- Page 1 and 2:
CRCLEME Cooperative Research Centre
- Page 3 and 4:
Electronic copies of the publicatio
- Page 5 and 6:
and, for Tertiary continental seque
- Page 7 and 8:
2. Analysis of a Plio-Pleistocene l
- Page 9 and 10:
Table A (cont.) Basin and related s
- Page 11 and 12:
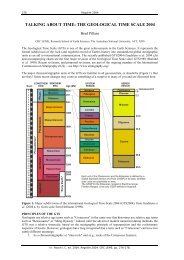
Figure A: Generalised climatic curv
- Page 13 and 14:
Carpenter, R.J., Hill, R.S., Greenw
- Page 15 and 16:
Hill, S.M., Eggleton, R.A. and Tayl
- Page 17 and 18:
Macphail, M.K. and Stone, M.S., 200
- Page 19 and 20:
Swenson, U., Backlund, McLoughlin,
- Page 22 and 23:
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY This review prese
- Page 24 and 25:
Temperature Climates in palaeo-sout
- Page 26 and 27:
SUMMARY OF INFERRED CRETACEOUS PALA
- Page 28 and 29:
INTRODUCTION Mineral resources, whe
- Page 30 and 31:
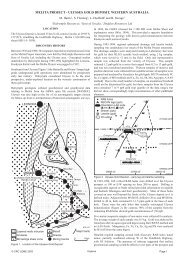
Professor B. Balme (Geology Departm
- Page 32:
Section 7 (Tertiary climates) This
- Page 35 and 36:
vegetation. Moreover, individual ta
- Page 37 and 38:
1.3 Flora, vegetation and climate 1
- Page 39 and 40:
TABLE 2: Classification of vegetati
- Page 41 and 42:
Figure 2: Relationship of different
- Page 43 and 44:
Accordingly, only at sites with exc
- Page 45 and 46:
2.1.3 Palaeoecology Palaeoecology i
- Page 47 and 48:
wind-pollinated trees and shrubs bu
- Page 49 and 50:
1. The usual practice of equating t
- Page 51 and 52:
1. Palaeontological evidence Like p
- Page 53 and 54:
5. Facies architecture and lithostr
- Page 55 and 56:
Subsequent developments include mel
- Page 58 and 59:
SECTION 4 (GEOGRAPHIC BOUNDARIES AN
- Page 60 and 61:
SECTION 5 (EARLY CRETACEOUS CLIMATE
- Page 62 and 63:
events on other continents and sugg
- Page 64 and 65:
If these considerations apply to th
- Page 66 and 67:
surrounding basins. Thick sands ero
- Page 68 and 69:
Haig and Lynch 1993, Erbacher et al
- Page 70 and 71:
SECTION 6 (LATE CRETACEOUS CLIMATES
- Page 72 and 73:
has highlighted the roles played by
- Page 74 and 75:
6.4.2 Palaeobotany Cenomanian flora
- Page 76 and 77:
Palaeo-southern Australia Dryland c
- Page 78 and 79:
6.7 Time Slice K-6. Late Campanian-
- Page 80 and 81:
7.1. Global backdrop SECTION 7 (TER
- Page 82 and 83:
Explanations for the PETM are centr
- Page 84 and 85:
East Antarctica and strengthening o
- Page 86 and 87:
amplifying, pacing and potentially
- Page 88 and 89:
southeastern Australia than elsewhe
- Page 90 and 91:
7.4 Time Slice T-1. Paleocene [65-5
- Page 92 and 93:
Palaeo-southern Australia Unlike no
- Page 94 and 95:
Palaeo-central Australia As for the
- Page 96 and 97:
7.6.2 Palaeobotany The palaeobotani
- Page 98 and 99:
Zone microfloras imply temporary wa
- Page 100 and 101:
in the Bass Basin, the basal Seaspr
- Page 102 and 103:
Similarly it is difficult to summar
- Page 104 and 105:
However, the data are emphatic that
- Page 106 and 107:
margin of plateau were cooler (~7 0
- Page 108 and 109:
fossil taxa that are morphologicall
- Page 110 and 111:
during Late Pleistocene glacial max
- Page 112 and 113:
SECTION 8 (CONCLUSIONS) Climatic in
- Page 114 and 115:
• On present indications, Early C
- Page 116 and 117:
TABLE 8a: INFERRED CRETACEOUS PALAE
- Page 118 and 119:
8.2 Results in prospect (recommenda
- Page 120 and 121:
The 10 μm sieved, oxidised extract
- Page 122 and 123:
phenology. The method also provides
- Page 124 and 125:
SECTION 9 (REFERENCES) Acton, G.D.
- Page 126 and 127:
Ashley, P.M., Duncan, R.A. and Feeb
- Page 128 and 129:
Birks, H.J.B. and Gordon, A.D., 198
- Page 130 and 131:
Burnham, R.J., 1989. Relationships
- Page 132 and 133:
Clarke, J.D.A., 1994. Evolution of
- Page 134 and 135:
Dettmann, M.E. and Playford, G., 19
- Page 136 and 137:
Evans, P.R., 1970b. Palynology of H
- Page 138 and 139:
Godthelp, H., Archer, M., Cifelli,
- Page 140 and 141:
Harris, W.K., 1974. Biostratigraphy
- Page 142 and 143:
Hill, R.S., 1994b. Nothofagus smith
- Page 144 and 145:
Holland, S.M. and Patzkowsky, M.E.,
- Page 146 and 147:
Australia: paleoceanographic implic
- Page 148 and 149:
Lindsay, J.M. and Harris, W.K., 196
- Page 150 and 151:
Macphail, M.K., Colhoun, E.A. and F
- Page 152 and 153:
McGowran, B. and Beecroft, A., 1985
- Page 154 and 155:
Morgan, R., 1977. Palynology of Ter
- Page 156 and 157:
Abstracts of the Annual General Mee
- Page 158 and 159:
Raymo, M.E., Grant, B., Horowitz, M
- Page 160 and 161:
Sereno, P.C., 1999. The evolution o
- Page 162 and 163:
Taylor, G., 1998. Prediction of mod
- Page 164 and 165:
Webb, L.G., 1968. Environmental rel
- Page 166 and 167:
Zachos, J.C., Stott, L.D. and Lohma
- Page 168 and 169:
APPENDIX 1 CRETACEOUS DATA 167
- Page 170 and 171:
1. TIME SLICE K-1 Age Range: Berria
- Page 172 and 173:
Australian assemblages, located on
- Page 174 and 175:
2. Officer Basin Dinoflagellates in
- Page 176 and 177:
2. TIME SLICE K-2 Age Range: Aptian
- Page 178 and 179:
Inferred climate The combined data
- Page 180 and 181:
Dettmann et al. (1992) have argued
- Page 182 and 183:
3. TIME SLICE K-3 Age Range: Cenoma
- Page 184 and 185:
3.2.2 North-East Australia 1. Carpe
- Page 186 and 187:
4. TIME SLICE K-4 Age Range: Turoni
- Page 188 and 189:
1. Otway Basin Limited data (Macpha
- Page 190 and 191:
5. TIME SLICE K-5 Age Range: Early
- Page 192 and 193:
Inferred climate The data indicate
- Page 194 and 195:
6. TIME SLICE K-6 Age Range: Late C
- Page 196 and 197:
Contrary to global cooling trends d
- Page 198 and 199:
Inferred climate The relatively goo
- Page 200 and 201:
Inferred climate As for regions to
- Page 202 and 203:
APPENDIX 2 TERTIARY DATA 201
- Page 204 and 205:
1. TIME SLICE T-1 Age Range: Paleoc
- Page 206 and 207:
also include relatively frequent No
- Page 208 and 209:
Inferred climate Some differences b
- Page 210 and 211:
Microfloras preserved in the Lower
- Page 212 and 213:
subtropical affinities are rare, hi
- Page 214 and 215:
2. TIME SLICE T-2 Age Range: Early
- Page 216 and 217:
Inferred climate Climates appear to
- Page 218 and 219:
northern New South Wales. The assem
- Page 220 and 221:
2.2.5 Central southern Australia Ha
- Page 222 and 223:
a number of distinctive Proteaceae
- Page 224 and 225:
Inferred climate The Regatta Point
- Page 226 and 227:
3. TIME SLICE T-3 Age Range: Middle
- Page 228 and 229: 2. Lake Torrens Basin Abundant leaf
- Page 230 and 231: Dominance is highly variable. For e
- Page 232 and 233: types (M.K. Macphail unpubl. data).
- Page 234 and 235: Dacrycarpus), Euphorbiaceae (Austro
- Page 236 and 237: (possibly upper mesotherm) and drie
- Page 238 and 239: Basin) on the Eyre Peninsula (Alley
- Page 240 and 241: explanation is that a warm water gy
- Page 242 and 243: several taxa, which first appear in
- Page 244 and 245: 4. TIME SLICE T-4 Age Range: Oligoc
- Page 246 and 247: Inferred climate The southern limit
- Page 248 and 249: The lowest and possibly the oldest
- Page 250 and 251: Dominants include fresh to brackish
- Page 252 and 253: Based on the relative abundance of
- Page 254 and 255: (Morgan 1977, McMinn 1981a, Martin
- Page 256 and 257: common (up to 5-6%) in the middle s
- Page 258 and 259: Polypodiaceae, Palmae (Dicolpopolli
- Page 260 and 261: Strasburgeriaceae. Proprietary info
- Page 262 and 263: Rare taxa which first appear in the
- Page 264 and 265: Correlative microfloras in the onsh
- Page 266 and 267: impression of floristic impoverishm
- Page 268 and 269: (Lophosoria) reached Tasmania befor
- Page 270 and 271: 2. Otway Basin Oxygen isotope strat
- Page 272 and 273: 5. TIME SLICE T-5 Age Range: Late M
- Page 274 and 275: Casuarinaceae, Cunoniaceae, Elaeoca
- Page 276 and 277: maximum temperature of the hottest
- Page 280: 5.2.7 Tasmania Late Neogene sedimen