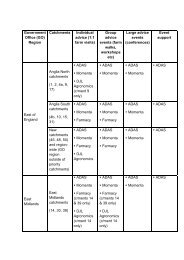
Review of the Food-borne Zoonoses Research ... - ARCHIVE: Defra
Review of the Food-borne Zoonoses Research ... - ARCHIVE: Defra
Review of the Food-borne Zoonoses Research ... - ARCHIVE: Defra
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
7. n<br />
Project code: OZ0402<br />
O<strong>the</strong>r zoonotic pathogens <strong>of</strong> interest<br />
Project title: What is <strong>the</strong> potential for human isolates <strong>of</strong> both<br />
genotypes <strong>of</strong> C. parvum to infect, colonise and be<br />
excreted by farm animals<br />
Start date (dd/mm/yy): 01/04/2000<br />
End date (dd/mm/yy): 31/03/2003<br />
£406,684<br />
Total cost:<br />
Affiliation: Veterinary Laboratories Agency,<br />
Sub-contractor(s):<br />
Project code: OZ0407<br />
Cryptosporidium Reference Group,<br />
HPA<br />
Project title: Evaluation and risk assessment <strong>of</strong> zoonotic<br />
transmission <strong>of</strong> Cryptosporidium<br />
Start date (dd/mm/yy): 01/04/2003<br />
End date (dd/mm/yy): 31/01/2008<br />
£783,631<br />
Total cost:<br />
Affiliation: VLA<br />
Sub-contractor(s):<br />
Abstract <strong>of</strong> research<br />
CREH Analytical Limited,<br />
PHLS Cryptosporidium Reference Unit, Swansea<br />
Public Health Laboratory<br />
Cryptosporidium infection in people can result in severe clinical disease, which in<br />
immuno-compromised patients can be fatal. Most human infection is with ei<strong>the</strong>r <strong>of</strong> two<br />
predominant species, C. hominis (thought until recently to be human specific) and C.<br />
parvum. Both cause sporadic cases and outbreaks <strong>of</strong> disease. However, <strong>the</strong> Health<br />
Protection Agency (HPA) and UK Cryptosporidium Reference Unit (CRU) have identified<br />
o<strong>the</strong>r species and genotypes previously associated with animals, including C.<br />
meleagridis, C. felis and C. canis in patients. Species identification is currently only<br />
possible by molecular analyses and is not undertaken during routine diagnosis in primary<br />
65