Spanish 3 – Unit 4 Patterns Study Sheet
Spanish 3 – Unit 4 Patterns Study Sheet Spanish 3 – Unit 4 Patterns Study Sheet
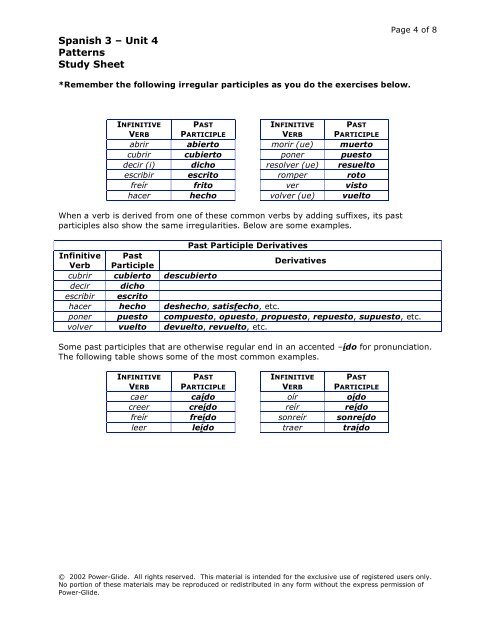
Spanish 3 – Unit 4 Patterns Study Sheet *Remember the following irregular participles as you do the exercises below. INFINITIVE PAST INFINITIVE PAST VERB PARTICIPLE VERB PARTICIPLE abrir abierto morir (ue) muerto cubrir cubierto poner puesto decir (i) dicho resolver (ue) resuelto escribir escrito romper roto freír frito ver visto hacer hecho volver (ue) vuelto When a verb is derived from one of these common verbs by adding suffixes, its past participles also show the same irregularities. Below are some examples. Page 4 of 8 Infinitive Verb Past Participle Past Participle Derivatives Derivatives cubrir cubierto descubierto decir dicho escribir escrito hacer hecho deshecho, satisfecho, etc. poner puesto compuesto, opuesto, propuesto, repuesto, supuesto, etc. volver vuelto devuelto, revuelto, etc. Some past participles that are otherwise regular end in an accented –ído for pronunciation. The following table shows some of the most common examples. INFINITIVE PAST INFINITIVE PAST VERB PARTICIPLE VERB PARTICIPLE caer caído oír oído creer creído reír reído freír freído sonreír sonreído leer leído traer traído © 2002 Power-Glide. All rights reserved. This material is intended for the exclusive use of registered users only. No portion of these materials may be reproduced or redistributed in any form without the express permission of Power-Glide.
Spanish 3 – Unit 4 Patterns Study Sheet Practice Questions To check your understanding of formation of perfect tenses and other uses of past participles, do the following exercises. A. Sentence Creation: Past Perfect or Pluperfect Page 5 of 8 Write what the following people had done before the arrival of the invited guests at a party. Use the pluperfect to describe their responsibilities in preparing for the social event. Modelo: Luis / invitar /a las personas. Luis había invitado a las personas. 1. María / traer / los refrescos. _____________________________________________________________________ 2. Josefina y Gregorio / preparar / la comida. _____________________________________________________________________ 3. Isaura / apagar / el televisor. _____________________________________________________________________ 4. Mi mamá / arreglar / la casa. _____________________________________________________________________ 5. Yo / comprar / platos de papel / vasos de papel. _____________________________________________________________________ 6. Víctor / arreglar / las sillas en la sala. _____________________________________________________________________ 7. Enrique y David / escoger/ los discos compactos. _____________________________________________________________________ 8. Tú / cortar / la carne para los tacos y enchiladas. _____________________________________________________________________ 9. Gabriela / preparar / las bebidas y los postres. _____________________________________________________________________ 10. Papá / pasar / la aspiradora. _____________________________________________________________________ © 2002 Power-Glide. All rights reserved. This material is intended for the exclusive use of registered users only. No portion of these materials may be reproduced or redistributed in any form without the express permission of Power-Glide.
- Page 1 and 2: Spanish 3 - Unit 4 Patterns Study S
- Page 3: Spanish 3 - Unit 4 Patterns Study S
- Page 7 and 8: Spanish 3 - Unit 4 Patterns Study S
<strong>Spanish</strong> 3 <strong>–</strong> <strong>Unit</strong> 4<br />
<strong>Patterns</strong><br />
<strong>Study</strong> <strong>Sheet</strong><br />
*Remember the following irregular participles as you do the exercises below.<br />
INFINITIVE<br />
PAST<br />
INFINITIVE<br />
PAST<br />
VERB PARTICIPLE<br />
VERB PARTICIPLE<br />
abrir abierto morir (ue) muerto<br />
cubrir cubierto poner puesto<br />
decir (i) dicho resolver (ue) resuelto<br />
escribir escrito romper roto<br />
freír frito ver visto<br />
hacer hecho volver (ue) vuelto<br />
When a verb is derived from one of these common verbs by adding suffixes, its past<br />
participles also show the same irregularities. Below are some examples.<br />
Page 4 of 8<br />
Infinitive<br />
Verb<br />
Past<br />
Participle<br />
Past Participle Derivatives<br />
Derivatives<br />
cubrir cubierto descubierto<br />
decir dicho<br />
escribir escrito<br />
hacer hecho deshecho, satisfecho, etc.<br />
poner puesto compuesto, opuesto, propuesto, repuesto, supuesto, etc.<br />
volver vuelto devuelto, revuelto, etc.<br />
Some past participles that are otherwise regular end in an accented <strong>–</strong>ído for pronunciation.<br />
The following table shows some of the most common examples.<br />
INFINITIVE<br />
PAST<br />
INFINITIVE<br />
PAST<br />
VERB PARTICIPLE<br />
VERB PARTICIPLE<br />
caer caído oír oído<br />
creer creído reír reído<br />
freír freído sonreír sonreído<br />
leer leído traer traído<br />
© 2002 Power-Glide. All rights reserved. This material is intended for the exclusive use of registered users only.<br />
No portion of these materials may be reproduced or redistributed in any form without the express permission of<br />
Power-Glide.