eq-ees-teacher-evaluation
eq-ees-teacher-evaluation eq-ees-teacher-evaluation
Title Description Teacher- Student relationships (d=0.72) Classroom Behavioral (d=0.71) Spaced vs. Mass practice (d=0.71) Meta-cognitive strategies (d=0.69) Interestingly, “when students, parents, teachers and principals were asked about what influences student achievement, all BUT the teachers emphasized the relationships between the teachers and the students.” “Building relationships implies agency, efficacy, respect by the teacher for what the student brings to the class (from home, culture, and peers) and recognition of the life of the student.”Facilitate student development by demonstrating that they care for the learning of each as a person Enforce specific and reasonable set of classroom rules increasing student control over himself/herself Frequency of different learning opportunities; three to four exposures to learning over several days before learning occurs. Spacing the practice of skills over a long period of time. Thinking about thinking; plan how to approach a given learning task; evaluate progress; monitor comprehension. Self-questioning is an example. ST 1 ST 2 ST 3 ST 4 ST 5 ST 6 ST 7 ST 8 ST 9 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 5 6 1 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 5 6 1 2 3 1 2 3 x x Hattie, John. (2009) Visible Learning: A Synthesis of over 800 meta-analyses relating to Achievement. New York: Routledge. x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
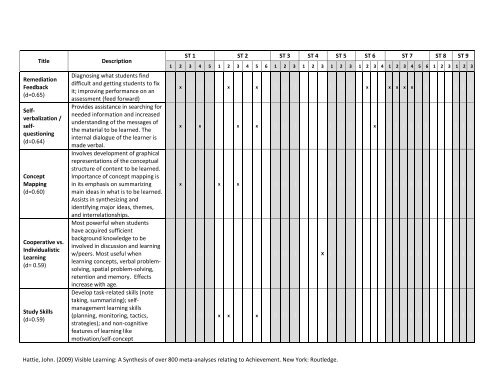
Title Description Remediation Feedback (d=0.65) Selfverbalization / selfquestioning (d=0.64) Concept Mapping (d=0.60) Cooperative vs. Individualistic Learning (d= 0.59) Study Skills (d=0.59) Diagnosing what students find difficult and getting students to fix it; improving performance on an assessment (feed forward) Provides assistance in searching for needed information and increased understanding of the messages of the material to be learned. The internal dialogue of the learner is made verbal. Involves development of graphical representations of the conceptual structure of content to be learned. Importance of concept mapping is in its emphasis on summarizing main ideas in what is to be learned. Assists in synthesizing and identifying major ideas, themes, and interrelationships. Most powerful when students have acquired sufficient background knowledge to be involved in discussion and learning w/peers. Most useful when learning concepts, verbal problemsolving, spatial problem-solving, retention and memory. Effects increase with age. Develop task-related skills (note taking, summarizing); selfmanagement learning skills (planning, monitoring, tactics, strategies); and non-cognitive features of learning like motivation/self-concept ST 1 ST 2 ST 3 ST 4 ST 5 ST 6 ST 7 ST 8 ST 9 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 5 6 1 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 5 6 1 2 3 1 2 3 x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x Hattie, John. (2009) Visible Learning: A Synthesis of over 800 meta-analyses relating to Achievement. New York: Routledge. X
- Page 173 and 174: Standard 2: Student Learning, Growt
- Page 175 and 176: MDQ 3.19 When the content involves
- Page 177 and 178: Standard 2: Student Learning, Growt
- Page 179 and 180: Standard 3: Curriculum Implementati
- Page 181 and 182: MDQ 2.11 The teacher asks inferenti
- Page 183 and 184: MDQ 4.22 The teacher engages them i
- Page 185 and 186: MDQ 2.10 During breaks in the prese
- Page 187 and 188: Standard 4: Critical Thinking Teach
- Page 189 and 190: MDQ 3.19 When the content involves
- Page 191 and 192: MDQ 5.24 The teacher scans the room
- Page 193 and 194: MD4.56 The teacher interacts with s
- Page 195 and 196: MDQ 5.25 The teacher uses academic
- Page 197 and 198: Standard 5: Positive Classroom Envi
- Page 199 and 200: Standard 6: Effective Communication
- Page 201 and 202: Standard 6: Effective Communication
- Page 203 and 204: Standard 6: Effective Communication
- Page 205 and 206: MDQ 4.21 The teacher organizes the
- Page 207 and 208: Standard 7: Student Assessment and
- Page 209 and 210: Standard 7: Student Assessment and
- Page 211 and 212: Standard 7: Student Assessment and
- Page 213 and 214: MD3.54 The teacher monitors and cha
- Page 215 and 216: Standard 8: Professionalism Teacher
- Page 217 and 218: Standard 9: Professional Collaborat
- Page 219 and 220: Research and Proven Practices of Dr
- Page 221 and 222: Hattie: Visible Learning Rank / Eff
- Page 223: Direct Instruction (d=0.82) Title D
- Page 227 and 228: Title Description Home Factors (d=0
- Page 229 and 230: Computerassisted instruction (d=0.3
- Page 231 and 232: Teacher Growth Guide 1.1 - Hattie R
- Page 233 and 234: Growth Guide 1.2 - Hattie Research
- Page 235 and 236: Standard 1: Content knowledge align
- Page 237 and 238: Growth Guide 1.5 - Hattie Research
- Page 239 and 240: Study Skills (.59 effect size) Deve
- Page 241 and 242: Standard 2: Student Learning, Growt
- Page 243 and 244: Standard 2: Student Learning, Growt
- Page 245 and 246: Meta-cognitive strategies (.69 effe
- Page 247 and 248: Standard 3: Curriculum Implementati
- Page 249 and 250: Standard 3: Curriculum Implementati
- Page 251 and 252: Standard 4: Critical Thinking Growt
- Page 253 and 254: Standard 5: Positive Classroom Envi
- Page 255 and 256: Standard 5: Positive Classroom Envi
- Page 257 and 258: Standard 6: Effective Communication
- Page 259 and 260: Standard 6: Utilizing Effective Com
- Page 261 and 262: Standard 7: Student Assessment and
- Page 263 and 264: Standard 7: Student Assessment and
- Page 265 and 266: Standard 7: Student Assessment and
- Page 267 and 268: Standard 8: Professionalism Quality
- Page 269 and 270: Standard 9: Professional Collaborat
- Page 271 and 272: Standard 9: Professional Collaborat
- Page 273 and 274: Introduction to Teach Like a Champi
Title Description<br />
Remediation<br />
Feedback<br />
(d=0.65)<br />
Selfverbalization<br />
/<br />
selfquestioning<br />
(d=0.64)<br />
Concept<br />
Mapping<br />
(d=0.60)<br />
Cooperative vs.<br />
Individualistic<br />
Learning<br />
(d= 0.59)<br />
Study Skills<br />
(d=0.59)<br />
Diagnosing what students find<br />
difficult and getting students to fix<br />
it; improving performance on an<br />
assessment (feed forward)<br />
Provides assistance in searching for<br />
needed information and increased<br />
understanding of the messages of<br />
the material to be learned. The<br />
internal dialogue of the learner is<br />
made verbal.<br />
Involves development of graphical<br />
representations of the conceptual<br />
structure of content to be learned.<br />
Importance of concept mapping is<br />
in its emphasis on summarizing<br />
main ideas in what is to be learned.<br />
Assists in synthesizing and<br />
identifying major ideas, themes,<br />
and interrelationships.<br />
Most powerful when students<br />
have acquired sufficient<br />
background knowledge to be<br />
involved in discussion and learning<br />
w/peers. Most useful when<br />
learning concepts, verbal problemsolving,<br />
spatial problem-solving,<br />
retention and memory. Effects<br />
increase with age.<br />
Develop task-related skills (note<br />
taking, summarizing); selfmanagement<br />
learning skills<br />
(planning, monitoring, tactics,<br />
strategies); and non-cognitive<br />
features of learning like<br />
motivation/self-concept<br />
ST 1 ST 2 ST 3 ST 4 ST 5 ST 6 ST 7 ST 8 ST 9<br />
1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 5 6 1 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 3 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 5 6 1 2 3 1 2 3<br />
x x x x x x x x<br />
x x x x x<br />
x x x<br />
x x x<br />
Hattie, John. (2009) Visible Learning: A Synthesis of over 800 meta-analyses relating to Achievement. New York: Routledge.<br />
X