br />
• Coimbatore – Thiruchirapalli National Highway<br />
• Erode – Tharapuram road<br />
• Moolanur road<br />
25
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
The details of the municipal roads is given in table 5.6<br />
Table 5.6 Category of roads<br />
Category Length in km % to total length<br />
National Highway 5.00 -<br />
<strong>Municipal</strong> Roads<br />
CC Roads 10.36 6<br />
BT Roads 106.88 61<br />
Earthen Road / WBM 57.26 33<br />
Total Length of <strong>Municipal</strong> Roads 174.50 100<br />
Source: Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity<br />
ii) Issues<br />
• 33% of the total <strong>Municipal</strong> roads are earthen and WBM roads<br />
• Differential settlements and potholed surfaces on the existing BT roads<br />
• Encroachments on main roads<br />
• Unorganized parking along main roads<br />
• Absence of traffic management plan- with demarcated pedestrian corridors, medians,<br />
signals and traffic islands<br />
iii) Demand Assessment<br />
The circulation network forms basic network of the town to move, to interact, and interlink the<br />
residentials, the work places, and other activity centers. A good road network is a necessity not<br />
only for growth and development of habitats, but also to sustain it in a progressive mode. The<br />
access roads in extension areas and the link roads, widening of major roads proposed in the<br />
DDPs need to be provided.<br />
iv) Proposals<br />
The town has 33% earthen road which should be upgraded to BT surface. Apart from this, the<br />
access roads in extension areas need to be covered. The projects proposed for the road<br />
improvement in Vellakoil town is as follows.<br />
Table 5.7 Road improvement - Proposals<br />
S.no Particulars Rs.in lakhs<br />
1 Upgradation of earthen road to BT (57 km) 1197.00<br />
2 Restoration of existing BT roads (106 km) 636.00<br />
3 Provision of medians (3km) 30.00<br />
4 Improvements to road geometry – provision of<br />
medians, traffic islands, Signals, signages etc<br />
30.00<br />
5 Pedestrian platform along main roads 50.00<br />
6 Widening of main roads and link roads 100.00<br />
Total Rs.2043.00 lakhs<br />
O&M 22.00<br />
Source: Analysis and discussions with municipal officials<br />
Therefore, the total investment required for the road improvement is Rs.2043.00 lakhs.<br />
26
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
5.1.7 BUS STAND<br />
i) Existing Status<br />
The town has a C class bus stand in an extent of 1 acre, within its limits maintained by the<br />
municipality. About 250 buses per day arrive in this bus stand. The municipality bus stand<br />
complex has 8 shops.<br />
ii) Issues<br />
• The flooring is damaged with differential settlements<br />
• Inadequate waiting sheds for passengers.<br />
• Inadequate space for buses<br />
• Inadequate space for parking of two wheelers<br />
• Inadequate water and toilet facilities<br />
iii) Proposals<br />
In order to bring the bus stand to effective functioning, the cooperation from the private and<br />
government bus operators, drivers and conductors and the public is necessary. The proposed<br />
expansion of bus stand with basic facilities work is under progress.<br />
5.1.8 BUS SHELTER<br />
The 6 bus stops in the town are provided with bus shelters. The construction of bus shelter at Old<br />
bus stand area for Rs.5.00 lakhs under MLA fund is in progress. New bus shelters (5 nos) are<br />
proposed to be constructed at Erode road – Arivoli Nagar stop, Trichy -Coimbatore main road –<br />
opp. to municipal office, Karattupalayam Pirivu, Madamedu piruvu (Mulanoor road),<br />
Theethampalyam at a cost of Rs.10.00 lakhs.<br />
It is also proposed to restore the existing bus shelters and provide space for information boards,<br />
space for advertisement and hoardings in the bus shelters which will generate revenue for the<br />
<strong>Municipal</strong>ity. The provision of bus shelters can be done with the help of NGOs and community<br />
organisations, industries etc.<br />
5.1.9 STREET LIGHTS<br />
i) Existing status<br />
The town is lit by 1986 street lights of which 89% of lights constitute tube light. About 40 number<br />
of timer switches are provided covering all street lights to minimize the energy consumption. The<br />
break-up details of the street lights in the town are as follows<br />
Table 5.8 Existing street lights and energy consumption<br />
S.No Existing Light details Numbers Percentage distribution Consumption in w<br />
1 Tube lights (40w) 1777 89 97735<br />
2 Sodium Vapour lamp (250w) 205 10 57810<br />
3 High Mast lights 4 1 -<br />
Total 1986 155545<br />
Per hour consumption 155545 W or (excluding high mast)<br />
155.545 kW/hr<br />
No of timer switches required 60<br />
Source: <strong>Municipal</strong> records, Analysis and calculations<br />
Therefore, the present level of energy consumption of street lights in Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity is<br />
664643 KW. i.e. Rs.23.26 lakhs per year on an average.<br />
27
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
ii) Proposals<br />
Proposals under CDP<br />
An Energy Service Company (ESCO) identifies and evaluates energy saving opportunities in<br />
industrial units, commercial complexes, hospitals, municipalities, buildings and utilities by using<br />
energy audit tools and recommends a package of improvements that can pay for itself through<br />
the resultant savings.<br />
ESCOs provide their clients with comprehensive services - encompassing audits for energy<br />
saving performance, design & implementation of conservation measures, maintenance,<br />
operation and management of the introduced facilities and procurement of project funds. ESCOs<br />
conduct retrofitting for energy conservation without damaging the environment. The ESCO will<br />
guarantee the savings that would meet or exceed the annual payments to cover up the entire<br />
project costs usually a period of 5 to 10 years. The savings can be shared proportionately with<br />
the institution for which the project is designed and implemented for.<br />
The salient features of performance contracting for energy savings through ESCO based<br />
business model are as under:<br />
1. 'Nil' investment by customer.<br />
2. ESCO to identify Energy Efficient Measures (EEMs) to replace / modify existing in<br />
efficient systems.<br />
3. ESCO supplies, installs and maintains the Energy Efficient Measures (EEMs) during the<br />
contract period.<br />
4. Contract period could be 3-5 years or as mutually agreed upon.<br />
5. Energy saving is shared between ESCO and customer as per agreed terms. Total project<br />
cost is funded by ESCO. The O & M expenses will be met by the <strong>Municipal</strong>ity.<br />
6. Guarantee Energy savings and recover its investment including interest & other costs out<br />
of generated energy savings.<br />
Proposals by ULB<br />
The components suggested for improvements of street lights are<br />
• Retrofitting of tube lights<br />
• Provision of new street lights<br />
• Provision of High mast lights at<br />
o Old bus stand<br />
o Bus stand<br />
Table 5.9 Street lights - Proposals<br />
S. No Description units Rs. in lakhs<br />
1 High mast lights at old bus stand and bus stand 2 14.00<br />
2 Installation of street lights with poles ( T5 lamps ) 28 4.00<br />
3 New street lights (SV lamps) 66 8.00<br />
4 New street lights for newly developing areas 700 90.00<br />
5 Central median lights at main roads for 3 km 100 45.00<br />
6 Provision of timer switches 20 2.00<br />
7 Retrofitting existing tube lights 1777 18.00<br />
8 Retrofitting existing SV lamps with energy efficient lights 62 1.00<br />
Total 182.00<br />
Annual O&M cost 5.00<br />
Source: Analysis and discussions with municipal officials<br />
28
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
Therefore, the total cost required for the street light improvements (short term) including the<br />
energy saving proposals is Rs.182.00 lakhs.<br />
5.2 SOCIAL INFRASTRUCTURE<br />
5.2.1 SLUM IMPROVEMENT<br />
i) Existing status<br />
The town has 16 slums with a total population of 7766 (6741+1025) which is about 16% of the<br />
total population. The details of the slums are given in table below.<br />
Table 5.10: Location of Existing Slum Areas<br />
S.No Name of Slum Notified /un notified Total No. of House Population<br />
1. Soriyankinathupalayam Notified 206 827<br />
2. Semmandemapalayam Notified 59 237<br />
3. Karattupalayam Notified 60 225<br />
4. Pullachellipalayam Notified 61 276<br />
5. Thaneerpanthal Notified 75 301<br />
6. Uppupalayam Notified 198 794<br />
7. Kallankattuvalasu Notified 81 326<br />
8. Reddivalasu Notified 65 262<br />
9. M.G.R.Nagar Notified 79 316<br />
10. Arivolzi Nagar Notified 70 281<br />
11. Indhira Nagar Notified 170 770<br />
12. Katcherivalasu Notified 86 442<br />
13. Theethampalayam Notified 84 379<br />
14. Agalarapalayampudur Notified 133 601<br />
15. Velagoundempalayam Notified 103 413<br />
16. Kadaiyuranvalasu Notified 72 291<br />
Total 1602 6741<br />
Source: Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity<br />
In addition to this the unapproved slums developed in recent years covers a population of about<br />
1025. The details of the unapproved slums are as follows<br />
Table 5.11: Details of Existing Slum Areas<br />
S. No Name Of The Slum No. of Households Total population<br />
1 Viraguthoppu 40 200<br />
2 Patchapali 30 160<br />
3 Nachipalayam 20 70<br />
4 Ganapathipalayam 20 100<br />
5 Subramaniyagoundenvalasu 10 25<br />
6 Cheran Nagar 50 220<br />
7 LKC nagar west side 60 250<br />
TOTAL 230 1025<br />
Source: Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity<br />
29
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
Upgradation of slums rejuvenates the existing community with minimum disruption and loss of<br />
physical and social assets. It also involves the improvement of access roads and community<br />
facilities. Slum improvement consists of physical, social, economic, organizational and<br />
environmental improvements undertaken cooperatively and locally among citizens, community<br />
groups, businesses and local authorities.<br />
Damaged roads, inadequate and damaged storm water drains, inadequate street lights and poor<br />
housing conditions are the issues identified in the slum areas.<br />
ii) Proposals<br />
It is proposed to improve the slums with provision of housing units and infrastructure facilities<br />
under IHSDP. The details of the proposals are given below<br />
Table 5.12: Slum - Proposals<br />
S. No Description Numbers Rs.in lakhs<br />
1 Shelter 599.00 Nos 479.20<br />
2 BT Road 6.712 k.m 76.40<br />
3 C.C Road 0.510 k.m 4.50<br />
4 Drain 6.213K.m 73.80<br />
5 Culvert 10Nos 6.25<br />
6 Retaining Wall 0.014k.m 0.75<br />
7 Extension of Pipe Line 2.500k.m 3.30<br />
8 Erecting of Motor 6 Nos 6.00<br />
9 Bore Well 8 Nos 4.80<br />
10 Street Light 90 Nos 18.00<br />
11 Toilet Block 6 Nos 36.00<br />
Total 709.00<br />
Source: Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity<br />
The total investment required for slum improvement is Rs.709.00 lakhs.<br />
5.2.2 PARKS AND PLAY FIELDS<br />
i) Existing status<br />
<strong>Municipal</strong>ity maintains one Children Park (G.K.Moopanar Park – 25 cents) located at<br />
Seerangarayagoundan valasu road. The park is provided with basic facilities.<br />
ii) Issues<br />
• Absence of recreational facilities<br />
• Lack of maintenance<br />
iii) Proposals<br />
The town has no approved layout open spaces to develop parks. The municipality should ensure<br />
the approved layout open spaces for park usage in future. Therefore it is proposed to develop<br />
and maintain the existing park with good landscaping, seating arrangements and play materials<br />
at a cost of Rs.20.00 lakhs.<br />
30
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
5.2.3 MARKET<br />
i) Existing status<br />
The municipality maintains a weekly market which is located behind the bus stand in an extent of<br />
3 acres. The market supplies groceries and vegetables to fulfill the daily needs of the local<br />
people. The daily market in this town lacks basic facilities and the shops are functioning in<br />
makeshift arrangements. The market needs to be improved with modern facilities.<br />
ii) Proposals<br />
It is proposed to construct a modern daily market complex and weekly market within the available<br />
3 acres of land.<br />
Table 5.13: Market - proposals<br />
S.No Description Rs. in lakhs<br />
1 Construction of Daily market with stalls, basic facilities such as water supply,<br />
sanitation, solid waste disposal and collection, loading, unloading etc<br />
75.00<br />
2 Construction of weekly market / shandy with stalls, basic facilties such as<br />
water supply, sanitation, solid waste disposal and collection, loading,<br />
unloading etc<br />
75.00<br />
Total Rs.150.00 lakhs<br />
O&M cost 3.00<br />
Source: Analysis and discussion with municipal officials<br />
Therefore the total cost required for market improvement is Rs.150.00 lakhs.<br />
5.2.4 PUBLIC CONVENIENCE<br />
The town has 6 public toilets located in the following areas:<br />
• Thiruvalluvar nagar<br />
• Indhira nagar<br />
• Amman koil street<br />
• Dharapuram road<br />
• Bus stand<br />
• Veerakumar nagar<br />
The local body has proposed for the construction of 8 VAMBAY toilets at Agalarapalayam<br />
Puthur, Uppupalayam, Kumaravalasu, MGR nagar, Arivoli Nagar, Karattupalayam, Thaneer<br />
Panthal area in addition to the existing ones. The total investment required is Rs.35.00 lakhs.<br />
5.2.5 SLAUGHTER HOUSE<br />
At present there is no slaughter house in this municipality. A slaughter house is proposed by the<br />
municipality within the market and the work is under progress.<br />
5.2.6 BURIAL GROUND<br />
The town has 2 number of burial ground maintained by the municipality. The burial grounds are<br />
provided with compound wall, shed and basic facilities. The municipality has proposed for<br />
installation of gasifier unit at a cost of Rs.100.00 lakhs.<br />
31
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
5.2.7 E-GOVERNANCE<br />
i. Existing Status<br />
E-governance is aimed to provide on-line citizen services, information to all hierarchies and<br />
monitor the performances. It is in practice that citizens are approaching the respective urban<br />
local bodies to pay their revenues, get certificates, approvals for construction of Building etc. By<br />
adopting E-governance, the above activities are simplified and made possible at their Information<br />
and Facilitation counter in the <strong>Municipal</strong>ity. By E-governance, the services of Vellakoil<br />
<strong>Municipal</strong>ity will be made easy, transparent, accountable and quick. The citizens may be<br />
informed about their dues and thus the revenue generation will be faster and easier. The<br />
modules online in this town are 6 and the rest of the modules will be made online shortly.<br />
Modules online – 6 (Property tax, Water tax, Professional tax, Salary, FAS, Birth and death)<br />
ii) Proposals<br />
It is proposed to provide 4 Seva centers at Booster house Moolanoor road, Natesan nagar,<br />
Erode road (near bus stand) and at municipal office. The total cost required is Rs.16.00 lakhs.<br />
5.2.8 URBAN GREENARY<br />
The main roads, residential avenues need to be provided with trees. It is proposed to provide<br />
2000 number of saplings/treelings planted along main roads. Private participation and<br />
involvement of SHGs and NGOs can make this task a success. The total investment required is<br />
Rs.10.00 lakhs. The annual Operation and maintenance cost is Rs.10000.<br />
5.3 OTHER PROJECTS<br />
The municipality has a community hall at Salavaiyalar colony and a shopping complex at<br />
Theerthampalayam with 4 shops.<br />
Construction of commercial building with an area of 5000 sq.ft at Erode road near the bus stand<br />
is proposed by the municipality. The demand for the commercial building may be assessed by<br />
the municipality. The cost required to implement the project is Rs.100.00 lakhs.<br />
5.3.1 UPDATION OF DATABASE ON GIS PLATFORM<br />
There is no realistic database for the town, in the form of topography, updated base map,<br />
assessment of properties in their location, size, use and intensity, assets -lands and structures in<br />
their location, status, extent, and quality, topography, land parcels by town survey, numbers and<br />
sub divisions and so on. All these can be updated with cent percent precision using high<br />
resolution satellite imageries supplemented by cent percent primary survey or aerial<br />
photographs. All these with spatial and non-spatial data can be had on a GIS format which, on a<br />
click at any feature or site on the town map will provide the entire details including the description<br />
of the feature / address of the owner including tax paid etc. This is a onetime comprehensive<br />
exercise to include the updated town map with town survey, land parcels, structures, service<br />
network, assets with the relevant details and description on a GIS format.<br />
In this ultra modern age, with high-tech interventions, this is considered a must for easy, efficient<br />
and flawless governance, administration and functional operation from local body level to the<br />
government level.<br />
32
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
This project may cost about Rs. 40.00 lakhs including the cost of high resolution satellite<br />
imageries. This entire amount may be obtained as grants from the government and it will take<br />
maximum one year for completion.<br />
a. Property Mapping<br />
Property taxes are the major source of revenue of ULBs in India. However, in most cities, not all<br />
properties are assessed, records are not updated regularly, and tax collection is far from<br />
satisfactory. ULBs can increase revenue by improving property inventories, record management,<br />
public awareness and participation, and tax collection.<br />
As a first step, the <strong>Municipal</strong>ity may initiate a door to door survey of all existing properties, with<br />
details on size & built up area of the property, present use, number of households, houses, size<br />
of families, etc. which would form a database for GIS projects. At the rate of Rs.10.00 per<br />
property, the estimated cost for the project would be Rs.4.30 lakhs. This would also aid in<br />
identifying unassessed and under assessed properties, rationalization of property tax etc.<br />
5.4 PROPOSALS TO BE IMPLEMENTED BY OTHER AGENCIES<br />
To make use of the inherent potential of the resources in the town, there are certain proposals<br />
which can be implemented by other agencies. Implementation of these proposals will enhance<br />
the development of the town. The proposals are put forward visualizing the optimal utilization of<br />
the resources available in and around the town.<br />
Table 5.14 Proposals to be implemented by other Agencies<br />
Sl.<br />
No<br />
Proposals Nodal agency<br />
1 Regional <strong>Development</strong> plan DTCP<br />
2<br />
Preparation of Integrated Solid waste Management Action<br />
<strong>Plan</strong><br />
CMA/TNUIFSL<br />
3 Preparation of Integrated Traffic management <strong>Plan</strong> Erode Corporation<br />
Panchayat Union/ Health<br />
4 Provision and up-gradation of Health facilities<br />
and Family Welfare<br />
Department<br />
5 ESCo Studies CMA/TNUIFSL<br />
6<br />
Awareness creation campaign for NGOs for – E<br />
governance, UGSS, Water Supply, Solid Waste<br />
Management and tax collection<br />
33<br />
Erode<br />
Corporation/RDMA,Tiruppur.
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
5.5 CAPITAL INVESTMENT PLAN<br />
The capital Investment for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity under CDP has been detailed out in the previous sections. The projects include major infrastructural<br />
projects initiated by the State government recently for water supply and drainage and, medium and small projects by way of meeting the long felt<br />
needs to provide comfortable living environment to the citizens of the town. In all, 16 capital projects are proposed of which 7 relate to provision of<br />
physical infrastructural facilities and, the rest relate to social infrastructure and commercial ventures. The capital investment plan is detailed in the<br />
table below:<br />
The year wise investment plan and prioritizations of all the projects included in the CDP are given in the table shown below:<br />
S.No<br />
Project Description<br />
Estimated capital<br />
cost (in lakhs)<br />
Table 5.15 Capital Investment Programme<br />
Year I Year II Year III Year IV Year V Medium<br />
Term 2025<br />
34<br />
Long term<br />
2040<br />
1 Water Supply 1199.12 1199.12 - - - - 825.00 2550.00<br />
2 Sewerage System 3300.00 - 1500.00 1800.00 - - 1190.00 4105.00<br />
3 Storm Water Drains 300.00 - 60.00 80.00 100.00 60.00 5848.00 5100.00<br />
4 Solid Waste management 800.00 300.00 600.00<br />
a Land cost for compost yard and regional 550.00<br />
land fill<br />
250.00 300.00<br />
b Improvements for existing and new compost<br />
yard<br />
200.00 200.00<br />
c Vehicles and equipments 50.00 25.00 25.00<br />
5 Roads 2043.00 0.00 3923.00<br />
a Upgradation & restoration of roads 1833.00 90.00 450.00 657.00 336.00 300.00<br />
b Improvements to road geometry 110.00 50.00 60.00<br />
c Widening of main & link roads 100.00 70.00 30.00<br />
6 Bus Shelter 10.00 6.00 4.00 - - - 0.00 0.00<br />
7 Street Lights 182.00 - - 255.00 653.00<br />
High mast lights at old bus stand and bus<br />
stand<br />
14.00 7.00 7.00
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
Installation of street lights & fittings 100.00 10.00 30.00 30.00 30.00<br />
Retrofitting & energy saving devices 23.00 23.00<br />
Central median lights for 3 km 45.00 40.00 5.00<br />
8 Slum Improvement 709.00 - 375.00 150.00 113.00 71.00 0.00 0.00<br />
9 Parks and Play Fields 20.00 - - - - 20.00 0.00 0.00<br />
10 Market 150.00 0.00 0.00<br />
a Construction of Daily market 75.00 75.00<br />
b Construction of weekly market 75.00 75.00<br />
11 Public Convenience 35.00 15.00 15.00 5.00 - - 0.00 0.00<br />
12 Burial Ground 100.00 - 100.00 - - - 0.00 0.00<br />
13 E-Governance 16.00 8.00 8.00 - - - 50.00 75.00<br />
14 Urban Greenery 10.00 - - - - 10.00 25.00 50.00<br />
15 Other Projects - Commercial building at 100.00<br />
Erode road near bus stand<br />
100.00<br />
16 Updation of Database - GIS 40.00 - - - - 40.00 0.00 200.00<br />
17 Property Mapping 4.30 4.30 - - - - 3.00 8.00<br />
Total 9018.42 1404.42 3067.00 3377.00 639.00 531.00 8496.00 17264.00<br />
The total capital investment required for the implementation of the identified projects in Vellakoil municipality is estimated at Rs.9018.12 lakhs,<br />
35
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
REFORMS AND ACTION PLAN FOR PROJECT IMPLEMENTATION<br />
A <strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> (CDP) is essentially a road map to achieve a set of development<br />
objectives within a specific period. This CDP has identified gaps in municipal service delivery<br />
and institutional management, ascertained by analysis and stakeholder feedback. The proposed<br />
interventions for the <strong>Municipal</strong>ity are in the form of reforms, action plans and strategies to<br />
achieve the same.<br />
Strategies and Action <strong>Plan</strong>s are the elements which bridge the gap between the Proposed<br />
Reforms and implementation. The following sections detail out the strategies and Action <strong>Plan</strong><br />
plans for the proposed Reforms and interventions in the areas of revenue enhancement,<br />
privatization, computerization initiatives, energy efficiency and municipal service delivery.<br />
6.1 PRESENT SCENARIO IN URBAN REFORMS<br />
“Reforms and change are critical elements in development process; they become more<br />
significant in urban development in the context of growth of towns and consequent pressure on<br />
infrastructure and services, growth of poverty, etc. This is compounded by institutional<br />
constraints like in capacity, fragmented structures, functional overlaps and outdated processes<br />
and procedures. In addition, there has been a paradigm shift in governance from the traditional<br />
top-down model. As a result governance reforms have become imperative for efficient delivery<br />
of services, provision and maintenance of infrastructure and to provide efficient and responsive<br />
governance to the people. Recognizing the significance of reforms to provide efficient and<br />
effective governance, the State Govt. has initiated and implementing several urban sector<br />
reforms during the last few years. “<br />
The following are the key reforms implemented by the GoTN and GoI :<br />
1. Devolution of funds: 3.5% of State’s total tax revenue passed on to urban local bodies.<br />
2. State Finance Commissions: Three consecutive state finance commissions were<br />
setup for recommendations to Government.<br />
3. Setting up of TNUDF: A successful private-public partnership initiative to tap the capital<br />
market.<br />
4. Accrual Based Accounting System: The new accounting system has been<br />
implemented in all the urban local bodies.<br />
5. Computerization and E-governance of select <strong>Municipal</strong> functions have been<br />
successfully implemented in all urban local bodies.<br />
6. Urban indicators: Performance assessment of ULBs initiated by the CMA, Government<br />
of Tamil Nadu.<br />
7. Revision of Property tax : With effect from April 1.2008, subject to a maximum of 1.25<br />
times the existing tax structure.<br />
8. Debt monitoring cell: It has been established with office of CMA with the objective of<br />
collecting financial information on individual ULBs, assisting them in making realistic<br />
financial projections and facilitating the Urban Local Bodies to access the Capital<br />
Markets by information dissemination from CMA office.<br />
36<br />
6
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
9. GIS for 5 urban local bodies: Consultancy for Preparation of Property mapping and<br />
Utility Mapping for Madurai, Coimbatore and Tiruchirappalli Corporations and<br />
Rajapalayam & Gobichettipalayam <strong>Municipal</strong>ities has been initiated as a pilot project by<br />
the office of CMA.<br />
10. ESCO Studies: TNUIFSL initiative for the Implementation of energy efficiency in Water<br />
pumping and Street lighting systems under performance contract.<br />
11. Right to Information Act, GoI : An Act to provide for setting out the practical regime of<br />
right to information for citizens to secure access to information under the control of public<br />
authorities, in order to promote transparency and accountability in the working of every<br />
public authority.<br />
12. The Public Disclosure Law:<br />
To reduce the workload of public officials increased due to additional responsibility of<br />
responding to RTI requests, the public disclosure law will require that information be<br />
published voluntarily by public authorities. This will significantly reduce the number of<br />
routine RTI requests. The Public Disclosure Law will complement the RTI Act. The<br />
Disclosure Law will provide for commonly requested information on a regular basis and<br />
the RTI Act may be used for more specific information.<br />
6.2 PROPOSED INTERVENTIONS AT STATE LEVEL<br />
a. Property Tax<br />
Implement a framework law for disputed properties, so that the assessees pay the tax first and<br />
then carry out necessary litigation as in Central Govt. Depts.<br />
b. Community participation law<br />
Enacting the “Community Participation Law” that will make it mandatory for the government and<br />
its agencies to get the view of citizens, mainly residents’ welfare associations and other citizens’<br />
groups, before starting any project.<br />
c. Initiatives in Private Participation<br />
In Tamil Nadu, PPP has been identified as a modality for development and the PPP cell has been<br />
formulated as the nodal agency to guide the various Govt. Agencies such as CMDA, TNSCB,TNAMB .<br />
The processes such as vetting of RFQ/RFP, Project preparation ,Procurement of private operator ,<br />
Approvals etc are being handled by the cell at present.<br />
The cell has also prepared training materials, presentations/handouts, compiled case studies<br />
etc, which are given as a part of capacity building Content for web hosting developed pending<br />
approval by Go TN.<br />
The way forward<br />
1. Information dissemination to public sector agencies and various ULBs through websites<br />
of the ULBs and CMA and organizing workshops with the aid of Anna Institute of<br />
Management, TNIUS, Council of Indian Industries etc.<br />
37
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
2. A database consisting of model bid documents, success models, sector wise PPP<br />
consultants and operators can also be formulated.<br />
Infrastructural Projects:<br />
Water supply project<br />
1. As regards water supply projects, the consultant proposes using available local sources<br />
(surface water) in lieu of capital intensive projects from far off sources. The enforcement of<br />
RWH in all buildings is a commendable initiative, which has proven successful in improving<br />
the quality and quantity of ground water table according to a recent study. Rejuvenation and<br />
protection of water bodies and recycling, reuse of water is also a major issue to be<br />
addressed in this regard. Participation of SHGS, voluntary organizations, resident welfare<br />
associations need to be sought.<br />
UGSS project<br />
1. Highly engineered and mechanized conventional sewage treatment requires large Capital<br />
Investment; demand high maintenance costs are not feasible for the developing countries<br />
like India. Capital intensive and highly technological waste disposal solutions, utilizing<br />
indiscriminate collection and large-scale disposal, do not consider the value of recovering<br />
organic waste resources and do not promote recycling. The land required for the disposal of<br />
treated wastewater in the conventional treatment systems is not readily available in and<br />
around urban area. Alternative treatment systems like Root zone treatment methods could<br />
be used.<br />
2. GoTN may also encourage recycle of water, to meet requisite standards rather than let them<br />
out into streams or sewage farms. This will not only promote water recycling , but also<br />
resource recovery of minerals.<br />
6.3 PROPOSED INTERVENTION AT MUNICIPAL LEVEL<br />
The Proposed <strong>Municipal</strong> intervention is broadly categorized under the heads of:<br />
1. Strategies for Environmental Improvement<br />
2. Reforms in Resource Mobilisation<br />
3. Privatisation Initiatives<br />
4. Energy & resource efficiency<br />
5. Computerization and E-governance<br />
6. Accounts and Auditing<br />
7. Institutional Management<br />
8. <strong>Municipal</strong> service delivery<br />
Strategies for Environmental Improvement<br />
It includes the following:<br />
38
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
• Formation of Sustained Economic <strong>Development</strong> Organisation<br />
• Regular monitoring and stringent enforcement of Pollution control regulations on the<br />
industries utilising the existing CETPs.<br />
• Initiate a ‘Pollution remediation Pooled fund for Tiruppur region‘ on the lines of<br />
AMBURTEC and VANITEC - A public-private partnership initiative, with contributions<br />
from Industrial establishments, Govt. and funding agencies.<br />
• Launch intensive water recharge activities to surface water bodies including open<br />
wells, Ooranis, odais and eris, to improve water quality and quantity in this region.<br />
Table 6.1Road map – Environmental Improvement<br />
S.N Reforms<br />
Year 1<br />
Year of Implementation<br />
Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Year 5<br />
1<br />
Business <strong>Plan</strong> for Industrial remediation<br />
measures<br />
<br />
2<br />
Implementation of Industrial remediation<br />
measures<br />
<br />
3 Intensive water recharge activities <br />
4<br />
Enforcement of Pollution control<br />
regulations<br />
<br />
6.3.1 Reforms In Resource Mobilisation<br />
In an environment in which business activity is booming and urban infrastructure threatens to<br />
become a constraint to growth, the municipalities are faced with an unprecedented need to find<br />
substantial resources for development, and an unprecedented opportunity to raise the same.<br />
The various options for enhancement of <strong>Municipal</strong> revenue based is discussed below:<br />
1. Improving revenue from own sources<br />
2. Improving revenue from user charges<br />
3. Formation of new sustainable revenue bases<br />
6.3.1.1 Improving Revenue from Own Sources<br />
Strategy options:<br />
i. Property and Profession tax<br />
1. Expanding Property tax and Profession tax base.<br />
Onetime assessment of all unassessed and under assessed properties. The project could be<br />
taken up as a door –to –door survey of all existing properties, with details on<br />
1. Size & built up area of the property<br />
2. Present use - residential, commercial, industrial or vacant.<br />
Street naming and property numbering already undertaken by Govt. of Tamil Nadu needs to be<br />
linked to this to streamline the study. Property mapping would form a database for GIS projects<br />
(Land use and Utility Mapping), which is a long term project and in the rationalization of tax<br />
structure.The issue omission of profession tax assesses within <strong>Municipal</strong> limits would also be<br />
39
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
addressed in this project. The participation of the SHGs, (youth and women) could be utilized<br />
for the purpose.<br />
2. Rebates on tax:<br />
Most of the collections take place during the last quarter of the year. This results in poor<br />
collection efficiency, wherein the ULB ends up collecting much less taxes than the tax demand<br />
raised. The option of providing rebates upto 10% for ‘early birds’ paying the tax during the 1 st<br />
and 2 nd quarter could be explored. This would ensure timely spending on capital and operating<br />
expenditure and efficient tax management systems.<br />
3. Regular and periodic increment of property tax at 15% every 5 years.<br />
4. Levy of penalty on unauthorised construction until regularization and approval.<br />
ii. Sustainable amendments regarding the above aspects may be considered.<br />
Identifying and including omitted Profession tax assessees. This project is to be linked to the<br />
property mapping exercise. An improvement of 20-30% on the existing tax base could be<br />
expected.<br />
Table 6.2 Road Map - Improving revenue from own sources<br />
S.N Reforms<br />
Year 1<br />
Year of Implementation<br />
Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Year 5<br />
1<br />
Property tax Reform<br />
i Property Mapping <br />
ii Rebates on Property tax<br />
iii Regular and periodic increment of property tax <br />
2 Levy of penalty on unauthorised construction. <br />
3<br />
Reassessment of omitted Professional tax<br />
assessees<br />
6.3.1.2 Improving Revenue from User Charges<br />
Strategy options<br />
i. Water supply and UGSS<br />
Fixing of bulk water meter at apartment complexes, commercial , industrial , hospitals,<br />
marriage halls and educational institutions.<br />
Approval of the <strong>Municipal</strong> council for the proposed tariff and deposit structure to enhance<br />
the public contribution and meet the entire O&M cost.<br />
Increase in the House Service Connections to at least 85% of the total assessments.<br />
This backed by higher collection efficiency and enforced leakage losses (less than 15%)<br />
would further improve service delivery.<br />
Levy Reasonable User Charges to recover full O&M Cost of water supply and UGSS.<br />
40
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
Implementation of graded tariff structure (UGSS) for domestic and non-domestic<br />
connections. This needs to be linked to property mapping project and type of<br />
assessment to be ensured.<br />
Mandatory Mobilization of deposits for Capital intensive WS or UGSS projects during<br />
pre-construction stage of the project.<br />
Regular and periodic increase in tariff and deposit structure every 5 years.<br />
ii. Solid Waste Management<br />
Approval of the <strong>Municipal</strong> council for the proposed Solid waste conservancy charges for<br />
commercial and industrial establishments during the base year and after 5 years for<br />
domestic assessments.<br />
For implementing collection of conservancy fee for Solid waste Management .The<br />
proposed tariff structure is given below:<br />
• Commercial - Rs.10 per ton.<br />
• Industrial - Rs.15 per ton.<br />
• Bio-medical - Collected by IMA.<br />
Privatisation of collection, transfer, construction and management of compost yard and<br />
compost production. This would reduce the O&M expenses of <strong>Municipal</strong>ity on SWM by<br />
30 to 40%.<br />
• Revenue generation from selling scrap after segregation at secondary collection point or<br />
compost yard at Rs.10 –Rs.15 per kg.<br />
Revenue Generation from sale of compost at the rate of Rs.1000 per one as bulk supply to<br />
nearby agricultural areas. Incidentally, the manure generated from <strong>Municipal</strong> garbage is found<br />
to be richer in NPK values compared to the one available in the market. This has resulted in<br />
producing better yield of agricultural products both in quantity and quality.<br />
Table 6.3 Road Map Improving revenue from user charges<br />
S.N Reforms<br />
Water Supply and UGSS<br />
Year 1<br />
Year of Implementation<br />
Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Year 5<br />
1<br />
i<br />
ii<br />
Increasing deposit and tariff<br />
Graded tariff for UGSS<br />
<br />
<br />
iii Pre mobilization of deposits <br />
2 Solid Waste Management<br />
ii<br />
iii<br />
Collection of conservancy fee for Commercial<br />
and Industrial Establishments<br />
Collection of conservancy fee for Domestic<br />
assessments<br />
41
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
6.3.1.3 Action <strong>Plan</strong>: Formation of New Sustainable Revenue Bases<br />
Strategy options<br />
i. Remunerative projects<br />
To improve the revenue base of the municipality, following are the remunerative proposals<br />
identified within municipal area.<br />
• Construction of Commercial building at Erode road near bus stand<br />
ii. Parking Regularisation <strong>Plan</strong><br />
Enforcing no-parking zones and identification of possible parking areas with the involvement of<br />
stakeholders would be the first step in mitigating congestion in the central areas of the town.<br />
Preparation of inventory for all roadside parking area within the town. Initiating time based pay<br />
and park facilities for vehicles. Appropriate rent structure from light carriage vehicles and heavy<br />
vehicles parking would also improve income generation.<br />
The proposed parking fee structure is:<br />
◊ Two wheelers - Rs.2.00 per day<br />
◊ Light Vehicles - Rs.5.00 per day<br />
◊ Heavy Vehicles - Rs.10.00 per day<br />
iii Advertisement Regularisation <strong>Plan</strong><br />
Identifying strategic locations such as bus shelters, road medians, for hoardings and poster<br />
places in <strong>Municipal</strong> area and levying advertisement tax at the rate of Rs.25 per sq. ft per annum.<br />
To prepare an inventory of advertisement spaces within their limits with size and type<br />
.Auctioning the entire rights to a single bidder on an annual basis is suggested. The initiative of<br />
GoTN to remove hoardings and encroachments is a welcome step to regularize the<br />
advertisements and hoardings<br />
Table 6.4 Road Map for Formation of new sustainable revenue bases<br />
S.N Reforms<br />
Year 1<br />
Year of Implementation<br />
Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Year 5<br />
1 Formation of new sustainable revenue bases<br />
i Remunerative Projects<br />
a. Premobilization of deposit for commercial<br />
building at Erode Road near bus stand<br />
<br />
ii Parking Regularization <br />
iii Advertisement Regularization <br />
6.3.2 Action <strong>Plan</strong>: Privatisation Initiatives<br />
The areas of privatization of the functions of the ULB in Tamil Nadu are<br />
i. Solid waste management<br />
42
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
ii. O&M of street lights.<br />
iii. O&M of water supply distribution.<br />
iv. AMC of public and pay & use toilet facilities.<br />
v. Parks and parking lots Maintenance and user charges collection.<br />
The GoTN states that the above list is indicative and the ULBs are free to explore more options.<br />
This would not only save the O&M expenses, but also indirectly in pension and gratuities. The<br />
various strategy options are presented below:<br />
Strategy options<br />
1. Privatisation of Collection mechanism<br />
Providing a computer fitted mobile van with online access to municipal database for spot billing<br />
and collection of all taxes. Performance based incentives can be given to the private operators<br />
at the rate of 5% of total collection .The support of the Youth / Women SHGs or fan clubs can<br />
be sought for the purpose of collection with adequate sensitization programmes.<br />
2. Improving community participation by organizing Public awareness campaigns and Training<br />
of Tax Inspectors, to improve the ‘willingness to pay’ of the users. The aid of SHGs, fan<br />
clubs, media could be utilized for the purpose. The following are the various avenues of<br />
revenue, the collection of which could be privatized.<br />
1. Property tax<br />
2. Profession tax<br />
3. Water - Deposits and tariff<br />
4. UGSS- Deposits and tariff<br />
5. Advertisement spaces /rights as a single contract<br />
6. Parking areas<br />
7. Solid waste conservancy fees(Domestic and non-domestic)<br />
3. Privatisation of Operation and Maintenance of the entire Water Supply and Distribution<br />
System.<br />
4. Privatisation of operation and maintenance of the UGSS.<br />
5. Privatisation of Solid waste management (Discussed in detail under Improving revenue from<br />
user charges)<br />
6. Privatisation of O&M of street lights & pumping machinery(detailed out in Action plan for<br />
energy & resource efficiency)<br />
7. Repair and maintenance of major <strong>Municipal</strong> roads for 3 years from the period of laying.<br />
8. Option of BOT, BOOT for parks & play grounds by implementing user charges for areas<br />
more than 5000 sft.<br />
9. Option of converting public toilets to Pay & Use type and privatization of O&M.<br />
10. Private participation in medical infrastructure like RCHP, maternity homes and adoption of<br />
premium and free facility programme in return for improved medical facility.<br />
43
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
Table 6.5 Road Map for Privatization initiatives<br />
S.N Reforms<br />
Year 1<br />
Year of Implementation<br />
Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Year 5<br />
1 Privatization of Operation and Maintenance<br />
i Water supply and Distribution system <br />
ii Sewer network & STP <br />
iv Street lights <br />
vi AMC of Public and pay % use toilet facilities <br />
vii<br />
Parks and parking lots Maintenance and user<br />
charges collections<br />
<br />
2<br />
Privatisation options in Solid Waste<br />
Management<br />
Privatization of Door to door collection of solid<br />
waste<br />
<br />
Compost yard management & sale of compost &<br />
scrap<br />
<br />
3 Privatization of Collection mechanism<br />
4<br />
5<br />
Spot billing and tax collection using mobile van <br />
Formation and sensitisation of youth & women <br />
SHGs<br />
Public awareness campaign for improving tax <br />
collection (IEC)<br />
6.3.3 Action <strong>Plan</strong>: Energy & Resource Efficiency<br />
Strategy options<br />
Conducting energy audits for water pumping machinery and street lights.<br />
Conducting leak detection studies, if transmission losses are more than 15%.<br />
All Head works and service reservoirs may be fitted with bulk water meter to assess the<br />
loss due to non revenue water and unaccounted water.<br />
Enforce regulations on illegal tapping of water.<br />
Fixing Flow Control Valves and meters for all water service connections.<br />
Provision of energy saving lights, and equipments like dimmer and timer switches to<br />
reduce energy consumption.<br />
Privatizing the maintenance of street lights to ESCO companies.<br />
Street lights<br />
TNUIFSL has initiated the study of Energy Saving Company (ESCO) for energy efficiency in the<br />
O&M of street lights and pumping machinery for select <strong>Municipal</strong>ities throughout Tamil Nadu.<br />
ESCOs provide comprehensive services - encompassing audits for energy saving performance,<br />
design & implementation of conservation measures, maintenance, operation and management<br />
of the introduced facilities and procurement of project funds. ESCOs conduct retrofitting for<br />
energy conservation without damaging the environment. The ESCO will guarantee the savings<br />
44
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
that would meet or exceed the annual payments to cover up the entire project costs usually a<br />
period of 5 to 10 years. The savings can be shared proportionately with the institution for which<br />
the project is designed and implemented for.<br />
The salient features of performance contracting for energy savings through ESCO based<br />
business model are as under:<br />
1 'Nil' investment by customer / ULB.<br />
2. ESCO to identify Energy Efficient Measures (EEMs) to replace / modify existing in<br />
efficient systems.<br />
3. ESCO supplies, installs and maintains the Energy Efficient Measures (EEMs) during the<br />
contract period.<br />
4. Contract period could be 3-5 years or as mutually agreed upon.<br />
5. Energy saving is shared between ESCO and customer as per agreed terms. Total<br />
project cost is funded by ESCO. The O & M expenses will be met by the <strong>Municipal</strong>ity.<br />
6. Guarantee Energy savings and recover its investment including interest & other costs<br />
out of generated energy savings.<br />
Table 6.6 Road Map for Energy and Resource efficiency<br />
Year of Implementation<br />
S.N Reforms<br />
Year 1<br />
Year<br />
2<br />
Year<br />
3<br />
Year<br />
4<br />
1 Energy audit<br />
i Leak detection study <br />
ii Fixing of bulk water meter <br />
iii Fixing flow control values and meters <br />
iv<br />
Implementing energy saving measures on street<br />
lights and pumping machineries (ESCo)<br />
<br />
6.3.4 Action <strong>Plan</strong>: Computerization and E-Governance<br />
Strategy options<br />
1. Launch data warehousing on a large scale, which would avoid cross-reference to paper<br />
record, which are time consuming and also preservation of paper media, which occupies<br />
space, could be avoided.<br />
2. Computerization of bill payment and facilitation of on line payments<br />
3. Computerisation of registration of land records within <strong>Municipal</strong> limit<br />
4. Digitisation of Birth and death certificates for the past 30 years<br />
5. Property Mapping to be computerised and details on area, year of construction, type of<br />
assessment to be computerized to facilitate calculation of property tax.<br />
6. Administration and issue of trade licenses to be on line, including payment and<br />
reconciliation of license fee.<br />
7. Computerization of birth and death certificates and on line issue of certificates.<br />
8. Computerization of public grievances and Redressal mechanism<br />
45<br />
Year<br />
5
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
9. Introduction of Asset Management System for all the available land and building assets<br />
available with the <strong>Municipal</strong>ity<br />
10. On-line submission of building plans and approval.<br />
11. Track O&M of assets and their replacement<br />
12. E-tendering processes.<br />
The above proposal can be taken up after giving sufficient training to <strong>Municipal</strong> staff in hard<br />
ware and software.<br />
Table 6.7 Road map for Computerization and E-Governance<br />
S.N Reforms<br />
Year 1<br />
Year of Implementation<br />
Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Year 5<br />
1 Computerization and E-governance<br />
i Digitizing municipal records (past 30 years) <br />
ii On-line bill payment <br />
iii Registration of Land records <br />
iv Digitization of old Birth and death certificates <br />
v On-line issue of Birth and Death certificates<br />
vi Property Mapping <br />
vii on-line Issue of trade license <br />
viii Online submission of building plans <br />
ix E-tendering <br />
6.3.5 Action <strong>Plan</strong>: Accounts and Auditing<br />
A Consultant committee of chartered accountants, consultants having experience in<br />
municipal accounting should be constituted to provide training to the <strong>Municipal</strong> employees.<br />
Timely Auditing should be performed with the use of private Chartered Accountants for<br />
routine audit and local audit to carry out proprietary audit.<br />
Closing all Auditing before September 30 of the next financial year and publishing the<br />
audited statement on the website.<br />
6.3.6 Action <strong>Plan</strong>: Institutional Management<br />
The constant change in urban sector in the context of reforms results in the need for continuous<br />
upgradation of the skills and knowledge of the ULB staff. TNUDP III has initiated the process of<br />
providing the required training to the staff during the current planning period. It is essential that<br />
the training process becomes a sustainable one with the introduction of an institutional<br />
framework which would ensure that the training is provided in a continuous manner.<br />
Training programmes need to be evolved depending upon whether they are Elected<br />
Representatives, Senior level officers, Middle level officers and staff in various sections of the<br />
ULBs. Training of public representatives and staff of ULBs will not only improve their skills but<br />
46
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
also exposes modern/scientific technological advancement in engineering, management and<br />
inter personal communication.<br />
The categorization of training is based upon the position at various levels focusing primarily of<br />
managerial aspects, technical knowledge, skills and management tasks and awareness about<br />
responsibilities.<br />
Strategy options<br />
A. CAPACITY BUILDING FOR ELECTED REPRESENTATIVES AND COMMITTEE<br />
MEMBERS<br />
The details of the various training requirements for elected representatives and Committee<br />
members are presented below.<br />
Table 6.8 Technical Assistance for Elected representatives<br />
Category Identified Training areas<br />
Elected representatives • Visioning, goal setting, <strong>Plan</strong>ning<br />
• Urban Governance, Management and <strong>Plan</strong>ning<br />
• Social management and Management of Urban Poor<br />
• Financial and cost management<br />
• Budget preparation<br />
• Tender procedure<br />
• Training in interpretation of various laws, rules, regulations and<br />
statutes that ULB is bound by<br />
• E - Governance<br />
• Redressal of public grievances<br />
• Environment management<br />
• JNNURM, UIDSSMT, IHSDP & BSUP<br />
• <strong>City</strong> Corporate <strong>Plan</strong>, Urban <strong>Development</strong> plans (Master plans, DDPs)<br />
• Solid waste management.<br />
• Disaster management<br />
• Managerial development and effectiveness<br />
• Public relations and Human resource development.<br />
• Crisis management and Stress management<br />
• Personality development and Motivation skill development<br />
• Written and Oral Communication skills<br />
Committee members • Tax appeal committee: tax assessment methods; interpretation of<br />
various laws, rules, regulations and statutes<br />
• Contracts committee: procurement procedures; interpretation of<br />
various laws, rules, regulations and statutes<br />
• Appointment committee: Interviewing skill and techniques<br />
47
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
B. Capacity Building for Ulb Staff<br />
The training areas identified for ULB staff in all position is classified as functional, managerial &<br />
behavior and attitude in short, medium and long term training. The details of the various training<br />
requirements for ULB staff are presented below.<br />
Table 6.9 Technical Assistance for ULB staff<br />
Category Identified Training areas<br />
Senior Management Staff • People management skills<br />
• Motivation and Interpersonal skills<br />
• Leadership and Public relations<br />
• Attitudes – both personal and organizational<br />
• Team Building, Human resource development<br />
• Goal setting, Budgeting<br />
• Written and Oral Communication skills<br />
• Effective use of computers especially for managerial decision<br />
making<br />
• Proper interpretation and effective use of MIS reports<br />
• Decision support systems<br />
• Training in interpretation of various laws, rules, regulations and<br />
statutes<br />
• Time management, Stress management<br />
• Change management<br />
• Effective urban management<br />
• Management principles, Managerial development and effectiveness<br />
• Interviewing skills<br />
• Social management and urban poor management<br />
• Citizen grievance handling<br />
• Project appraisal, Project Management and project financing<br />
• Contract management, Bid management, Costing<br />
• Procurement procedures<br />
• Pricing and tariffs/taxation methodologies<br />
• Operations research<br />
• Quality control<br />
• Public private partnerships and opportunities for ULB in the same<br />
• Reforms at the ULB level<br />
• Financial and cost management<br />
• Environment management<br />
• Disaster management<br />
• Solid waste management<br />
• Systems management (improving citizen service and ULB<br />
efficiency)<br />
• Strategic urban planning<br />
• Performance management system and key result areas.<br />
Supervisory Staff • Motivation and Interpersonal skill development<br />
48
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
Training for Operational<br />
staff<br />
Source: CMA Records.<br />
Sl.N<br />
o<br />
1<br />
• Effective use of computers<br />
• Training in interpretation of various laws, rules, regulations and<br />
statutes<br />
• Training for development of a positive attitude<br />
• Citizen handling and grievance handling<br />
• Managing urban poor, education and health services<br />
• Implementation skills<br />
• Training in developing a Performance Management Systems (PMS)<br />
and key Result Areas (KRA)<br />
• Functional skills required in their respective function<br />
- Training in office Procedures<br />
- Training in computers<br />
- Training in team work<br />
• Training in general office administration and management<br />
- Training in effective servicing<br />
- Training in communication<br />
- Training in equipment usage<br />
Table 6.10 Road map for Accounts & auditing and Institutional Management<br />
Reforms<br />
Year 1<br />
Year of Implementation<br />
Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Year 5<br />
Accounts and Auditing with charted<br />
accountant<br />
I<br />
Appointing private charted accountant<br />
consultant<br />
<br />
Ii Closing of audit and accounts (Sept 30th) <br />
iii<br />
Online publication of audited statement (Oct<br />
30 th )<br />
2 Institutional Management<br />
i<br />
Capacity Building for Elected<br />
Representatives<br />
ii Capacity Building for ULB staffs<br />
49
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
Table 6.11 Road Map for Implementation of all Projects<br />
S.N Project Items<br />
Implementing<br />
Agency<br />
Funding<br />
pattern<br />
(G:L:M)<br />
Amount<br />
(in<br />
lakhs) Year 1<br />
Short term (Rs. In lakhs)<br />
Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 Year 5<br />
1 Water Supply TWAD Board 71:25:4 1199.12 1199.12<br />
2 Under Ground Sewerage System TWAD Board 35:37:28 3300.00 1500.00 1800.00<br />
3 Storm Water drains <strong>Municipal</strong>ity 90:00:10 300.00 60.00 80.00 100.00 60.00<br />
5 Solid Waste management 800.00<br />
a Land cost for compost yard and regional land fill<br />
100:0:0 550.00 250.00 300.00<br />
b Improvements for existing and new compost yard <strong>Municipal</strong>ity 0:0:100 200.00 200.00<br />
c Vehicles and equipments 50:00:50 50.00 25.00 25.00<br />
6 Roads 2043.00<br />
a Upgradation and restoration of roads<br />
1833.00 90.00 450.00 657.00 336.00 300.00<br />
b Improvements to road geometry <strong>Municipal</strong>ity 90:00:10 110.00 50.00 60.00<br />
c Widening of main roads and link roads 100.00 70.00 30.00<br />
7 Bus Shelter Pvt. Operator 100% private 10.00 6.00 4.00<br />
8 Street lights 182.00<br />
High mast lights at old bus stand and bus stand<br />
100:00:00 14.00 7.00 7.00<br />
Installation of street lights and fittings <strong>Municipal</strong>ity 50:00:50 100.00 10.00 30.00 30.00 30.00<br />
Central median lights at main roads for 3km 90:00:10 45.00 40.00 5.00<br />
Retrofitting and energy saving devices Pvt. Operator 100% private 23.00 23.00<br />
9 Slum improvement <strong>Municipal</strong>ity 100:0:0 709.00 375.00 150.00 113.00 71.00<br />
10 Parks and Playfields <strong>Municipal</strong>ity 70:00:30 20.00 20.00<br />
11 Market 150.00<br />
Construction of Daily market<br />
Construction of weekly market<br />
<strong>Municipal</strong>ity 0:0:100<br />
75.00<br />
75.00<br />
75.00<br />
75.00<br />
10 Public Convenience <strong>Municipal</strong>ity 50:00:50 35.00 15.00 15.00 5.00<br />
12 Burial ground <strong>Municipal</strong>ity 50:00:50 100.00 100.00<br />
13 E-Governance <strong>Municipal</strong>ity 100:0:0 16.00 8.00 8.00<br />
14 Urban Greenery Pvt. Operator 100% private 10.00 10.00<br />
15 Other Projects 100.00<br />
a commercial building at Erode road near bus stand <strong>Municipal</strong>ity 00:90:10 100.00 100.00<br />
16 Updation of Database On GIS <strong>Municipal</strong>ity 90:00:10 40.00 40.00<br />
17 Property mapping <strong>Municipal</strong>ity 0:0:100 4.30 4.30<br />
Note:<br />
G:L:M – Grants : Loan : <strong>Municipal</strong> Own Fund<br />
50
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
6.3.7 REFORMS IN MUNICIPAL SERVICE DELIVERY<br />
The reform agenda for municipal service delivery is given in the following table<br />
Table 6.12 Reform Agenda - <strong>Municipal</strong> Service Delivery<br />
Sector Particulars<br />
Benchmark<br />
considered Existing<br />
Year 1 Year 2<br />
Target<br />
Year 3 Year 4 Year 5<br />
Outcome<br />
After 5<br />
years<br />
Net Supply per capita 135 lpcd 70 lpcd Period<br />
135 lpcd<br />
WAETR<br />
SUPPLY<br />
HSCs - % of assessed<br />
properties<br />
Frequency of Supply - Hours<br />
per day<br />
≥85%<br />
24x7 hours<br />
29%<br />
Once in<br />
4 days<br />
of<br />
Implem<br />
entatio<br />
n - -<br />
≥85%<br />
- - 24x7<br />
SEWERAGE<br />
HSC coverage ≥85% Nil -<br />
Period of<br />
≥85%<br />
SYSTEM Coverage of UGSS network - %<br />
of road length<br />
100% Nil -<br />
Implementation<br />
100%<br />
SOLID WASTE<br />
MANAGEMENT<br />
ROADS,<br />
STORM<br />
WATER DRAIN,<br />
STREET<br />
LIGHTS<br />
Source: Analysis and research<br />
Availability of Composting<br />
facility<br />
100%<br />
available<br />
51<br />
Availabl<br />
e<br />
Collection efficiency 100% 85%<br />
Surfaced roads- % of total road<br />
length<br />
Storm water drains - % of total<br />
road length<br />
Average spacing between<br />
Street lights<br />
Period of Implementation<br />
100% 67% Period of Implementation<br />
100% available<br />
100%<br />
130% 11% - Period of Implementation<br />
30 m 88 m Period of Implementation<br />
100%<br />
30m
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
52<br />
7<br />
ASSETS MANAGEMENT PLAN<br />
All the assets developed, operated and maintained by the <strong>Municipal</strong>ity are termed as municipal<br />
assets and comprise roads, bridges, culvert, water supply & distribution system, UGSS network,<br />
STPs, drains, and street lights. <strong>Municipal</strong> Assets also includes social infrastructure assets such as<br />
municipal owned schools, hospitals, parks and playgrounds, community halls, shopping complexes,<br />
stadium, and vacant lands.<br />
<strong>Municipal</strong> assets are normally classified into movable and immovable assets. Immovable assets<br />
attain importance as indicators for the financial worth which would help in its borrowing capacity and<br />
credit worthiness of Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity.<br />
The management of assets in the local bodies is at the initial stage where, only the assets are listed<br />
and status is described. Invariably, in all the cases, the management component is missing as to the<br />
techniques and methods of managing the assets either in improving their state and value or in<br />
sustaining them with a growth motive. There is hardly any case where a local body has made use of<br />
its immovable assets for raising loans or improving its borrowing capacity. It requires an overall<br />
approach outlining the alternative options of maintaining and managing the assets in a worthwhile<br />
mode.<br />
7.1 ACTIVITIES OF ASSET MANAGEMENT PLAN (AMP)<br />
The Asset Management <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity would comprise the following 5 steps as<br />
explained below:<br />
1. Asset identification<br />
All movable and immovable equipments, immovable municipal properties, assets of <strong>Municipal</strong>ity that<br />
have been developed, handed over or acquired over time from various sources and departments<br />
have to be identified and traced. This would include the detection of unrecorded infrastructure<br />
facilities and properties; scrutiny of records, land registers and land surveys, etc.<br />
2. Audit and reconciliation of records<br />
The <strong>Municipal</strong>ity should record all movable and immovable municipal properties and assets and<br />
infrastructure facilities. Maps and master plans should be crosschecked and an infrastructure<br />
facilities audit should be prepared or updated (if already existing). Current asset values should be<br />
assigned based on a ‘condition-survey’ of the infrastructure facilities.<br />
Land and property records should be crosschecked and municipal registers to be updated to include<br />
previously undetected land, properties and development. A comprehensive list of municipal land,<br />
properties and development should be compiled with approximate assigned.
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
3. Assessment of Remunerative potential<br />
<strong>Municipal</strong>ity should review the existing revenue earning potential of all its assets. New projects or<br />
initiatives should be taken to maximize the revenue earning potential of assets including<br />
infrastructure facilities. The intangible benefits of social facilities also need to be considered in the<br />
process.<br />
4. Digitisation of asset register<br />
Focus should be placed on designing, testing and installing a database management system for<br />
municipal assets. All data, once complied should be classified on the basis of sector specific<br />
infrastructure facilities, land and properties. Specific software should be customized to suit local<br />
requirements and data should be translated into specified formats.<br />
5. Training in database management<br />
Training is the most important part of an asset management plan. Training should emphasize<br />
methods of simplified updation of data, and methods of monitoring and follow-up relating to<br />
infrastructure facilities management, land use, litigation, encroachment, values, expenditure and<br />
revenue flows.<br />
7.2 PRIORITY ASSET MANAGEMENT OPTIONS<br />
There are remunerative and non-remunerative assets of the municipality on which the municipality<br />
incur considerable expenditure for operation and maintenance. The commercial complexes in the<br />
town, Shops in the bus stand, Markets, Slaughterhouse, Pay and Use toilets, etc are all<br />
remunerative. Non-remunerative assets of the municipality are the burial ground, public toilets,<br />
compost yard, parks and playfields etc,. The list of land assets are given in the table below:<br />
Sl.<br />
No<br />
Name of the Asset<br />
1 Water supply &<br />
distribution system<br />
Table 7.1 Priority <strong>Municipal</strong> Assets – Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity<br />
Revenue Income<br />
from the asset<br />
(2006-07)<br />
53<br />
Revenue Expenditure<br />
on the Asset during<br />
(2006-07)<br />
27.84 Lakhs 44.84 Lakhs<br />
Suggested<br />
Improvement options<br />
Leak detection study<br />
Esco Study<br />
2 Drainage Nil 6.80 Lakhs Improvement of SW<br />
network & rain water<br />
harvest.<br />
Proposed UGSS to<br />
improve environment<br />
and revenue to<br />
<strong>Municipal</strong>ity.<br />
3 Pay and use Toilet 1.38 Lakhs Nil Privatisation of<br />
maintenance through<br />
SHGs<br />
4 Street lights Nil 24.69 Lakhs Esco Study, -Energy<br />
efficiency & man power<br />
optimization
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
5 Markets 6.86 Lakhs Nil Proposed new market<br />
with basic facilities<br />
6 Commercial complexes 2.32 Lakhs Nil -<br />
7 Bus stand 3.25 Lakhs Nil Proposed expansion of<br />
bus stand with the<br />
provision of basic<br />
facilities<br />
Two / four wheeler<br />
8<br />
parking areas<br />
9 Water Connection<br />
Charges<br />
7.3 LAND ASSETS<br />
1.01 Lakhs Nil<br />
Proposed renovation of<br />
existing parking area.<br />
0.86 Lakhs 14.33 Lakhs Proposed new scheme<br />
to improve coverage of<br />
service connections<br />
The land varies in its value from location to location and time to time as per the weight age of the<br />
area arrived at based on various factors. It is invariably found that, the value of the municipal land<br />
varies substantially from that of the adjacent private land for obvious reasons. These differences<br />
need a practical moderation to estimate the true credit worthiness of the local body.<br />
The rate of increase of the <strong>Municipal</strong> land in its value, vis-à-vis that of the adjacent private land at<br />
the various locations will be useful in drawing up a reasonable assets management technique.<br />
The proposals for efficient utilization of land assets are given in the table below:<br />
Table 7.2 Proposed Use – Land Asset<br />
Sl. No Location of Land Asset Present Use Proposed Use<br />
1 Ayyasamay colony Vacant land Over Head Tank<br />
2 Udaiyar colony Vacant land Over Head Tank<br />
3 Tiruppur road Vacant land Over Head Tank<br />
4 Agalarapalayam Vacant land Sanitary complex<br />
5 Puthur Vacant land Sanitary complex<br />
6 Uppupalayam Vacant land Sanitary complex<br />
7 Soriankinathupalayam Vacant land Sanitary complex<br />
8 Kumaravalasu Vacant land Sanitary complex<br />
9 MGR nagar Vacant land Sanitary complex<br />
10 Arivoli nagar Vacant land Sanitary complex<br />
11 Karattupalayam Vacant land Sanitary complex<br />
12 Thanner Panthal area Vacant land Sanitary complex<br />
13 Market area Weekly market Slaughter house<br />
14 Booster house Moonoor road - Seva center<br />
15 Natesan Nagar - Seva center<br />
16 Erode road (near bus stand) - Seva center<br />
17 At municipal office Administrative use Seva center<br />
54
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
7.4 MANAGEMENT OPTIONS FOR LAND ASSETS<br />
The foregoing account of the movable and immovable assets of the <strong>Municipal</strong>ity includes basically<br />
lands, parts of which are occupied by construction of structures for various uses. The structural<br />
elements in the form of buildings including OHTs, flow elements relating to essential services such<br />
as water supply, drainage, UGD, street lights and the like are designed with a design life time. The<br />
lands however as a base have no such limiting factor in terms of time. Thus the super structures and<br />
the constructed elements below the ground are depreciating in their values as they age. But the land<br />
assets both constructed and un-constructed keep appreciating in the standard and market values. In<br />
fact, the rate of appreciation of the lands is of great significance from the point of worthiness of the<br />
concerned local body and, it is invariably much faster in its appreciating value compared to the rate<br />
of depreciation of structures imposed on them. Also, the rate of depreciation standardized for<br />
various items of the structures is much more than the actual while taking into consideration the life<br />
time of such structures till the point of their condemnation.<br />
Generally, the assets of the local body, particularly the lands are rarely maintained and their values<br />
in the management of the resources of the local body are little considered. There must be a scientific<br />
approach town wise to evolve a dynamic model of the changing values of the assets both in terms of<br />
appreciation and depreciation from time to time, particularly when sizable developments take place.<br />
It is important to keep in view that as per the objectives of the devolution of functions and powers to<br />
the urban local bodies under the 74 th Constitutional Amendment Act, the value of the lands and<br />
properties are necessarily to be assessed depending on their location, land use and intensity of<br />
development over a time scale. In order to systemize the highly dynamic factor of values of the<br />
properties under local body, it is essential for an efficient management of the total assets owned by<br />
local body.<br />
The suggestions for the improvement of land asset management are listed below:<br />
1. Implementation of Asset Management <strong>Plan</strong><br />
2. Establishment of GIS inventory mapping for <strong>Municipal</strong>ity owned lands.<br />
3. Use of land assets for borrowing loans from capital market.<br />
4. Identifying the most remunerative activity by public–private participation, BOT, BOOT<br />
initiatives.<br />
5. Removal of encroachments on <strong>Municipal</strong> land parcels.<br />
6. Explore possibilities of acquiring additional land parcels for future requirements<br />
7.5 PROPOSED NEW ASSETS<br />
The assets creation by way of the projects proposed under CCCBP for implementation in the years<br />
to come are indicated with the capital investment values as in table below<br />
Table 7.3 New Assets for the year - 2010 to 2015<br />
S.N Physical Infrastructure facilities Amount<br />
( in lakhs)<br />
1 Water Supply 1199.12<br />
2 Sewerage System 3300.00<br />
3 Storm Water Drains 300.00<br />
55
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
4 Solid Waste management 800.00<br />
5 Roads 2043.00<br />
7 Bus Shelter 10.00<br />
8 Street Lights 182.00<br />
9 Slum Improvement 709.00<br />
10 Parks and Play Fields 20.00<br />
11 Market 150.00<br />
12 Public Convenience 35.00<br />
13 Burial Ground 100.00<br />
14 E-Governance 16.00<br />
15 Urban Greenery 10.00<br />
16 Other Projects 100.00<br />
17 Updation of Database on GIS Platform 4000<br />
18 Property Mapping 4.30<br />
Total 9018.42<br />
Source: Analysis and calculation<br />
All these assets are elements that drive the business plan and ensure the timely availability of<br />
resources to sustain the assets in an acceptable condition for better service delivery. In addition to<br />
increasing the revenue potential, it is equally important to manage the assets in terms of their<br />
maintenance and rehabilitation. This would ensure reducing costs, improving reliability, and ensuring<br />
sustainability. Hence it is imperative for the municipality to have a highly simplified approach with a<br />
long-term schedule of delivery of actions and a set of short-term measures.<br />
56
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
8.1 CAPITAL INVESTMENT PLAN<br />
57<br />
8<br />
FINANCIAL OPERATING PLAN<br />
The proposed projects for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity taking in to account its resources and the existing<br />
shortfall in services are given below. The projects have been phased out taking in to account the<br />
time-span required for implementation of the project and the availability of the funds (loans, grants<br />
and municipality’s own resources) for the same.<br />
Table 8.1 Projects to be executed by the <strong>Municipal</strong>ity<br />
S.No. Particulars 2009-10 2010-11 2011-12 2012-13 2013-14 Total<br />
A Physical Infrastructure Facilities<br />
I Water Supply<br />
a) Improvements to Water Supply 1199.12 - - - - 1199.12<br />
II Sewerage & Sanitation<br />
a) New Underground Sewerage Scheme - 1500.00 1800.00 - - 3300.00<br />
III Strom Water Drains<br />
Construction of new drains and<br />
a) providing mesh covers - 60.00 80.00 100.00 60.00 300.00<br />
IV Solid Waste Management<br />
a) Cost of land fill site and compost yard<br />
Land fill site & compost yard<br />
- 250.00 300.00 - - 550.00<br />
b) development<br />
Vehicles & equipment for primary &<br />
- - 200.00 - - 200.00<br />
c) secondary colln 25.00 25.00 - - - 50.00<br />
V Roads<br />
a) Upgradation and Restoration of Roads 90.00 450.00 657.00 336.00 300.00 1833.00<br />
b) Improvements to Road Geometry<br />
Widening of Main Roads and Link<br />
- - 50.00 60.00 - 110.00<br />
c) Roads - 70.00 30.00 - - 100.00<br />
VI Bus Shelter<br />
a) Construction of New Bus Shelter 6.00 4.00 - - - 10.00<br />
VII Street Lights<br />
High mast lights at Old & New Bus<br />
a) Stand 7.00 7.00 - - - 14.00<br />
b) Installation of Street Lights & Fittings 10.00 - 30.00 30.00 30.00 100.00<br />
c) Retrofitting and energy saving devices<br />
Central Median lights at main roads for<br />
- 23.00 - - - 23.00<br />
d) 3Km 40.00 5.00 - - - 45.00<br />
B Social Infrastructure Facilities
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
I Slum Improvements<br />
a) Improvement to Slums - 375.00 150.00 113.00 71.00 709.00<br />
II Parks & Playgrounds<br />
a)<br />
Improvement of parks, construction of<br />
compound wall<br />
for play ground & play equipments<br />
- - - - 20.00 20.00<br />
III Market<br />
a) Construction of Daily Market - 75.00 - - - 75.00<br />
b) Construction of Weekly Market - - 75.00 - - 75.00<br />
IV Burial Ground / Crematorium<br />
a) Burial Ground with Gasifier - 100.00 - - - 100.00<br />
V Public Convenience<br />
a) Improvement to Public Convenience 15.00 15.00 5.00 - - 35.00<br />
C Other Projects<br />
I Remunerative Projects<br />
a)<br />
Commercial Building (G+2) at Erode<br />
Road near<br />
Bus Stand<br />
- 100.00 - - - 100.00<br />
II Urban Greenary<br />
a) <strong>Plan</strong>ting New Trees - - - - 10.00 10.00<br />
III E-Governance<br />
a) E-Governance 8.00 8.00 - - - 16.00<br />
b) Updation of Database on GIS - - - - 40.00 40.00<br />
c) Property Mapping 4.30 - - - - 4.30<br />
Total 1404.42 3067.00 3377.00 639.00 531.00 9018.42<br />
The initial building blocks of the Corporate <strong>Plan</strong> are the ‘elements’ required to sustain the town’s<br />
growth; public utility, urban environment, economic and social development, land use and<br />
transportation, municipal resources, urban governance and capital facilities. The projects in the plan<br />
were developed through a consultative process carried out between the Local Body Officials,<br />
Council Staff and Elected Officials, Public Interest Groups, Project Stakeholders and the local<br />
citizens.<br />
The projects have been prioritized in the following order :<br />
a) Water Supply<br />
b) Sewerage and Sanitation<br />
c) Solid Waste Management<br />
d) Storm Water Drains<br />
e) Urban Service for Poor (Slum Upgradation)<br />
f) Roads, traffic and transportation<br />
g) Street Lighting<br />
58
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
8.2 OTHER PROJECTS AND ON GOING PROJECTS<br />
The details of projects identified to be executed by other departments / agencies and the ongoing<br />
projects that are being executed by the <strong>Municipal</strong>ity are given below :<br />
Table 8.2 Projects to be executed by Other Agencies<br />
S.No Particulars Total Funding By<br />
I Regional Level<br />
a) District Regional <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> 10.00 DTCP<br />
b) Improvement to Odais and Canals - PWD Department<br />
c) Preparation of Integrated Solid Waste<br />
Management Action <strong>Plan</strong><br />
2.00<br />
CMA / TNUIFSL<br />
d) Preparation of Integrated Traffic<br />
Management <strong>Plan</strong><br />
2.00 Erode Corporation<br />
II Town Level<br />
a) Provision and upgradation of Health<br />
- Education Department<br />
Facilities<br />
Dept of Tamilnadu<br />
b) ESCO Studies 2.00 CMA / TNUIFSL,<br />
c)<br />
Awareness creation campaign for NGOs<br />
for - E Governance, UGSS, Water Supply,<br />
Solid Waste Management and Tax<br />
Collection<br />
3.00<br />
Total 19.00<br />
S.N Particulars<br />
1<br />
2<br />
3<br />
4<br />
59<br />
Erode Corporation /<br />
RDMA, Tiruppur<br />
Table 8.3 Projects under Implementation by the <strong>Municipal</strong>ity<br />
Total<br />
Cost<br />
Loan<br />
Grant<br />
Mun<br />
Cont.<br />
Providing Cement Concrete 50.00 25.00 20.00<br />
Road to Bus Stand<br />
Construction of additional first<br />
-<br />
Floor building at <strong>Municipal</strong> 25.00 25.00 -<br />
Office<br />
-<br />
Construction of Modern 25.00 10.00 15.00<br />
Slaughter House<br />
-<br />
85.00 51.00 34.00<br />
Improvement to Bus Stand<br />
-<br />
Total 185.00 0.00 111.00 74.00<br />
Funding By<br />
SFC Infrastructure<br />
Gap Filling Fund (2007-08)<br />
SFC Infrastructure<br />
Gap Filling Fund (2007-08)<br />
SFC Infrastructure<br />
Gap Filling Fund (2007-08)<br />
SFC Infrastructure<br />
Gap Filling Fund (2008-09)
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
8.3 MEANS OF FINANCE<br />
The means of finance for each individual project identified taking in to account whether the same is<br />
remunerative or non-remunerative and the availability of Grants from various sources is given below<br />
Table 8.4 Multi Year Investment <strong>Plan</strong> and Means of Finance<br />
Multi Year Investment <strong>Plan</strong><br />
S.No. Particulars 2009-10 2010-11 2011-12 2012-13 2013-14 Total<br />
A Physical Infrastructure Facilities<br />
1 Water Supply<br />
Total Project Cost 1199.12 - - - - 1199.12<br />
Add : Price Inflation @ 7% 83.94 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 83.94<br />
Total 1283.06 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 1283.06<br />
Means of Finance<br />
TNUIFSL Loan 320.76 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 320.76<br />
Grant 910.97 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 910.97<br />
<strong>Municipal</strong>ity Own Funds 51.32 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 51.32<br />
Total 1283.06 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 1283.06<br />
2 Sewerage<br />
Total Project Cost - 1500.00 1800.00 - - 3300.00<br />
Add : Price Inflation @ 7% 0.00 217.35 405.08 0.00 0.00 622.43<br />
Total 0.00 1717.35 2205.08 0.00 0.00 3922.43<br />
Means of Finance<br />
TNUIFSL Loan 0.00 635.42 815.88 0.00 0.00 1451.30<br />
Grant 0.00 601.07 771.78 0.00 0.00 1372.85<br />
<strong>Municipal</strong>ity Own Funds 0.00 480.86 617.42 0.00 0.00 1098.28<br />
Total 0.00 1717.35 2205.08 0.00 0.00 3922.43<br />
3 Storm Water Drains<br />
Total Project Cost - 60.00 80.00 100.00 60.00 300.00<br />
Add : Price Inflation @ 7% 0.00 8.69 18.00 31.08 24.15 81.93<br />
Total 0.00 68.69 98.00 131.08 84.15 381.93<br />
Means of Finance<br />
Grant 0.00 61.82 88.20 117.97 75.74 343.74<br />
<strong>Municipal</strong>ity Own Funds 0.00 6.87 9.80 13.11 8.42 38.19<br />
Total 0.00 68.69 98.00 131.08 84.15 381.93<br />
4A SWM - Cost of land fill site<br />
Total Project Cost - 250.00 300.00 - - 550.00<br />
Add : Price Inflation @ 7% 0.00 36.23 67.51 0.00 0.00 103.74<br />
Total 0.00 286.23 367.51 0.00 0.00 653.74<br />
Means of Finance<br />
Grant 0.00 286.23 367.51 0.00 0.00 653.74<br />
Total 0.00 286.23 367.51 0.00 0.00 653.74<br />
60
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
4B<br />
SWM - Land fill site & compost yard<br />
devt<br />
Total Project Cost - - 200.00 - - 200.00<br />
Add : Price Inflation @ 7% 0.00 0.00 45.01 0.00 0.00 45.01<br />
Total<br />
Means of Finance<br />
0.00 0.00 245.01 0.00 0.00 245.01<br />
<strong>Municipal</strong>ity Own Funds 0.00 0.00 245.01 0.00 0.00 245.01<br />
Total 0.00 0.00 245.01 0.00 0.00 245.01<br />
4C SWM - Vehicles & Equipments<br />
Total Project Cost 25.00 25.00 - - - 50.00<br />
Add : Price Inflation @ 7% 1.75 3.62 0.00 0.00 0.00 5.37<br />
Total<br />
Means of Finance<br />
26.75 28.62 0.00 0.00 0.00 55.37<br />
Grant 13.38 14.31 0.00 0.00 0.00 27.69<br />
<strong>Municipal</strong>ity Own Funds 13.38 14.31 0.00 0.00 0.00 27.69<br />
Total 26.75 28.62 0.00 0.00 0.00 55.37<br />
5A Roads - Upgradation & Restoration<br />
Total Project Cost 90.00 450.00 657.00 336.00 300.00 1833.00<br />
Add : Price Inflation @ 7% 6.30 65.21 147.85 104.43 120.77 444.55<br />
Total<br />
Means of Finance<br />
96.30 515.21 804.85 440.43 420.77 2277.55<br />
Grant 86.67 463.68 724.37 396.38 378.69 2049.80<br />
<strong>Municipal</strong>ity Own Funds 9.63 51.52 80.49 44.04 42.08 227.76<br />
Total 96.30 515.21 804.85 440.43 420.77 2277.55<br />
5B<br />
Roads - Improvements to Road<br />
Geometry<br />
Total Project Cost - - 50.00 60.00 - 110.00<br />
Add : Price Inflation @ 7% 0.00 0.00 11.25 18.65 0.00 29.90<br />
Total<br />
Means of Finance<br />
0.00 0.00 61.25 78.65 0.00 139.90<br />
Grant 0.00 0.00 55.13 70.78 0.00 125.91<br />
<strong>Municipal</strong>ity Own Funds 0.00 0.00 6.13 7.86 0.00 13.99<br />
Total 0.00 0.00 61.25 78.65 0.00 139.90<br />
5C Roads - Widening<br />
Total Project Cost - 70.00 30.00 - - 100.00<br />
Add : Price Inflation @ 7% 0.00 10.14 6.75 0.00 0.00 16.89<br />
Total<br />
Means of Finance<br />
0.00 80.14 36.75 0.00 0.00 116.89<br />
Grant 0.00 72.13 33.08 0.00 0.00 105.20<br />
<strong>Municipal</strong>ity Own Funds 0.00 8.01 3.68 0.00 0.00 11.69<br />
Total 0.00 80.14 36.75 0.00 0.00 116.89<br />
61
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
6 Bus Shelter<br />
Total Project Cost 6.00 4.00 - - - 10.00<br />
Add : Price Inflation @ 7% 0.42 0.58 0.00 0.00 0.00 1.00<br />
Total<br />
Means of Finance<br />
6.42 4.58 0.00 0.00 0.00 11.00<br />
Grant 6.42 4.58 0.00 0.00 0.00 11.00<br />
Total 6.42 4.58 0.00 0.00 0.00 11.00<br />
7A Street Lights - High Mast Lights<br />
Total Project Cost 7.00 7.00 - - - 14.00<br />
Add : Price Inflation @ 7% 0.49 1.01 0.00 0.00 0.00 1.50<br />
Total<br />
Means of Finance<br />
7.49 8.01 0.00 0.00 0.00 15.50<br />
Grant 7.49 8.01 0.00 0.00 0.00 15.50<br />
Total 7.49 8.01 0.00 0.00 0.00 15.50<br />
7B Street Lights - Street Lights & Fittings<br />
Total Project Cost 10.00 - 30.00 30.00 30.00 100.00<br />
Add : Price Inflation @ 7% 0.70 0.00 6.75 9.32 12.08 28.85<br />
Total<br />
Means of Finance<br />
10.70 0.00 36.75 39.32 42.08 128.85<br />
Grant 5.35 0.00 18.38 19.66 21.04 64.43<br />
Municiplaity Own Funds 5.35 0.00 18.38 19.66 21.04 64.43<br />
Total 10.70 0.00 36.75 39.32 42.08 128.85<br />
7C Street Lights - Retrofitting of Lights<br />
Total Project Cost - 23.00 - - - 23.00<br />
Add : Price Inflation @ 7% 0.00 3.33 0.00 0.00 0.00 3.33<br />
Total 0.00 26.33 0.00 0.00 0.00 26.33<br />
Means of Finance<br />
ESCO 0.00 26.33 0.00 0.00 0.00 26.33<br />
Total 0.00 26.33 0.00 0.00 0.00 26.33<br />
7D Street Lights - Central Median Lights<br />
Total Project Cost 40.00 5.00 - - - 45.00<br />
Add : Price Inflation @ 7% 2.80 0.72 0.00 0.00 0.00 3.52<br />
Total 42.80 5.72 0.00 0.00 0.00 48.52<br />
Means of Finance<br />
Grant 38.52 5.15 0.00 0.00 0.00 43.67<br />
Municiplaity Own Funds 4.28 0.57 0.00 0.00 0.00 4.85<br />
Total 42.80 5.72 0.00 0.00 0.00 48.52<br />
B Social Infrastructure Facilities<br />
1 Slum Improvements<br />
Total Project Cost - 375.00 150.00 113.00 71.00 709.00<br />
Add : Price Inflation @ 7% 0.00 54.34 33.76 35.12 28.58 151.80<br />
62
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
Total<br />
Means of Finance<br />
0.00 429.34 183.76 148.12 99.58 860.80<br />
Grant 0.00 429.34 183.76 148.12 99.58 860.80<br />
Total 0.00 429.34 183.76 148.12 99.58 860.80<br />
2 Parks & Playgrounds<br />
Total Project Cost - - - - 20.00 20.00<br />
Add : Price Inflation @ 7% 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 8.05 8.05<br />
Total 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 28.05 28.05<br />
Means of Finance<br />
Grant 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 19.64 19.64<br />
<strong>Municipal</strong>ity Own Funds 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 8.42 8.42<br />
Total 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 28.05 28.05<br />
3A Market - Daily Market<br />
Total Project Cost - 75.00 - - - 75.00<br />
Add : Price Inflation @ 7% 0.00 10.87 0.00 0.00 0.00 10.87<br />
Total 0.00 85.87 0.00 0.00 0.00 85.87<br />
Means of Finance<br />
<strong>Municipal</strong>ity Own Funds 0.00 85.87 0.00 0.00 0.00 85.87<br />
Total 0.00 85.87 0.00 0.00 0.00 85.87<br />
3B Market - Weekly Market<br />
Total Project Cost - - 75.00 - - 75.00<br />
Add : Price Inflation @ 7% 0.00 0.00 16.88 0.00 0.00 16.88<br />
Total 0.00 0.00 91.88 0.00 0.00 91.88<br />
Means of Finance<br />
<strong>Municipal</strong>ity Own Funds 0.00 0.00 91.88 0.00 0.00 91.88<br />
Total 0.00 0.00 91.88 0.00 0.00 91.88<br />
4 Burial Ground with Gasifier<br />
Total Project Cost - 100.00 - - - 100.00<br />
Add : Price Inflation @ 7% 0.00 14.49 0.00 0.00 0.00 14.49<br />
Total 0.00 114.49 0.00 0.00 0.00 114.49<br />
Means of Finance<br />
Grant 0.00 57.25 0.00 0.00 0.00 57.25<br />
<strong>Municipal</strong>ity Own Funds 0.00 57.25 0.00 0.00 0.00 57.25<br />
Total 0.00 114.49 0.00 0.00 0.00 114.49<br />
5 Public Convenience<br />
Total Project Cost 15.00 15.00 5.00 - - 35.00<br />
Add : Price Inflation @ 7% 1.05 2.17 1.13 0.00 0.00 4.35<br />
Total 16.05 17.17 6.13 0.00 0.00 39.35<br />
Means of Finance<br />
Grant 8.03 8.59 3.06 0.00 0.00 19.67<br />
<strong>Municipal</strong>ity Own Funds 8.03 8.59 3.06 0.00 0.00 19.67<br />
63
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
Total 16.05 17.17 6.13 0.00 0.00 39.35<br />
C Other Projects<br />
1 Commercial Building<br />
Total Project Cost - 100.00 - - - 100.00<br />
Add : Price Inflation @ 7% 0.00 14.49 0.00 0.00 0.00 14.49<br />
Total 0.00 114.49 0.00 0.00 0.00 114.49<br />
Means of Finance<br />
Loan 0.00 103.04 0.00 0.00 0.00 103.04<br />
<strong>Municipal</strong>ity Own Funds 0.00 11.45 0.00 0.00 0.00 11.45<br />
Total 0.00 114.49 0.00 0.00 0.00 114.49<br />
2 Urban Greenary<br />
Total Project Cost - - - - 10.00 10.00<br />
Add : Price Inflation @ 7% 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 4.03 4.03<br />
Total 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 14.03 14.03<br />
Means of Finance<br />
Grant 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 14.03 14.03<br />
Total 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 14.03 14.03<br />
3A E-Governance<br />
Total Project Cost 8.00 8.00 - - - 16.00<br />
Add : Price Inflation @ 7% 0.56 1.16 0.00 0.00 0.00 1.72<br />
Total 8.56 9.16 0.00 0.00 0.00 17.72<br />
Means of Finance<br />
Grant 8.56 9.16 0.00 0.00 0.00 17.72<br />
Total 8.56 9.16 0.00 0.00 0.00 17.72<br />
3B GIS Mapping<br />
Total Project Cost - - - - 40.00 40.00<br />
Add : Price Inflation @ 7% 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 16.10 16.10<br />
Total 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 56.10 56.10<br />
Means of Finance<br />
Grant 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 50.49 50.49<br />
<strong>Municipal</strong>ity Own Funds 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 5.61 5.61<br />
Total 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 56.10 56.10<br />
3C Property Mapping<br />
Total Project Cost 4.30 - - - - 4.30<br />
Add : Price Inflation @ 7% 0.30 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.30<br />
Total 4.60 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 4.60<br />
Means of Finance<br />
<strong>Municipal</strong>ity Own Funds 4.60 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 4.60<br />
Total 4.60 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 4.60<br />
The consolidated ‘Means of Finance’ for all the projects put-together is summarized below :<br />
64
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
S.No. Particulars<br />
Table8.5 Consolidated Means of Finance<br />
Multi Year Investment <strong>Plan</strong><br />
2009-10 2010-11 2011-12 2012-13 2013-14 Total<br />
I Project Cost<br />
Total Project Cost 1404.42 3067.00 3377.00 639.00 531.00 9018.42<br />
Add : Price Inflation @ 7% 98.31 444.41 759.97 198.60 213.75 1715.04<br />
Total 1502.73 3511.41 4136.97 837.60 744.75 10733.46<br />
II Means of Finance<br />
<strong>Municipal</strong>ity Own Funds<br />
(including Deposits from Public)<br />
96.58 725.29 1075.83 84.68 85.56 2067.94<br />
Grant 1085.38 2021.32 2245.26 752.92 659.20 6764.08<br />
TNUIFSL Loan 320.76 738.46 815.88 0.00 0.00 1875.10<br />
BOOT / Private Sector 0.00 26.33 0.00 0.00 0.00 26.33<br />
Total 1502.73 3511.41 4136.97 837.60 744.75 10733.46<br />
8.4 FINANCIAL SUSTAINABILITY<br />
The sustainability analysis assumes that the <strong>Municipal</strong>ity will carry out reforms indicated as<br />
assumptions for financial projections. A Financial and Operating <strong>Plan</strong> (FOP) prepared which<br />
evaluates the <strong>Municipal</strong>ity Fund status for the Full Project scenario.<br />
The FOP is a cash flow stream of the ULB based on the regular <strong>Municipal</strong>ity revenues, expenditures<br />
and applicability of surplus funds to support project sustainability. The FOP horizon is determined to<br />
assess the impact of full debt servicing liability resulting from the borrowings to meet the identified<br />
interventions. The proposed capital investments are phased over 5 years investment from FY 2009-<br />
10 to FY 2013-14.<br />
The full project investment scenario is based on all the proposed investments identified for Vellakoil<br />
<strong>Municipal</strong>ity and the requirement for upgrading the town’s infrastructure is estimated and phased<br />
based on the construction activity. Implications of this investment in terms of external borrowings<br />
required, resultant debt service commitment and additional operation and maintenance expenditure<br />
are worked out to ascertain sub-project cash flows. Revenue surpluses of the existing operations are<br />
applied to the sub-project cash flows emerging from full project investments – the <strong>Municipal</strong>ity fund<br />
net surpluses indicates the ULB’s ability to sustain full investments.<br />
FY 2009-10 is taken as the base year and FY 2028-29 is assumed as the reference year (20 years)<br />
to determine the net surpluses and whether the <strong>Municipal</strong>ity maintains a debt / revenue surplus ratio<br />
as an indication of the ULB’s ability to sustain investments.<br />
8.5 BASIC ASSUMPTIONS FOR PROJECTIONS :<br />
The FOP is based on a whole range of assumptions related to income and expenditure. These are<br />
critical to ascertain the investment sustenance and would also provide a tool to test certain specific<br />
policy decisions regarding revenue and expenditure drivers on the overall <strong>Municipal</strong>ity fiscal<br />
situation. This section elucidated the key assumptions adopted for the FOP scenario.<br />
65
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
The growth rates for the various heads of income and expenditure have been arrived based on the<br />
past growth rates and the future estimated population growth. Improvements to the existing current<br />
and arrears collection percentages have been assumed for the various revenues directly collected<br />
by the <strong>Municipal</strong>ity, which implies that the <strong>Municipal</strong>ity would have to improve its collection<br />
mechanism to sustain full investments.<br />
Given below are the various assumptions forming part of the FOP workings :<br />
8.5.1 INCOME<br />
a) Property Tax<br />
The population of Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity is estimated to grow at around 2.5% p.a. Based on the same<br />
Property Tax Revenue are assumed to increase @ 2.5% per annum. The last revision of Property<br />
Tax was carried out on 1-10-98 and it is assumed that the next revision will be carried out in the<br />
current year. It is assumed that there will be an increase of 25% due to revision in 2008-09 & that<br />
revision would be done @ 15% every 5 years.<br />
It has also been established as per the Survey in 2002 that around 27% of the properties are<br />
unassessed and further 20-25% of the properties are unassessed. Considering the above, it is<br />
assumed that the same shall be set right and together these shall contribute to increase in property<br />
tax revenue by 20% from next year viz. 2009-10, after completion of GIS mapping.<br />
The Property Tax income is divided between Revenue, Water Supply and Education Fund in the<br />
following ratio:<br />
Table: 8.6 Ratio of Property tax<br />
Description Per Annum<br />
General 4.000%<br />
Scavanging 2.000% Revenue & Capital Fund<br />
Lighting 1.000%<br />
Water Tax 2.000% Water Supply & Drainage Fund<br />
Drainage 1.000%<br />
Education - Education Fund<br />
Total 10.000%<br />
b) Profession tax<br />
Income from Profession Tax is assumed to increase @ 5% per annum. The Profession Tax was last<br />
revised on 1.10.2003 and the next revision is due in 2008-09. It is assumed that every revision<br />
would contribute to 15% increase<br />
Besides, the profession tax base would be increased by carrying out survey in 2010-11. It is<br />
assumed that the survey would increase the profession tax base by 20% in 2010-11.<br />
c) Assigned revenue<br />
Assigned Revenue comprises Entertainment Tax and Surcharge on Stamp Duty. It is assumed the<br />
same shall increase as under :<br />
Duty on Transfer of Property : 5%<br />
Entertainment Tax : 1%<br />
66
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
d) Devolution Fund<br />
Devolution Fund is also assumed to increase by 7.5% per annum<br />
e) Service charges and fees<br />
Service Charges and Fees are assumed to increase @ 5% per annum<br />
f) Grant and Contribution<br />
No Grant has been assumed in the financial projections.<br />
g) Sales and Hire charges<br />
Nil income assumed from Sales & Hire Charges.<br />
h) Other Income<br />
Other Income comprising basically fees and other rental income are assumed to increase @ 5% per<br />
annum.<br />
i) Water Supply Charges<br />
The present connection charges/deposit and tariff for water are as below :<br />
Table 8.7 Water supply Charges - Existing<br />
Type of service connections Connection Tariff<br />
Residential Rs .3000 Rs.65.00 Per month<br />
Commercial Rs. 6000 Rs.115.00 per month<br />
Industrial Rs .6000 Rs.105.00 per month<br />
It is assumed that after completion of water supply improvements work, the house service<br />
connections will be equal to 80% of property tax assessments.<br />
The water charges shall be revised as below :<br />
Residential - Rs.75.00 p.m<br />
Commercial – Rs.150.00 p.m<br />
Industrial - Rs. 150.00 p.m.<br />
It is also assumed that the water connection charges shall be revised as under :<br />
Residential - Rs.5000<br />
Commercial - Rs.10000<br />
Industrial - Rs.10000<br />
It is assumed that water charges shall be increased as below every 5 years :<br />
Residential - Rs.15.00 p.m<br />
Commercial & industrial – Rs.25.00 p.m<br />
67
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
It is assumed that water connection charges shall increase every 5 years as below :<br />
Residential - Rs.1000<br />
Commercial & industrial – Rs.2000<br />
The house service connection as % of property tax assessments is as below:<br />
Table 8.8 House Service Connections - Percentage<br />
Year 2004-05 Property tax assessments HSCs %<br />
Residential 11236 3910 35%<br />
Commercial 1047 45 2%<br />
Industrial & Govt. 1649 57 3%<br />
The improvements in water supply shall result in increase in operation & maintenance by Rs.35.00<br />
lakhs per annum and the same shall increase @ 5% per annum.<br />
j) Drainage Charges<br />
The <strong>Municipal</strong>ity does not have Under Ground Sewerage System. A new underground sewerage<br />
system is proposed to be built at a cost of Rs. 3300 lakhs. The implementation period is 2 years<br />
starting from 2010-11 to 2011-12. On completion of the scheme, it is assumed that around 70% of<br />
the property tax assessments would have sewerage connection. It is assumed that the scheme shall<br />
be completed as below :<br />
2010-11 60%<br />
2011-12 40%<br />
The Deposits and Charges shall be collected accordingly.<br />
It is assumed that the sewerage charges will be collected as below :<br />
Table 8.9 Sewage Charges<br />
%<br />
Tariff per<br />
Domestic Connections Connection month<br />
< 500 Sq.ft. 34% Rs.5000 Rs.70<br />
500 -1200 Sq.ft. 31% Rs.7000 Rs.100<br />
1200-2400 Sq.ft. 23% Rs.9000 Rs.150<br />
Above 2400 Sq.ft. 12% Rs.15000 Rs.200<br />
Special - Rs.18000 Rs.250<br />
Non Domestic Connection Tariff<br />
< 500 Sq.ft. 35% Rs.10000 Rs.140<br />
500 -1200 Sq.ft. 28% Rs.21000 Rs.300<br />
1200-2400 Sq.ft. 20% Rs.27000 Rs.450<br />
Above 2400 Sq.ft. 17% Rs.75000 Rs.1000<br />
Special - Rs.90000 Rs.1250<br />
68
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
It is assumed that the Domestic & Non Domestic drainage charges shall be increased every 5 years<br />
as below :<br />
Table 8.10 Increase in Tariff - Sewage Charges<br />
Domestic Non Domestic<br />
< 500 Sq.ft. Rs.15 Rs.20<br />
500 - 1200 Sq.ft. Rs.20 Rs.30<br />
1200 - 1400 Sq.ft. Rs.25 Rs.45<br />
Above 2400 Sq.ft. Rs.50 Rs.75<br />
It is assumed that the Domestic & Non Domestic connection charges shall be increased every 5<br />
years as below :<br />
Table 8.11 Increase in Deposit - Sewage Charges<br />
Domestic Non Domestic<br />
Up to 500 Sq.ft. Rs.1000 Rs.2000<br />
500 - 1200 Sq.ft. Rs.1500 Rs.4000<br />
1200 - 2400 Sq.ft. Rs.2000 Rs.5000<br />
Above 2400 Sq.ft. Rs.3000 Rs.10000<br />
The O&M charges shall be Rs. 99.00 lakhs per annum and the same shall increase @ 5% per<br />
annum.<br />
k) Solid waste Management<br />
It has been estimated that solid waste generation per day shall be around 14 MTs. 1/3 rd out of the<br />
same shall comprise Bio-degradable waste and the manure generation would be 1/3 rd of the same.<br />
Thus the estimated saleable manure generation per day would be 1.56 MTs. The same shall<br />
increase @ 5% per annum.<br />
The revenue from solid waste disposal shall be Rs.1000.00 per MT. The same shall increase by<br />
Rs.100.00 every 5 years. The number of assets covered by solid waste management scheme shall<br />
be equal to 70% of property tax assessments. The conservancy fees collected shall be as below to<br />
be collected after 10 years :<br />
Domestic - Rs.10.00 per month<br />
Commercial - Rs.20.00 per month<br />
Industrial/Government - Rs.30.00 per month<br />
The same shall increase as below every 5 years ;<br />
Domestic - Rs.5.00/-<br />
Commercial/ Industrial/Government - Rs.10.00/-<br />
69
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
The cost of the scheme is Rs. 800 lakhs and the O&M cost shall be equal to around Rs. 12.50 lacs<br />
per annum. The same shall increase @ 5% per annum.<br />
l) Commercial Buildings<br />
Commercial Buildings shall be constructed at 1 place and the rent collection and deposit<br />
mobilization from the same shall be as below :<br />
Rent Deposit<br />
Erode Road Rs. 100000 p.m. Rs. 2500000<br />
The rent shall increase @ of 15% every 3 years.<br />
Rental holiday of 2 years shall be provided against rental deposit collected.<br />
The operation & maintenance of the commercial building is estimated at Rs. 3 lacs per annum and<br />
the same shall increase @ 5% per annum.<br />
m) Bus Stand<br />
The income from Bus Stand shall increase by 15% on completion of ongoing improvements.<br />
n) Markets<br />
It is estimated that Daily Market shall fetch rental income of Rs. 15 lacs per annum. The Weekly<br />
Market / shandy shall fetch rental income of Rs. 10 lacs per annum. The rental income shall<br />
increase @ 15% every 3 years.<br />
The additional operation & maintenance of markets is estimated at Rs. 3 lacs per annum and the<br />
same shall increase @ 5% per annum.<br />
o) Slaughter House & Gasifier Crematorium<br />
The Slaughter House shall be let out on lease @ Rs. 1.5 lacs per annum.<br />
The Gasifier Crematorium shall result in income of Rs. 1.5 lacs per annum.<br />
The O&M charges of Slaughter House shall be Rs. 0.75 lacs per annum.<br />
The O&M charges of Burial Ground shall be Rs. 1 lac per annum.<br />
The income shall increase @ 15% every 3 years and the expenditure shall increase @ 5% per<br />
annum.<br />
p) Advertisements<br />
Bill Boards would be put at 20 places through out the <strong>Municipal</strong>ity. Rent shall be earned @<br />
Rs.500.00 per Bill board per month. The rent shall increase @ Rs. 100/- every 3 years.<br />
q) Parking Rent<br />
The income from parking shall be Rs. 1 lac per annum. The same shall increase @ 15% every 3<br />
years.<br />
70
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
8.5.2 EXPENDITURE<br />
a) Increase in Expenditure<br />
The expenses are assumed to increase as under :<br />
Table 8.12 Assumptions - Increase in Expenditure<br />
Personnel Cost – Salaries 7.50%<br />
Personnel Cost – Others 5.00%<br />
Terminal & Retirement Benefits 5.00%<br />
Operative Expenses 7.50%<br />
Repairs & Maintenance 5.00%<br />
Program Expenses 2.50%<br />
Administrative Expenses 7.50%<br />
b) Operation and Maintenance<br />
The additional operation & maintenance expenses to be incurred are as below:<br />
Table 8.13 Assumptions – O&M<br />
Ongoing Projects Rs. in lakhs<br />
Various Projects 5.55<br />
New Projects (other than Sewerage & Water supply) Rs. in lakhs<br />
Strom Water Drains 4.50<br />
Solid Waste Management 12.50<br />
Roads 22.00<br />
Street Lights 5.00<br />
Slum Improvement 15.00<br />
Parks & Playfields 0.40<br />
Market 3.00<br />
Public Convenience 0.50<br />
Slaughter House 1.00<br />
Burial Ground 0.50<br />
E-Governance 0.10<br />
Urban Greenary 0.10<br />
Commercial Buildings 3.00<br />
Updation of Database on GIS 1.00<br />
Property Mapping 0.15<br />
Total 74.30<br />
The same shall increase @ 5% per annum.<br />
c) Power charges<br />
There will be a savings of around 40% in power charges due to installation of energy saving lights.<br />
As the same will be installed by private players, the savings in power charges have not been<br />
factored in the financial projections for the first 15 years. It is assumed that the savings in power<br />
charges would be utilised towards returns of the private player towards capital cost and interest.<br />
71
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
d) Interest<br />
Interest on loan have been provided based on the sanction rate for each loan. Repayment of loans<br />
are based on the repayment schedule of each loan.<br />
Sewerage & Water Supply Loan<br />
It is assumed that all new loan shall carry interest rate of 9.5% per annum.<br />
The loan from TNUIFSL shall be repaid over a period of 20 years with 5 years moratorium.<br />
Other Projects Loan<br />
It is assumed that all new loan shall carry interest rate of 9.5% per annum.<br />
The loan from TNUIFSL shall be repaid over a period of 10 years with 2 years moratorium.<br />
e) Depreciation<br />
Depreciation is provided based on the rates adopted by the <strong>Municipal</strong>ity for previous years.<br />
f) Provision of doubtful debts<br />
Doubtful debts have been provided as under :<br />
Table 8.14 Assumptions – Provision of doubtful debts<br />
Provision for Doubtful Debts is assumed @ 2% on total revenue for Revenue Fund<br />
8.5.3 Collections<br />
a) Property tax<br />
Table 8.15 Assumptions – Property tax collection<br />
The current property tax collection is 97% The same shall improve to 97%<br />
The arrears property tax collection is 21% The same shall improve to 50%<br />
b) Profession tax<br />
Table 8.16 Assumptions – Profession tax<br />
The current profession tax collection is 89% The same shall improve to 100%<br />
The arrears profession tax collection is 100% The same shall improve to 100%<br />
c) Other Non Tax Income<br />
Table 8.17 Assumptions – Other Non Tax Income<br />
The current rental / lease collection is 99% The same shall be 100%<br />
The arrears collection % of rent / lease 30% The same shall improve to 60%<br />
d) Water Charges<br />
Table 8.18 Assumptions – Water Charges<br />
The current water charges collection is 99% The same shall improve to 85%<br />
The arrears water charges collection is 56% The same shall improve to 60%<br />
72
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
e) Drainage Charges<br />
Table 8.19 Assumptions – Drainage Charges<br />
The current drainage collection is Nil The same shall be 80%<br />
The arrears drainage collection is Nil The same shall be 60%<br />
f) Other income<br />
The collection % of all other income is taken at 100%<br />
h) Others<br />
The collection % of all other items of income is taken at 100%<br />
8.5.4 Annuity Factor<br />
The Annuity Factor for the new loans works out as under :<br />
Table 8.20 Terms of Loan Funding for Proposed Investments<br />
Tenor 20 years 10 years<br />
Interest Rate 9.50% 9.50<br />
Repayment Period 15 years 8 years<br />
Moratorium 5 years 2 years<br />
Repayment Factor 0.13 0.18<br />
Conversion Factor Calculation<br />
a. Rate of Interest 9.5% 9.5%<br />
b. Repayment Period 15 8<br />
c. Loan Amount 17.00 1.00<br />
Conversion Factor 2.17 0.18<br />
Total Conversion Factor 2.36<br />
Note : Sewerage and Water Supply Loan works out to 17% of total project cost identified. Other<br />
Loans works out to 1% of total project cost identified.<br />
8.6 PROJECT CASH FLOWS AND FOP RESULTS :<br />
Detailed cash flows are worked out for each of the sub projects based on the assumptions with<br />
regards investment phasing, financing pattern, additional operation and maintenance expenditure<br />
and additional income out to proposed capital investments for the full project scenario. The net<br />
project cash flows are then loaded on the existing revenues to test their impact on the overall<br />
<strong>Municipal</strong>ity fiscal situation.<br />
a) Income and Expenditure projections<br />
Table 8.21 captures the Income and Expenditure projections for the next 20 years with potential<br />
improvements and borrowings :<br />
73
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
Table 8.21Consolidated Income & Expenditure for next 20 years (up to FY 2028-29)<br />
S.No Particulars 2007-08 2008-09 2009-10 2010-11 2011-12 2012-13 2013-14 2014-15 2015-16 2016-17 2017-18<br />
I Income<br />
a) Property Tax 45.43 54.11 62.79 64.36 65.97 67.62 76.07 77.97 79.92 81.92 83.97<br />
b) Other Taxes 10.88 6.26 6.57 7.88 8.28 8.69 9.99 10.49 11.02 11.57 12.15<br />
c) Assigned Revenue 25.74 26.99 28.31 29.69 31.14 32.66 34.26 35.94 37.70 39.55 41.49<br />
d) Devolution Fund 108.14 90.00 96.75 104.01 111.81 120.19 129.21 138.90 149.31 160.51 172.55<br />
e) Service Charges & Fees 46.33 42.68 44.44 143.61 166.83 430.83 441.92 453.30 497.30 510.10 568.45<br />
f) Grants & Contribution 1.05 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00<br />
g) Sale & Hire Charges 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00<br />
h) Other Income 54.36 32.52 37.84 39.55 47.94 73.23 75.16 93.45 97.73 99.95 125.42<br />
Total Income 291.93 252.56 276.70 389.10 431.96 733.23 766.61 810.06 872.98 903.59 1004.02<br />
II Expenditure<br />
a) Personnel Salaries Cost 48.53 52.17 56.08 60.29 64.81 65.62 70.54 75.83 81.51 87.63 94.20<br />
b) Personnel Cost - Others 1.39 1.49 1.61 1.73 1.86 2.00 2.15 2.31 2.48 2.66 2.86<br />
b) Terminal & Ret Benefits 3.64 3.82 4.01 4.21 4.42 4.65 4.88 5.12 5.38 5.65 5.93<br />
c) Operating Expenses 58.48 68.42 103.61 184.70 195.75 306.49 323.91 342.37 361.91 382.61 404.55<br />
d) Repairs & Maintenance 70.74 74.28 77.99 81.89 85.98 90.28 94.80 99.54 104.52 109.74 115.23<br />
e) Program Expenses 0.31 2.50 2.56 2.63 2.69 2.76 2.83 2.90 2.97 3.05 3.12<br />
f) Administration Expenses 10.41 11.24 12.09 12.99 13.97 15.02 16.14 17.35 18.66 20.05 21.56<br />
g) Finance Expenses 13.40 32.90 57.70 126.88 202.88 205.93 203.02 199.29 192.93 181.32 168.53<br />
h) Depreciation 122.76 118.52 142.15 347.12 685.99 854.96 842.92 713.66 526.00 406.18 328.15<br />
Total Expenditure 329.66 365.35 457.80 822.44 1258.36 1547.70 1561.18 1458.36 1296.35 1198.90 1144.14<br />
Surplus / (Deficit) (37.73) (112.79) (181.11) (433.34) (826.40) (814.47) (794.57) (648.30) (423.36) (295.31) (140.12)<br />
Profit before Depreciation 85.03 5.73 -38.95 -86.22 -140.41 40.49 48.35 65.35 102.63 110.88 188.04<br />
74
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
S.No Particulars 2018-19 2019-20 2020-21 2021-22 2022-23 2023-24 2024-25 2025-26 2026-27 2027-28 2028-29<br />
I Income<br />
a) Property Tax 94.66 97.02 99.45 101.94 104.49 118.00 120.95 123.97 127.07 130.25 147.35<br />
b) Other Taxes 13.97 14.67 15.40 16.17 16.98 19.53 20.50 21.53 22.61 23.74 27.30<br />
c) Assigned Revenue 43.52 45.66 47.91 50.27 52.74 55.34 58.07 60.93 63.94 67.09 70.41<br />
d) Devolution Fund 185.49 199.40 214.36 230.44 247.72 266.30 286.27 307.74 330.82 355.63 382.31<br />
e) Service Charges & Fees 583.06 598.07 650.02 666.74 735.05 753.95 773.34 834.60 856.07 935.97 960.03<br />
f) Grants & Contribution 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00<br />
g) Sale & Hire Charges 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00<br />
h) Other Income 130.78 133.81 142.63 148.73 164.91 175.36 182.66 186.96 198.92 221.76 227.04<br />
Total Income 1051.49 1088.64 1169.77 1214.28 1321.89 1388.48 1441.79 1535.74 1599.43 1734.44 1814.43<br />
II Expenditure<br />
a) Personnel Salaries Cost 101.26 108.86 117.02 125.80 135.24 145.38 156.28 168.00 180.60 194.15 208.71<br />
b) Personnel Cost - Others 3.08 3.31 3.56 3.83 4.11 4.42 4.75 5.11 5.49 5.90 6.35<br />
b) Terminal & Ret Benefits 6.23 6.54 6.86 7.21 7.57 7.95 8.34 8.76 9.20 9.66 10.14<br />
c) Operating Expenses 427.79 452.42 478.52 506.19 535.52 566.62 586.56 620.56 656.62 694.85 735.40<br />
d) Repairs & Maintenance 120.99 127.04 133.39 140.06 147.06 154.42 162.14 170.24 178.76 187.69 197.08<br />
e) Program Expenses 3.20 3.28 3.36 3.45 3.53 3.62 3.71 3.80 3.90 4.00 4.10<br />
f) Administration Expenses 23.18 24.91 26.78 28.79 30.95 33.27 35.77 38.45 41.33 44.43 47.76<br />
g) Finance Expenses 155.88 144.22 134.05 123.76 114.74 104.89 94.79 85.50 75.61 67.15 57.59<br />
h) Depreciation 276.04 240.17 214.59 195.62 180.99 169.26 159.52 151.19 143.89 137.35 131.41<br />
Total Expenditure 1117.65 1110.74 1118.13 1134.70 1159.71 1189.83 1211.87 1251.63 1295.39 1345.18 1398.53<br />
Surplus / (Deficit) (66.16) (22.11) 51.64 79.58 162.19 198.65 229.92 284.11 304.03 389.26 415.90<br />
Profit before Depreciation 209.89 218.06 266.22 275.20 343.17 367.91 389.45 435.30 447.92 526.62 547.31<br />
It may be observed from the above table that the <strong>Municipal</strong>ity has incurred surplus prior to depreciation in 17 out of the next 20 years<br />
and the cumulative cash flows are positive for all the years.<br />
75
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
b) Balance Sheet - Table 8.22 Consolidated Balance Sheet for next 20 years (up to FY 2028 – 29)<br />
S.No Particulars 2007-08 2008-09 2009-10 2010-11 2011-12 2012-13 2013-14 2014-15 2015-16 2016-17 2017-18<br />
I Liabilities<br />
a) Liabilities<br />
Loans 236.29 172.09 462.33 1080.06 1878.24 1860.54 1842.85 1803.77 1722.32 1586.49 1450.66<br />
Contn from <strong>Municipal</strong> Fund 90.68 164.68 261.26 986.56 2062.39 2147.07 2232.62 2232.62 2232.62 2232.62 2232.62<br />
Contribution from Government 167.32 201.00 201.00 201.00 201.00 201.00 201.00 201.00 201.00 201.00 201.00<br />
Grant 173.07 284.07 1369.45 3390.77 5636.03 6388.95 7048.15 7048.15 7048.15 7048.15 7048.15<br />
Accumulated Depreciation 431.05 539.54 681.69 1028.81 1714.80 2569.76 3412.67 4126.33 4652.33 5058.51 5386.67<br />
b) Current Liabilities<br />
Reserve for Doubtful Colln 1.86 6.91 12.44 20.23 28.87 43.53 58.86 75.06 92.52 110.60 130.68<br />
Tender Deposits - Contractors 14.65 20.00 20.00 20.00 20.00 20.00 20.00 20.00 20.00 20.00 20.00<br />
Security & Deposit Others 17.54 20.00 20.00 20.00 20.00 20.00 20.00 20.00 20.00 20.00 20.00<br />
Other Deposit 1.77 5.00 5.00 5.00 5.00 5.00 5.00 5.00 5.00 5.00 5.00<br />
Water Connection Deposit - 3.09 132.04 354.46 480.25 501.73 523.76 546.34 574.10 602.57 631.74<br />
Sewerage Deposit - 0.00 0.00 230.40 47.36 396.26 433.62 471.92 511.17 551.45 600.53<br />
Library Cess Payable 9.54 10.00 10.00 10.00 10.00 10.00 10.00 10.00 10.00 10.00 10.00<br />
Interest Payable Account 58.52 65.00 65.00 65.00 65.00 65.00 65.00 65.00 65.00 65.00 65.00<br />
IT & ST Deduction - Conts 0.64 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00<br />
Recoveries - Staff 1.33 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50<br />
Accounts Payable - Suppliers 7.07 10.00 10.00 10.00 10.00 10.00 10.00 10.00 10.00 10.00 10.00<br />
Accounts Payable - Expenses 0.15 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00<br />
Other Recoveries & Payables 0.70 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50<br />
c) Accumulated Surplus -117.17 -229.97 -411.08 -844.42 -1670.82 -2485.29 -3279.86 -3928.16 -4351.52 -4646.83 -4786.95<br />
Total 1095.01 1279.40 2847.15 6585.88 10516.11 11761.55 12611.68 12715.03 12820.70 12882.56 13033.10<br />
76
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
S.No Particulars 2018-19 2019-20 2020-21 2021-22 2022-23 2023-24 2024-25 2025-26 2026-27 2027-28 2028-29<br />
I Liabilities<br />
a) Liabilities<br />
Loans 1332.52 1214.38 1096.25 978.11 859.97 741.83 623.70 505.56 387.42 269.28 151.15<br />
Contn from <strong>Municipal</strong> Fund 2232.62 2232.62 2232.62 2232.62 2232.62 2232.62 2232.62 2232.62 2232.62 2232.62 2232.62<br />
Contribution from Government 201.00 201.00 201.00 201.00 201.00 201.00 201.00 201.00 201.00 201.00 201.00<br />
Grant 7048.15 7048.15 7048.15 7048.15 7048.15 7048.15 7048.15 7048.15 7048.15 7048.15 7048.15<br />
Accumulated Depreciation 5662.71 5902.88 6117.47 6313.09 6494.08 6663.34 6822.86 6974.06 7117.94 7255.30 7386.71<br />
b) Current Liabilities<br />
Reserve for Doubtful Colln 151.71 173.48 196.87 221.16 247.60 275.37 304.20 334.92 366.91 401.59 437.88<br />
Tender Deposits - Contractors 20.00 20.00 20.00 20.00 20.00 20.00 20.00 20.00 20.00 20.00 20.00<br />
Security & Deposit Others 20.00 20.00 20.00 20.00 20.00 20.00 20.00 20.00 20.00 20.00 20.00<br />
Other Deposit 5.00 5.00 5.00 5.00 5.00 5.00 5.00 5.00 5.00 5.00 5.00<br />
Water Connection Deposit 661.64 692.29 728.95 766.52 805.03 844.50 884.95 932.35 980.93 1030.72 1081.76<br />
Sewerage Deposit 650.83 702.39 755.24 809.46 873.85 939.85 1007.50 1076.84 1147.98 1230.86 1315.81<br />
Library Cess Payable 10.00 10.00 10.00 10.00 10.00 10.00 10.00 10.00 10.00 10.00 10.00<br />
Interest Payable Account 65.00 65.00 65.00 65.00 65.00 65.00 65.00 65.00 65.00 65.00 65.00<br />
IT & ST Deduction - Contrs 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00 2.00<br />
Recoveries - Staff 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50<br />
Accounts Payable - Suppliers 10.00 10.00 10.00 10.00 10.00 10.00 10.00 10.00 10.00 10.00 10.00<br />
Accounts Payable - Expenses 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00 1.00<br />
Other Recoveries & Payables 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50<br />
c) Accumulated Surplus -4853.11 -4875.21 -4823.58 -4743.99 -4581.81 -4383.16 -4153.24 -3869.13 -3565.10 -3175.83 -2759.93<br />
Total 13226.08 13429.99 13690.98 13964.12 14318.49 14701.50 15109.75 15574.37 16055.85 16631.69 17233.14<br />
77
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
S.No Particulars 2007-08 2008-09 2009-10 2010-11 2011-12 2012-13 2013-14 2014-15 2015-16 2016-17 2017-18<br />
II Assets<br />
a) Fixed Assets 1042.31 1227.29 2703.27 6212.81 10378.40 11216.00 11960.75 11960.75 11960.75 11960.75 11960.75<br />
b) Current Assets<br />
Stock 0.93 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50<br />
Property Tax Rec - Current 0.97 1.62 1.88 1.93 1.98 2.03 2.28 2.34 2.40 2.46 2.52<br />
Property Tax Rec - Arrears 1.59 2.05 3.16 4.10 4.59 4.73 4.40 4.48 4.58 4.69 4.80<br />
Profession Tax Rec - Current 5.38 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00<br />
Profession Tax Rec - Arrears - 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00<br />
Lease Amount Rec -Arrears - 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00<br />
Lease Amount Rec-Current 0.06 0.04 0.03 0.01 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00<br />
Water Charges Rec - Current - 4.89 5.02 19.81 23.21 23.79 24.38 24.99 30.46 31.22 32.00<br />
Water Charges Rec - Arrears - 0.00 6.85 9.77 31.64 45.15 51.36 54.68 56.86 65.39 69.87<br />
Sewerage Charges - Current - 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 51.91 53.20 54.53 55.90 57.29 67.77<br />
Sewerage Charges - Arrears - 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 51.91 73.97 84.12 89.55 93.11<br />
Specific Grant Receivable 4.47 4.47 4.47 4.47 4.47 4.47 4.47 4.47 4.47 4.47 4.47<br />
Deposits Recoverable 2.24 5.00 5.00 5.00 5.00 5.00 5.00 5.00 5.00 5.00 5.00<br />
Staff Advance Recoverable 0.43 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50<br />
Other Advance - Recoverable 11.84 15.00 15.00 15.00 15.00 15.00 15.00 15.00 15.00 15.00 15.00<br />
Other Assets 0.44 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50<br />
c) Cash & Bank Balances 24.35 11.54 94.97 305.49 44.32 385.98 431.43 507.32 593.67 639.24 770.30<br />
Total 1095.01 1279.40 2847.15 6585.88 10516.11 11761.55 12611.68 12715.03 12820.70 12882.56 13033.10<br />
78
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
S.No Particulars 2018-19 2019-20 2020-21 2021-22 2022-23 2023-24 2024-25 2025-26 2026-27 2027-28 2028-29<br />
II Assets<br />
a) Fixed Assets 11960.75 11960.75 11960.75 11960.75 11960.75 11960.75 11960.75 11960.75 11960.75 11960.75 11960.75<br />
b) Current Assets<br />
Stock 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50<br />
Property Tax Rec - Current 2.84 2.91 2.98 3.06 3.13 3.54 3.63 3.72 3.81 3.91 4.42<br />
Property Tax Rec - Arrears 4.92 5.30 5.56 5.76 5.94 6.10 6.59 6.92 7.18 7.40 7.61<br />
Profession Tax Rec - Current 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00<br />
Profession Tax Rec - Arrears 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00<br />
Lease Amount Rec -Arrears 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00<br />
Lease Amount Rec-Current 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00<br />
Water Charges Rec - Current 32.80 33.62 39.95 40.95 41.97 43.02 44.10 51.40 52.69 54.00 55.35<br />
Water Charges Rec - Arrears 72.75 75.03 77.09 86.76 92.03 95.57 98.46 101.12 112.41 118.73 123.10<br />
Sewerage Charges - Current 69.46 71.20 72.98 74.80 86.91 89.08 91.30 93.59 95.93 109.90 112.65<br />
Sewerage Charges - Arrears 105.01 111.47 115.79 119.30 122.52 135.91 143.44 148.68 153.06 157.15 172.76<br />
Specific Grant Receivable 4.47 4.47 4.47 4.47 4.47 4.47 4.47 4.47 4.47 4.47 4.47<br />
Deposits Recoverable 5.00 5.00 5.00 5.00 5.00 5.00 5.00 5.00 5.00 5.00 5.00<br />
Staff Advance Recoverable 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50<br />
Other Advance - Recoverable 15.00 15.00 15.00 15.00 15.00 15.00 15.00 15.00 15.00 15.00 15.00<br />
Other Assets 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50 2.50<br />
c) Cash & Bank Balances 945.56 1137.74 1383.91 1640.76 1973.26 2335.55 2729.51 3176.22 3638.05 4187.88 4764.53<br />
Total 13226.08 13429.99 13690.98 13964.12 14318.49 14701.50 15109.75 15574.37 16055.85 16631.69 17233.14<br />
The full projects investment scenario indicates that Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity would end up with a cumulative cash surplus of Rs. 4765<br />
lacs by the end of FY 2028-29 (after 20 years)<br />
79
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
8.7 IMPACT OF POTENTIAL IMPROVEMENTS<br />
Vellakoil’s ability to improve on its financial performance hinges primarily on its ability to sustain and<br />
improve on the revenue growth noticeable in recent years.<br />
Specific interventions with respect to revenue realization and cost management are detailed in<br />
chapter 6 of the report. On ‘Full Project Investment Scenario’ basis, Vellakoil’s own revenues<br />
(comprising taxes, user charges and other income) could grow from Rs. 158 lacs in FY 2006-07 to<br />
Rs. 1302 lacs by FY 2028-29, implying an absolute growth of 36%. Vellakoil has vast potential for<br />
increasing its own income given the growth achieved in the last few years. Areas for revenue<br />
enhancement in own revenue include :<br />
Property Tax – through an enhanced revision in ARV, widening assessee base and closer<br />
scrutiny. Besides periodic increase (every 5 years) in property tax rates.<br />
Professional Tax – sustaining a higher assessment growth.<br />
User Charges – periodic increases in user charges for water connections and sewerage<br />
connections. The <strong>Municipal</strong>ity could generate additional Rs. 910 lacs (exclusive of Deposits) of<br />
income per annum by FY 2028-29 by providing water connections to 80% of property tax<br />
assessments and sewerage connections to 70% of property tax assessments.<br />
Vellakoil also needs to explore scope for private sector participation for development of<br />
remunerative projects and city beautification projects that have been identified by Vellakoil.<br />
While there is potential for expenditure control in certain areas (as in the case of energy costs and<br />
leakage in water supply), the focus of cost management should be to shift expenditure from<br />
administration to better asset management and service levels. We have not factored in any cost<br />
reduction in the FOP and have assumed that any savings generated from cost reduction would go<br />
into augmenting service levels and better asset management.<br />
A comprehensive energy audit is required, given that 60% of its operations and maintenance<br />
expenditure is spent on electricity charges. Plugging leakage in the water supply network and<br />
installation of timers and energy savers on the street light network are important interventions<br />
needed in the context of Vellakoil’s high power costs.<br />
8.8 ESTIMATION OF INVESTMENT CAPACITY<br />
8.8.1 Scenario I – Estimation of Investment Capacity on as is where basis<br />
We carried out the exercise of arriving at the Investment and Borrowing Capacity on as is where<br />
basis without any financial reforms being carried out. The borrowing capacity has been arrived by<br />
taking the NPV over the next 20 years on the minimum of the following :<br />
30% of revenue projections<br />
Primary Operating Surplus (Surplus before Interest & Depreciation)<br />
The investment capacity has been arrived @ of 4 times the borrowing capacity assuming that loans<br />
constitute 25% of total investment requirement.<br />
In such a scenario, the Investment and Borrowing Capacity works out as below :<br />
81
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
Table8.23 Summary of Borrowing and Investment Capacity – Scenario I<br />
Borrowing Capacity Rs. 373.26 lacs<br />
Investment Capacity (BC x 4 times) Rs. 1493.02 lacs<br />
8.8.2 Scenario II - Estimation of Investment Capacity with Projects & Growth Rate of 7.5%<br />
for Devolution Funds<br />
In Scenario II, the financial projections have been worked out for the next 30 years assuming that<br />
the income from Devolution Funds would grow @ 7.5% p.a. But the financial projections for the next<br />
20 years have been taken to arrive at the Borrowing & Investment capacity. The borrowing capacity<br />
of Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity has been arrived on the minimum of the following :<br />
30% of revenue projections<br />
50% of Primary Operating Surplus less Debt Service<br />
The overall financing mix has been arrived to include 18% Loans, 63% Grants and 19% own funds.<br />
The repayment period of loans has been taken at 5+15 years for Sewerage and Water Supply Loans<br />
and 2+8 years for other project loans. The above factors have been taken in to account for arriving<br />
at the Annuity Factor, which has been applied on the lowest of the above to arrive at the overall<br />
borrowing capacity and investment capacity.<br />
Table8.24 Summary of Borrowing and Investment Capacity – Scenario II<br />
Borrowing Capacity Rs. 744.13 lacs<br />
Investment Capacity (BC/0.14) Rs. 4134.08 lacs<br />
Investment Requirement Rs. 9018.12 lacs<br />
Sustainable Investment Capacity % - IC / IR 46%<br />
Thus the sustainable investment capacity works out to 46% in case the growth in Devolution Funds<br />
is taken @ 7.5% p.a.<br />
8.8.3 Scenario III - Estimation of Investment Capacity with Projects & Growth Rate of 10%<br />
for Devolution Funds<br />
In Scenario III, the financial projections have been worked out for the next 30 years assuming that<br />
the income from Devolution Funds would grow @ 10% p.a. But the financial projections for the next<br />
20 years have been taken to arrive at the Borrowing & Investment capacity. The borrowing capacity<br />
of Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity has been arrived on the minimum of the following :<br />
30% of revenue projections<br />
50% of Primary Operating Surplus less Debt Service<br />
The overall financing mix has been arrived to include 18% Loans, 63% Grants and 19% own funds.<br />
The repayment period of loans has been taken at 5+15 years for Sewerage and Water Supply Loans<br />
and 2+8 years for other project loans. The above factors have been taken in to account for arriving<br />
at the Annuity Factor, which has been applied on the lowest of the above to arrive at the overall<br />
borrowing capacity and investment capacity.<br />
82
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
Table8.25 Summary of Borrowing and Investment Capacity – Scenario III<br />
Borrowing Capacity Rs. 937.48 lacs<br />
Investment Capacity (BC/0.14) Rs. 5208.24 lacs<br />
Investment Requirement Rs. 9018.12 lacs<br />
Sustainable Investment Capacity % - IC / IR 57.75%<br />
Thus the sustainable investment capacity works out to 58% of the total investment requirement at<br />
Rs. 5210 lacs in case the growth in Devolution Funds is taken @ 10% p.a.<br />
8.9 KEY INDICATORS<br />
The key Indictors of the <strong>Municipal</strong>ity based on the financial projections of Scenario II (Growth Rate<br />
of Devolution Funds @ 7.5% p.a.) works out as below :<br />
Table 8.26 Key Indicators<br />
Minimum Maximum Average<br />
Existing (2001-02 to 2006-07)<br />
Operating Ratio 0.71 1.01 0.85<br />
Debt Service Ratio 0% 6% 2%<br />
Category<br />
Short Term (2009-10 to 2013-14)<br />
1<br />
Operating Ratio 0.92 1.33 1.07<br />
Debt Service Ratio 28% 49% 34%<br />
Category<br />
Long Term (2009-10 to 2028-29)<br />
3<br />
Operating Ratio 0.70 1.33 0.84<br />
Debt Service Ratio 6% 49% 22%<br />
Category 1<br />
Note : 1 – Financially Sound; 2 – Financially Fragile; 3 – Financially Insolvent<br />
The financials and the ratios of the <strong>Municipal</strong>ity are not good in the short term due to high operating<br />
ratio and debt service ratio. But in the long run, the same have improved and is good due to higher<br />
number of commercial and industrial assessments.<br />
8.10 INFERENCE<br />
The investment capacity of Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity on ‘As is Where Basis’ works out to Rs. 1493<br />
lacs.<br />
The investment capacity of Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity works to 46% in case of Scenario II (Growth<br />
Rate of Devolution Funds assumed @ 7.5% p.a.) and 58% in case of Scenario III (Growth Rate<br />
of Devolution Funds assumed @ 10% p.a.).<br />
In value terms the investment capacity works out to Rs. 4135 lacs under Scenario II and Rs.<br />
5210 lacs under Scenario III.<br />
It may be observed that the investment capacity has improved with the introduction of new<br />
projects as compared to ‘As is Where Basis’ scenario. The same is on account of the fact that<br />
83
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
the <strong>Municipal</strong>ity has large number of commercial and industrial assessments, which are<br />
presently untapped on account of water and sewerage connections.<br />
Thus it can be inferred that the investment capacity of the <strong>Municipal</strong>ity is around 46% of the total<br />
investment requirement.<br />
Based on the above, it can be inferred that the <strong>Municipal</strong>ity can take up only the small projects,<br />
where the funding is mostly by way of Grants as given below :<br />
Table 8.27 Priority projects suggested under CDP<br />
S.No. Particulars Total Priority Funding By<br />
A Physical Infrastructure Facilities L : G : O<br />
I Water Supply<br />
a) Improvements to Water Supply 1199.20 A 0:90:10<br />
II Sewerage & Sanitation<br />
a) New Underground Sewerage Scheme 3300.00 A 37:35;28<br />
Total 4499.20<br />
The above two projects can be taken up by the <strong>Municipal</strong>ity as there are large number of<br />
commercial and industrial assessments and on stand alone basis these projects are viable at the<br />
funding pattern given above.<br />
Besides the above, the following other small projects can be taken up, where the funding pattern<br />
is mainly by way of grants and deposit mobilization :<br />
Table 8.27a Priority projects suggested under CDP<br />
S.No. Particulars Total Priority Funding By<br />
A Physical Infrastructure Facilities L : G : O<br />
I Strom Water Drains<br />
a) Construction of new drains and providing mesh covers 300.00 A 0:90:10<br />
II Bus Shelter<br />
a) Construction of New Bus Shelter 10.00 A 100% Grant<br />
III Street Lights<br />
a) High mast lights at Old & New Bus Stand 14.00 A 100% Grant<br />
b) Retrofitting and energy saving devices 23.00 A ESCO<br />
c) Central Median lights at main roads for 3Km 45.00 A 0:90:10<br />
B Social Infrastructure Facilities<br />
I Slum Improvements<br />
a) Improvement to Slums 709.00 B 100% Grant<br />
II Market<br />
a) Construction of Daily Market 75.00 A 100% ULB<br />
b) Construction of Weekly Market 75.00 A 100% ULB<br />
C Other Projects<br />
I Remunerative Projects<br />
a) Commercial Building (G+2) at Erode Road near 50.00 A 100% ULB<br />
84
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
Bus Stand<br />
II E-Governance<br />
a) E-Governance 16.00 A 100% Grant<br />
b) Updation of Database on GIS 40.00 C 0:90:10<br />
c) Property Mapping 4.30 A 100% ULB<br />
Total 1361.30<br />
As regards other projects with large financial cost, the <strong>Municipal</strong>ity would require more support<br />
from the Government towards both capital cost and operation & maintenance expenses. Thus it<br />
would be possible to take up those projects if more support is provided by the Government and<br />
by improving own sources of income.<br />
85
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
86<br />
PUBLIC CONSULTATION PROCESS<br />
The <strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> is a tool which adapts a corporate approach to plan and implement<br />
projects in a participatory mechanism involving users, elected councilors, line agencies, private<br />
organizations, NGOs and CBOs. The broad purpose of stake holders’ participation is to involve<br />
the stakeholders in the development plan for the city. In this process, residents of various<br />
sections of the communities in the town were enquired into at random during surveys and visits<br />
to the sites and also otherwise suggested by the elders.<br />
This plan focuses largely on the totally implementable urban infrastructure and other projects to<br />
adequately meet the present and future demands of the growing town. The attendant results and<br />
concomitant effects in terms of town’s economic development, societies’ standard of living,<br />
improvement in the living environment, equality in the access to the necessary services, facilities<br />
and amenities for all the sections of people largely sub-serving alleviation of the urban poverty<br />
element, on the completion of the project proposals.<br />
At the initial stage, the Councilors, the Chairman and the <strong>Municipal</strong> Officials were individually<br />
discussed with. The consultants gathered information on ward and town level requirements<br />
relating to <strong>Municipal</strong> services and other promotive projects. As a second step, a public<br />
consultation meeting was arranged and the details are as below:<br />
Minutes of the stake holder’s meeting<br />
The stake holder’s meeting was held in Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity at Venkatesan Marriage Hall,<br />
Vellakoil on 22/05/08 at 10.30 am with an introduction given by the Chairman followed by SMEC<br />
Consultant Mrs. S. Rajalakshmi. An discussion on the town requirement was thrown open with<br />
the ward councilors, Senior Citizens of the town, Teachers, working staff, Government official,<br />
Chairman, and public.<br />
The stakeholders have been invariably very co-operative and practical about the needs of the<br />
town at ward and town levels. During the meeting, participants were asked to describe the<br />
desired future vision for their town. The participants were given a chance to comment on the<br />
strategic options put forth in broad terms and on the local strength and weaknesses affecting<br />
city’s future development. These comments were considered while developing strategic options<br />
for the plan.<br />
At the end of the workshop, consulting team organized for written feed backs from the<br />
stakeholders, to be incorporated to the CDP. The major issues highlighted during the meeting<br />
and the solution initiatives are given below:<br />
9
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
Table 9.1 Major issues and solution initiatives<br />
NO MAJOR ISSUES RAISED SOLUTION INITIATIVES<br />
1 Implement the source segregation method in<br />
solid waste management.<br />
Source segregation and preparation of compost is<br />
proposed<br />
2 Set up crematorium for this Vellakoil town A gasifier crematorium is proposed.<br />
3 Take steps to come all the buses in to bus<br />
stand.<br />
4 Improve the basic amenities in Weekly<br />
market.<br />
5 Improve the basic amenities of Bus stand.<br />
6 Require Public Toilet facility at MGR Nagar.<br />
7 Regulate the house tax for improve the<br />
financial status of Town<br />
8 improve the bus shelter facilities through Lions<br />
Club<br />
Cooperation from the private and government bus<br />
operators, Drivers and conductors and the public is<br />
essential<br />
Reconstruction of weekly market with basic<br />
amenities is proposed.<br />
Expansion of bus stand with basic amenities is<br />
proposed<br />
About 10 numbers of public toilets are proposed at<br />
various locations including MGR nagar.<br />
Reforms in property tax collection are proposed will<br />
improve the financial condition of the town.<br />
5 number of new bus shelters has been proposed<br />
to be implemented by NGOs and Voluntary<br />
agencies.<br />
The suggestions and feed backs from all attendees of the workshop are listed below:<br />
Table 9.2 Minutes of the consultative process meeting<br />
Chairman: Mrs. Shanthi Introduction given for <strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity<br />
Kandasamy<br />
Assistant Director, Regional Briefed about the importance of <strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> plan and need for<br />
District <strong>Municipal</strong><br />
development in public toilet facilities, road works, street light, water<br />
Administration,<br />
supply, bus stand, Park and play ground.<br />
V.V.Thambidurai, Ex. Ward • Widening of Tharapuram road.<br />
Councilor,<br />
• In new layouts need road facilities, public water stand post.<br />
• This town requires UGD and street light facility for all the roads.<br />
DMK Secretary, Vellakoil DMK • Increase the number of municipality workers involved with water<br />
supply, sanitary workers.<br />
• Implement the source segregation method in solid waste<br />
management.<br />
• Require park, play ground and entertainment facilities.<br />
P.K. Kumarasamy, President, • Require Public Toilet facility at MGR Nagar.<br />
Saiva Sidhantha Group<br />
• Remove and stop the brick industries in settlement area.<br />
Panner selvam, Lions club • Park should be set up in town center.<br />
• Set up crematorium for this Vellakoil town.<br />
• Lions club will help to improve the bus shelter facilities.<br />
Gurusamy, Financier • Bus stand should be transferred from old location to new location.<br />
Because buses are not coming to bus stand.<br />
Periyasamy<br />
• Give importance to Improvement of bus stand and buses<br />
operation.<br />
• Require road improvement and clear the road side encroachment.<br />
• Improve the storm water drains, daily market, Government collage,<br />
Farmers daily market<br />
• Upgrade the Primary health center as Town hospital.<br />
• Improve the Electric supply of this town.<br />
87
<strong>City</strong> <strong>Development</strong> <strong>Plan</strong> for Vellakoil <strong>Municipal</strong>ity SMEC India Pvt Ltd<br />
Final Report TNUDP III<br />
Jothi, Secretary, Communist<br />
Party of India (Marxsist)<br />
Deluxe Mani, 3 rd ward Council<br />
member<br />
• Develop basic amenities in textile mills.<br />
• Construct community marriage hall and recreation facilities.<br />
• Arrange the facility of free ambulance service.<br />
• Improve the basic amenities of Bus stand.<br />
• Improve the basic amenities in Weekly market.<br />
• Remove the encroachment in the town.<br />
• Require Park and Play ground facilities.<br />
• Stop the collection of fees for birth and death certificate.<br />
• Provide the basic amenities in Arivoli nagar.<br />
• Take steps to come all the buses in to bus stand.<br />
• Stop the stray dogs menace.<br />
• Improve the basic amenities based on population.<br />
• Regulate the house tax for improve the financial status of Town.<br />
• Provide patta for all resident of town.<br />
• Take steps to restrict the cotton export.<br />
• Provide uninterrupted power supply for Water supply. Take<br />
immediate action against mixing of sewage water in to drinking<br />
water.<br />
88