The role of implicit attitudes towards food and ... - ResearchGate
The role of implicit attitudes towards food and ... - ResearchGate
The role of implicit attitudes towards food and ... - ResearchGate
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
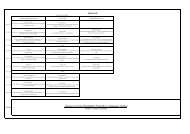
Table 3<br />
Regression analyses predicting AMBI change during treatment from <strong>implicit</strong> attitudinal change <strong>towards</strong> PA <strong>and</strong> <strong>food</strong> during treatment<br />
Adj.<br />
R 2<br />
boys. Age was a marginal significant predictor, β =.35; t(18)=2.14, p =.06, indicating that decrease in overweight<br />
was related to a younger age (see Table 3).<br />
3.4.2. Implicit <strong>attitudes</strong> <strong>towards</strong> <strong>food</strong><br />
In a second model, ABMI change during treatment was the dependent variable, <strong>and</strong> the change in attitude <strong>towards</strong><br />
unhealthy <strong>food</strong> (RT), <strong>towards</strong> healthy <strong>food</strong> (RT), <strong>towards</strong> unhealthy <strong>food</strong> (PE), <strong>towards</strong> healthy <strong>food</strong> (PE), baseline<br />
ABMI, age <strong>and</strong> sex were entered as independent variables. <strong>The</strong> model accounted for 69% <strong>of</strong> the variance, F(7, 18)=<br />
6.75, pb.01. Attitudinal change <strong>towards</strong> healthy <strong>food</strong> (PE), was a significant predictor, β=.39; t(18)=2.49, pb.05,<br />
indicating that decrease in overweight was related to a more positive attitude <strong>towards</strong> healthy <strong>food</strong> at the end <strong>of</strong><br />
the treatment, adjusted for age, sex <strong>and</strong> baseline ABMI. Further, again baseline ABMI, β=−.62; t(18) =4.59, pb.01,<br />
<strong>and</strong> sex, β =.49; t(18)=3.62, p b.01, were significant predictors, <strong>and</strong> age was a marginal significant predictor,<br />
β =.30; t(18)=2.07, p =.06 (see Table 3).<br />
3.4.3. Self-reported <strong>attitudes</strong> <strong>towards</strong> physical activity.<br />
In a third model, ABMI change during treatment was the dependent variable, <strong>and</strong> the change in attitude <strong>towards</strong><br />
sedentary activity, <strong>towards</strong> moderate intense PA, <strong>towards</strong> high intense PA, baseline ABMI, age <strong>and</strong> sex were entered as<br />
independent variables. <strong>The</strong> model accounted for 49% <strong>of</strong> the variance, F(6, 18)=3.88, pb.05. Only baseline ABMI<br />
<strong>and</strong> sex were significant predictors, respectively β=−.64; t(18) =3.06, pb.05 <strong>and</strong> β=.49; t(18) =2.65, pb.05 (see<br />
Table 4).<br />
Table 4<br />
Regression analyses predicting AMBI change during treatment from self-reported attitudinal change <strong>towards</strong> PA <strong>and</strong> <strong>food</strong> during treatment<br />
Adj.<br />
R 2<br />
Significant<br />
correlates<br />
M. Craeynest et al. / Eating Behaviors 9 (2008) 41–51<br />
Significant correlates St<strong>and</strong>ard coefficient<br />
beta<br />
St<strong>and</strong>ard coefficient<br />
beta<br />
Adj.<br />
R 2<br />
Significant<br />
correlates<br />
PA Food<br />
Total model: .49 Total model: .61<br />
F(6, 18)=3.88⁎ F(5, 18)= 6.73⁎⁎<br />
Sex .49⁎ Sex .53⁎⁎<br />
Age .21 Age .30<br />
Baseline ABMI −.64⁎ Baseline ABMI −.72⁎⁎<br />
Sedentary activity −.03 Unhealthy <strong>food</strong> .17<br />
Mod. intense PA .09 Healthy <strong>food</strong> .30<br />
High intense PA −.02<br />
⁎pb.05; ⁎⁎pb.01.<br />
Adj.<br />
R 2<br />
Significant<br />
correlates<br />
PA Food<br />
Total model: .73 Total model: .69<br />
F(9, 18)=6.51⁎⁎ F(7, 18)=6.75⁎⁎<br />
Sex .64⁎⁎ Sex .49⁎⁎<br />
Age .35 Age .30<br />
Baseline ABMI −.57⁎⁎ Baseline ABMI −.62⁎⁎<br />
Sedentary activity (RT) −.02 Unhealthy <strong>food</strong> (RT) −.14<br />
Mod. intense PA (RT) −.26 Healthy <strong>food</strong> (RT) −.03<br />
High intense PA (RT) .51⁎<br />
Sedentary activity (PE) .06 Unhealthy <strong>food</strong> (PE) −.01<br />
Mod. intense PA (PE) −.06 Healthy <strong>food</strong> (PE) .39⁎<br />
High intense PA (PE) .13<br />
⁎ pb.05; ⁎⁎ pb.01.<br />
47<br />
St<strong>and</strong>ard coefficient<br />
beta<br />
St<strong>and</strong>ard coefficient<br />
beta