Analysis and modelling of the seismic behaviour of high ... - Ingegneria
Analysis and modelling of the seismic behaviour of high ... - Ingegneria
Analysis and modelling of the seismic behaviour of high ... - Ingegneria
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
3. SEISMIC BEHAVIOUR OF BOLTED END PLATE BEAM-TO-COLUMN STEEL JOINTS<br />
• analysing <strong>the</strong> <strong>seismic</strong> performance <strong>of</strong> partial strength bolted extended end<br />
plate joints with fillet welds, which represent an alternative to fully welded<br />
connections for use in <strong>seismic</strong> force resisting moment frames;<br />
• verifying in a low-cycle fatigue regime <strong>the</strong> feasibility <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> mechanical<br />
approach adopted for joints undergoing monotonic loading, whereby <strong>the</strong><br />
properties <strong>of</strong> a complete joint are understood <strong>and</strong> obtained by assembling<br />
<strong>the</strong> properties <strong>of</strong> its component parts.<br />
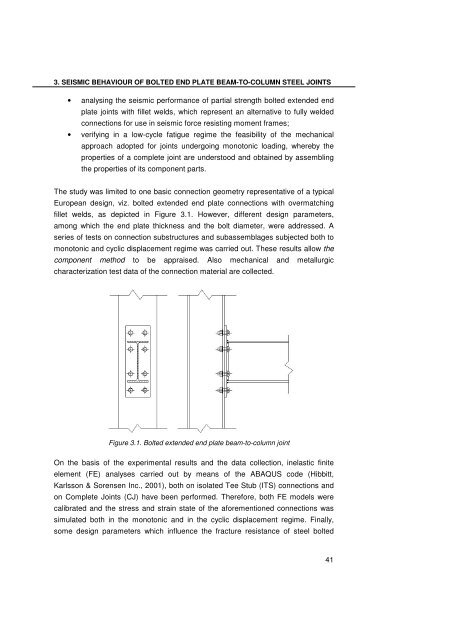
The study was limited to one basic connection geometry representative <strong>of</strong> a typical<br />
European design, viz. bolted extended end plate connections with overmatching<br />
fillet welds, as depicted in Figure 3.1. However, different design parameters,<br />
among which <strong>the</strong> end plate thickness <strong>and</strong> <strong>the</strong> bolt diameter, were addressed. A<br />
series <strong>of</strong> tests on connection substructures <strong>and</strong> subassemblages subjected both to<br />
monotonic <strong>and</strong> cyclic displacement regime was carried out. These results allow <strong>the</strong><br />
component method to be appraised. Also mechanical <strong>and</strong> metallurgic<br />
characterization test data <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> connection material are collected.<br />
Figure 3.1. Bolted extended end plate beam-to-column joint<br />
On <strong>the</strong> basis <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> experimental results <strong>and</strong> <strong>the</strong> data collection, inelastic finite<br />
element (FE) analyses carried out by means <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> ABAQUS code (Hibbitt,<br />
Karlsson & Sorensen Inc., 2001), both on isolated Tee Stub (ITS) connections <strong>and</strong><br />
on Complete Joints (CJ) have been performed. Therefore, both FE models were<br />
calibrated <strong>and</strong> <strong>the</strong> stress <strong>and</strong> strain state <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> aforementioned connections was<br />
simulated both in <strong>the</strong> monotonic <strong>and</strong> in <strong>the</strong> cyclic displacement regime. Finally,<br />
some design parameters which influence <strong>the</strong> fracture resistance <strong>of</strong> steel bolted<br />
41