Analysis and modelling of the seismic behaviour of high ... - Ingegneria
Analysis and modelling of the seismic behaviour of high ... - Ingegneria
Analysis and modelling of the seismic behaviour of high ... - Ingegneria
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
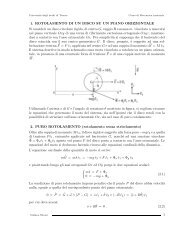
4. SEISMIC RESPONSE OF PARTIAL-STRENGTH COMPOSITE JOINTS<br />
<strong>the</strong> S.L.S. According to a Poisson model, this corresponds to a reference<br />
return period <strong>of</strong> 95.4 years.<br />
iii. Calculating <strong>the</strong> structural dem<strong>and</strong> for <strong>the</strong> pre-selected earthquake<br />
intensity. The dem<strong>and</strong> parameters, such as <strong>the</strong> maximum interstory drift, are<br />
computed using st<strong>and</strong>ard methods <strong>of</strong> structural analysis (Non-linear Pushover<br />
analysis <strong>and</strong> Time-History analysis) taking into account possibly stiffness<br />
deterioration <strong>and</strong> strength degradation <strong>of</strong> members <strong>and</strong> connections <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong><br />
structure (<strong>the</strong> effect <strong>of</strong> residual drift contributes about one-third to <strong>the</strong> loss in<br />
frame stability, <strong>and</strong> <strong>the</strong> remaining two-third drop is due to stiffness/strength<br />
degradation).<br />
iv. Determination <strong>of</strong> global <strong>and</strong> local collapse capacity, i.e. estimating <strong>the</strong><br />
capacity <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> structure <strong>and</strong> <strong>of</strong> its components (maximum rotation, interstorey,<br />
etc) for <strong>the</strong> defined limit states (damage <strong>and</strong> <strong>the</strong> collapse limit state).<br />
Local Drift Capacity will be determined from cyclic tests <strong>of</strong> full-size connection<br />
specimens conducted by <strong>the</strong> Laboratory <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> University <strong>of</strong> Pisa. The cyclic<br />
tests are used to determine load-deformation hysteresis <strong>behaviour</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong><br />
system <strong>and</strong> <strong>the</strong> maximum drift for which gravity loads may still be carried by<br />
<strong>the</strong> girders. This gravity-induced drift limit is reached when a low-cycle fatigue<br />
crack develops in <strong>the</strong> end plate or <strong>the</strong> load-deformation <strong>behaviour</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong><br />
moment connection has completely deteriorated. A st<strong>and</strong>ard test protocol,<br />
based on <strong>the</strong> ECCS Procedure (1986) was used for <strong>the</strong> tests. The moment vs.<br />
plastic rotation <strong>of</strong> a beam-column assembly representative <strong>of</strong> a single test is<br />
shown in Figure 4.15. The hysteretic <strong>behaviour</strong> is characterized by gradual<br />
strength degradation with increasing plastic rotation. For <strong>the</strong> specific<br />
connection tested, it appeared that <strong>the</strong> shear-carrying capacity was reached at<br />
a plastic rotation <strong>of</strong> about 0.06 radians. In order to use such data in <strong>the</strong><br />
reliability framework it is necessary to have several such tests, from which we<br />
can obtain statistics on <strong>the</strong> likely distribution <strong>of</strong> important design parameters,<br />
such as plastic rotation at peak load <strong>and</strong> plastic rotation at loss <strong>of</strong> capacity.<br />
Statistics that must be obtained include <strong>the</strong> median value <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> parameter <strong>and</strong><br />
<strong>the</strong> st<strong>and</strong>ard deviation <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> logarithm <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> values obtained from <strong>the</strong> testing.<br />
Global Drift Capacity <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> prototype building will <strong>the</strong>n be determined using <strong>the</strong><br />
non-linear pushover analysis (NLP) or <strong>the</strong> incremental dynamic analysis (IDA)<br />
procedure that is based on <strong>the</strong> use <strong>of</strong> non-linear time-history analysis. It is<br />
important that <strong>the</strong> analytical model used for determining <strong>the</strong> global drift<br />
dem<strong>and</strong> reproduces <strong>the</strong> major features <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> measured response such as<br />
sudden loss <strong>of</strong> strength. This means that <strong>the</strong> measured hysteresis <strong>behaviour</strong><br />
must be modeled reasonably well <strong>and</strong> <strong>the</strong> model must include all significant<br />
components <strong>of</strong> building stiffness, strength <strong>and</strong> damping.<br />
125