May - Library
May - Library
May - Library
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
35<br />
Equipment Readiness and Visibility Using Honeycomb Maps<br />
104.00%<br />
98.12%<br />
92.25%<br />
86.38%<br />
80.50%<br />
74.62%<br />
68.75%<br />
62.87%<br />
57.00%<br />
Jun 03 Jul 03 Jul 03 Aug 03 Aug 03 Sep 03 Sep 03<br />
Last 12 Weekly Observations<br />
MR Ratings for Light Tactical Vehicle<br />
Data<br />
The S-rating measures the number of equipment items on-hand<br />
(both available and in maintenance) against the planned<br />
authorizations. While the S-rating provides information on the number<br />
of units on hand relative to that which is authorized, the R-rating, or<br />
maintenance rating, evaluates the amount of equipment that is combat<br />
ready relative to the amount available. The MR-rating is summary<br />
rating that is the product of the S and R ratings. Thus, if a Marine<br />
Corps unit has 125 units, but only 100 are authorized, then the S-rating<br />
would be 125%, indicating that there are pieces of equipment in<br />
excess to that which was authorized. These excess units can be<br />
located by Marine organizational units through MERIT view changes.<br />
However, if 50 units were under repair, then the R-rating would only<br />
be 60% (75/125). The MR-rating would be the product of these<br />
measures, or 75%. The MR is the percent of combat ready pieces to<br />
authorization. These measures are very consistent with the broader<br />
class of equipment availability measures suggested in the To t a l<br />
Productive Maintenance literature.<br />
These measures can now be incorporated into the size and<br />
color characteristics of the honeycomb map. The Exhibit 2 view<br />
shows the honeycomb cell size to be the current S-rating and the color<br />
to be the current MR-rating. The S, R, or MR ratings for diff e rent time<br />
periods can be selected from the drop-down list to prepare different<br />
honeycomb views. Functional Area (FA) cells are one level higher in<br />
the hierarc h y. Each of these cells are positioned on the map<br />
according to equipment density. To illustrate, FA-10 Radios has the<br />
highest density of equipment in the Marine Corps, and thus is<br />
displayed upper-left on the view. The colors designate the curre n t<br />
MR-rating. Green colors indicate MR-ratings above 92%, yellow<br />
colors indicate MR-ratings from 85-92% while red colors are MRratings<br />
below 85%. Among the radios the A1955 (radio terminal set)<br />
has an MR rating below 85%, which would indicate the need for<br />
additional management oversight.<br />
In this example, because the S Rating sets sizing, the individual<br />
pieces of equipment are arrayed within their functional groups so that<br />
the highest S-rated equipment is positioned in the upper left-hand<br />
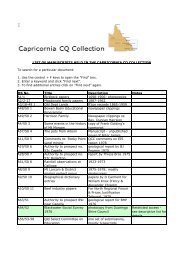
Exhibit 3. Performance Control Chart<br />
A(+/-) line indicating three standard deviations from the historical mean MR rating.<br />
B(+/-) line indicating two standard deviations from the historical mean MR rating.<br />
C(+/-) line indicating one standard deviation from the historical mean MR rating.<br />
The historical mean MR rating.<br />
c o rner (green corner) and the lowest rated weapon systems are<br />
positioned in the lower right-had corner of the group box (red corn e r ) .<br />
Thus, among the radios, the A2171 radio has the largest cell are a ,<br />
which represents the highest S-Rating among the radios. A click on<br />
the box will show the actual S, R, and MR perf o rmance attributes over<br />
designated time periods. Thus, users have a quick visual display of<br />
the multiple dimensions of equipment availability. Naturally, the<br />
honeycomb can be filtered along any of the equipment or perf o rm a n c e<br />
metric dimensions to focus on a particular class of equipment or<br />
readiness issue. While viewing the maps from an equipment<br />
perspective is important, MERIT also arrays the data from an<br />
organizational perspective which allows analysts to quickly focus on<br />
organizations that are experiencing problems.<br />
In addition, the system archives historical S, R, and MR ratings by<br />
equipment type for control charting. Thus, an analyst can click on an<br />
equipment cell and request the system to prepare a control chart of<br />
the maintenance perf o rmance for variable timeframes such as the<br />
last 24 months. Exhibit 3 provides an example for a Light Ta c t i c a l<br />
Vehicle using assumed data. Over the last 12 weeks it has been<br />
experiencing declining MR performance.<br />
The resulting honeycomb maps have allowed Corps personnel to<br />
move energy and time away from data gathering, accumulation, and<br />
re p o rting; towards solving and preventing critical readiness pro b l e m s .<br />
F o rce Commanders are given clear visibility of readiness tre n d s ,<br />
revealing potential problems and associated causes.<br />
System Structure and Development<br />
Methodology<br />
The honeycomb map by itself provides a multi-dimensional view<br />
of perf o rmance, but does not provide the management inform a t i o n<br />
needed to influence the causes of the perf o rmance. In order to<br />
accomplish this objective, supply chain variables must be connected<br />
to the honeycomb items (equipment). In this way, perf o rm a n c e ,<br />
underlying causes, and associated responses can be linked. MERIT<br />
accomplishes this linkage.