Analysis and modelling of the seismic behaviour of high ... - Ingegneria
Analysis and modelling of the seismic behaviour of high ... - Ingegneria
Analysis and modelling of the seismic behaviour of high ... - Ingegneria
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
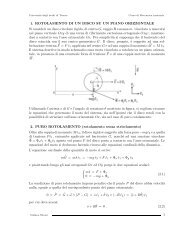
4. SEISMIC RESPONSE OF PARTIAL-STRENGTH COMPOSITE JOINTS<br />
4.8 Cyclic tests <strong>of</strong> full-scale composite joint subassemblages<br />
This Section presents results obtained from tests carried on three full-scale<br />
composite beam-to-column joint subassemblages, which were replicas <strong>of</strong> parts <strong>of</strong><br />
<strong>the</strong> two-storey prototype structure. One monotonic test <strong>and</strong> one test in cyclic<br />
regime both on an interior (CJ-INT) <strong>and</strong> an exterior (CJ-EXT) joint were conducted.<br />
The steelwork connection consists <strong>of</strong> an extended end plate welded to <strong>the</strong> beam<br />
end <strong>and</strong> bolted to <strong>the</strong> column flange. As illustrated in Figure 4.16 <strong>and</strong> Figure 4.17,<br />
all <strong>the</strong> specimens had steel deck supported concrete slab acting compositely with<br />
<strong>the</strong> beam <strong>and</strong> partially encased steel-concrete composite columns. Moment–<br />
rotation curves obtained from <strong>the</strong> tests are compared with those predicted by an<br />
analytical model. Plastic analysis based on <strong>the</strong> <strong>the</strong>oretical developments <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong><br />
previous sections is used to develop <strong>the</strong> analytical model for <strong>the</strong> prediction <strong>of</strong><br />
moment capacity. A rotational spring model for <strong>the</strong> composite beam, as proposed<br />
in revised Annex J <strong>of</strong> EC4, combined with a translational spring model for <strong>the</strong> steel<br />
web panel, is used to assess <strong>the</strong> strength <strong>and</strong> <strong>the</strong> stiffness <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> composite joints.<br />
The model tends to over-predict <strong>the</strong> <strong>behaviour</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> joint. To better underst<strong>and</strong><br />
<strong>the</strong> transfer mechanism activated in <strong>the</strong> composite beam <strong>and</strong> in <strong>the</strong> web panel<br />
numerical finite element (FE) analyses were carried out by means <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> ABAQUS<br />
code. The FE model was calibrated <strong>and</strong> <strong>the</strong> stress <strong>and</strong> strain state <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong><br />
aforementioned connections was simulated in <strong>the</strong> monotonic displacement regime.<br />
4.8.1 Test set-up <strong>and</strong> procedure<br />
The basic set-up included a test frame <strong>and</strong> a loading system (Figure 4.18). The<br />
test frame was designed to be sufficiently stiff to minimize <strong>the</strong> lateral movement <strong>of</strong><br />
<strong>the</strong> system. The lower hinges were fastened directly to <strong>the</strong> test floor. The horizontal<br />
displacement-controlled load was applied by a hydraulic jack at <strong>the</strong> upper end <strong>of</strong><br />
<strong>the</strong> composite column. The jack was mounted on <strong>the</strong> pedestal <strong>and</strong> was connected<br />
to <strong>the</strong> column through a load cell. The height <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> columns <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> test specimens,<br />
measured from <strong>the</strong> point <strong>of</strong> load application to <strong>the</strong> center <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> hinge, was 3500<br />
mm, which was <strong>the</strong> storey height <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> prototype structure. This selection was<br />
made by assuming that <strong>the</strong> points <strong>of</strong> contra-flexure occurred at <strong>the</strong> midheight <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong><br />
adjacent stories.<br />
In order to characterize <strong>the</strong> <strong>behaviour</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> specimens under hysteretic loading a<br />
predefined representative displacement history was applied. The procedure follows<br />
<strong>the</strong> ECCS recommendation n° 45 (1986), as illustrated in Chapter 2. The<br />
instrumentation <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> specimens was designed to determine <strong>the</strong> applied loads, to<br />
127