Processing kodak motion picture films, module 3 analytical procedures
Processing kodak motion picture films, module 3 analytical procedures
Processing kodak motion picture films, module 3 analytical procedures
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
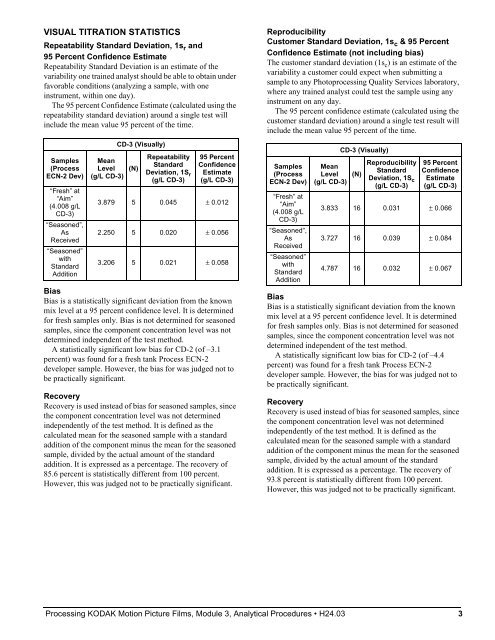
VISUAL TITRATION STATISTICS<br />
Repeatability Standard Deviation, 1s r and<br />
95 Percent Confidence Estimate<br />
Repeatability Standard Deviation is an estimate of the<br />
variability one trained analyst should be able to obtain under<br />
favorable conditions (analyzing a sample, with one<br />
instrument, within one day).<br />
The 95 percent Confidence Estimate (calculated using the<br />
repeatability standard deviation) around a single test will<br />
include the mean value 95 percent of the time.<br />
Samples<br />
(Process<br />
ECN-2 Dev)<br />
“Fresh” at<br />
“Aim”<br />
(4.008 g/L<br />
CD-3)<br />
“Seasoned”,<br />
As<br />
Received<br />
“Seasoned”<br />
with<br />
Standard<br />
Addition<br />
Mean<br />
Level<br />
(g/L CD-3)<br />
CD-3 (Visually)<br />
(N)<br />
Repeatability<br />
Standard<br />
Deviation, 1S r<br />
(g/L CD-3)<br />
95 Percent<br />
Confidence<br />
Estimate<br />
(g/L CD-3)<br />
3.879 5 0.045 ± 0.012<br />
2.250 5 0.020 ± 0.056<br />
3.206 5 0.021 ± 0.058<br />
Bias<br />
Bias is a statistically significant deviation from the known<br />
mix level at a 95 percent confidence level. It is determined<br />
for fresh samples only. Bias is not determined for seasoned<br />
samples, since the component concentration level was not<br />
determined independent of the test method.<br />
A statistically significant low bias for CD-2 (of –3.1<br />
percent) was found for a fresh tank Process ECN-2<br />
developer sample. However, the bias for was judged not to<br />
be practically significant.<br />
Recovery<br />
Recovery is used instead of bias for seasoned samples, since<br />
the component concentration level was not determined<br />
independently of the test method. It is defined as the<br />
calculated mean for the seasoned sample with a standard<br />
addition of the component minus the mean for the seasoned<br />
sample, divided by the actual amount of the standard<br />
addition. It is expressed as a percentage. The recovery of<br />
85.6 percent is statistically different from 100 percent.<br />
However, this was judged not to be practically significant.<br />
Reproducibility<br />
Customer Standard Deviation, 1s c & 95 Percent<br />
Confidence Estimate (not including bias)<br />
The customer standard deviation (1s c ) is an estimate of the<br />
variability a customer could expect when submitting a<br />
sample to any Photoprocessing Quality Services laboratory,<br />
where any trained analyst could test the sample using any<br />
instrument on any day.<br />
The 95 percent confidence estimate (calculated using the<br />
customer standard deviation) around a single test result will<br />
include the mean value 95 percent of the time.<br />
Samples<br />
(Process<br />
ECN-2 Dev)<br />
“Fresh” at<br />
“Aim”<br />
(4.008 g/L<br />
CD-3)<br />
“Seasoned”,<br />
As<br />
Received<br />
“Seasoned”<br />
with<br />
Standard<br />
Addition<br />
Mean<br />
Level<br />
(g/L CD-3)<br />
CD-3 (Visually)<br />
Bias<br />
Bias is a statistically significant deviation from the known<br />
mix level at a 95 percent confidence level. It is determined<br />
for fresh samples only. Bias is not determined for seasoned<br />
samples, since the component concentration level was not<br />
determined independent of the test method.<br />
A statistically significant low bias for CD-2 (of –4.4<br />
percent) was found for a fresh tank Process ECN-2<br />
developer sample. However, the bias for was judged not to<br />
be practically significant.<br />
Recovery<br />
Recovery is used instead of bias for seasoned samples, since<br />
the component concentration level was not determined<br />
independently of the test method. It is defined as the<br />
calculated mean for the seasoned sample with a standard<br />
addition of the component minus the mean for the seasoned<br />
sample, divided by the actual amount of the standard<br />
addition. It is expressed as a percentage. The recovery of<br />
93.8 percent is statistically different from 100 percent.<br />
However, this was judged not to be practically significant.<br />
<strong>Processing</strong> KODAK Motion Picture Films, Module 3, Analytical Procedures H24.03 3<br />
(N)<br />
Reproducibility<br />
Standard<br />
Deviation, 1S c<br />
(g/L CD-3)<br />
95 Percent<br />
Confidence<br />
Estimate<br />
(g/L CD-3)<br />
3.833 16 0.031 ± 0.066<br />
3.727 16 0.039 ± 0.084<br />
4.787 16 0.032 ± 0.067