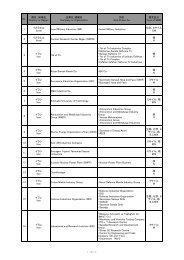
GHS Classification Guidance for the Japanese Government
GHS Classification Guidance for the Japanese Government
GHS Classification Guidance for the Japanese Government
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
whereas <strong>the</strong> reference value is set in mg/L in <strong>the</strong> column of vapour inhalation of <strong>the</strong> main body<br />
of <strong>the</strong> table since a test described as conducted <strong>for</strong> “vapour” actually has “inclusion of mist” in<br />
some cases, in which cases <strong>the</strong> concentration cannot be indicated accurately unless indicated in<br />
mg/L. The values shown here are <strong>the</strong> same as <strong>the</strong> classification reference values of gas. In text<br />
3.1.2.6.2, <strong>the</strong> same point is repeatedly described.<br />
In accordance with <strong>the</strong> gist of Note (d) of Table 3.1.1. and <strong>the</strong> text paragraph 3.1.2.6.2 of <strong>the</strong><br />
UN <strong>GHS</strong> second revised edition, classification of acute toxicity in <strong>the</strong> case of “inhalation” is<br />
per<strong>for</strong>med as follows.<br />
1) As <strong>for</strong> gas based on <strong>the</strong> definition of <strong>GHS</strong>, <strong>the</strong> category reference values (ppmV) of gas<br />
are applied.<br />
2) When an experiment is per<strong>for</strong>med at <strong>the</strong> concentration of <strong>the</strong> saturated vapour pressure or<br />
more with <strong>the</strong> vapour generated from liquids, <strong>the</strong> substance is determined as “mists”, and<br />
<strong>the</strong> category reference values of “dusts and mists” are applied.<br />
3) When an experiment is per<strong>for</strong>med at <strong>the</strong> concentration of <strong>the</strong> saturated vapour pressure or<br />
less with <strong>the</strong> vapour generated from liquids, <strong>the</strong> substance is handled as “vapours”. When<br />
handled as "vapours", since <strong>the</strong>re are cases where mists are estimated to be included and<br />
where mist is estimated to be hardly included in accordance with <strong>GHS</strong>, categorization is<br />
per<strong>for</strong>med based on <strong>the</strong> following a) to d).<br />
a) When mists are estimated to be included, categorization is per<strong>for</strong>med based on <strong>the</strong><br />
reference values in <strong>the</strong> unit of mg/L shown in <strong>the</strong> row of “vapours” in <strong>the</strong> Table.<br />
b) When mist is estimated to be hardly included, categorization is per<strong>for</strong>med based on <strong>the</strong><br />
reference values (<strong>the</strong> same values as <strong>for</strong> gases) in <strong>the</strong> unit of ppmV shown in <strong>the</strong> Note<br />
(d) of Table 3.1.1<br />
c) When <strong>the</strong> ATE(LC50)value obtained from a test is between <strong>the</strong> value <strong>for</strong> <strong>the</strong> saturated<br />
vapour pressure concentration of <strong>the</strong> substance and a value corresponding to that of <strong>the</strong><br />
saturated vapour pressure concentration, <strong>the</strong> substance is determined as “vapour with<br />
included mists” with consideration of <strong>the</strong> possibility of mist inclusion, and 1) is applied.<br />
In case of lower concentration, <strong>the</strong> substance is determined as “vapour with hardly<br />
included mist”, and 2) is applied.<br />
d) When description in a document is in mg/L, values <strong>the</strong>rein are converted into those in<br />
ppmV based on <strong>the</strong> molecular weight and temperature, and <strong>the</strong> above method is applied.<br />
If <strong>the</strong> temperature during <strong>the</strong> inhalation test is not described, <strong>the</strong> unit conversion is<br />
per<strong>for</strong>med by assuming that <strong>the</strong> temperature is 25°C and <strong>the</strong> volume of gas of 1 mole is<br />
24.45 L.<br />
4) When it is described that a test is conducted definitely <strong>for</strong> “mists”, <strong>the</strong> substance tested is<br />
treated as mist.<br />
5) Since it is also presumed that vapour generated from solid is inhaled, <strong>the</strong> vapour which is<br />
112