- Page 1 and 2:
I / The Coking Properties of Coal a
- Page 3 and 4:
Procedure : Hand picked lunips of c
- Page 5 and 6:
Apparatus: The equipment for this t
- Page 7 and 8:
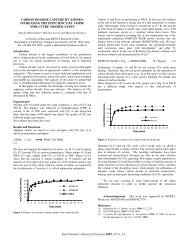
the total pressure on the swelling
- Page 9 and 10:
A comparison of the results obtaine
- Page 11 and 12:
was used, however, general trends a
- Page 13 and 14:
1 D 13 3 G
- Page 16 and 17:
Table 8 L_ Effect os FaeO Compo.lrl
- Page 18 and 19:
i-l SPARE SAblPLE Plortlc 209 Figur
- Page 20 and 21:
- z c 100,000 50,000 10,000 0 n 5,0
- Page 22 and 23:
Flnure 9 SWELLltlG PROPERTIES OF PI
- Page 24 and 25:
Fi ure 13 EFFECT OF TOTAL PRESSQRE,
- Page 26 and 27:
TABLE 1. OPERATING CONDITIONS Opera
- Page 28 and 29:
1. . 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. REFERE
- Page 30 and 31:
Figure 4. SCANNING ELECTRON MICROGR
- Page 32 and 33:
Turkgodan et al. (18) studied the p
- Page 34 and 35:
Materidl balance on packed bed Boun
- Page 36 and 37:
These phenomena iiiay be described
- Page 38 and 39: Walker, P. L., Rusinko, F., and Aus
- Page 40 and 41: -""I- *I,".. I Dlrf".,on Co.1flcl.n
- Page 42 and 43: After a variable residence time, th
- Page 44 and 45: Changes in Char Chemistry The infra
- Page 46 and 47: 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28.
- Page 48 and 49: 0s-a 00-a OS'S 00-E os-2 00-2 02.1
- Page 50 and 51: COAL PYROLYSIS AT HIGH TEMPERATURES
- Page 52 and 53: actions, decreasing the secondary c
- Page 54 and 55: 01 40 60 TI MEISeC) 80 100 120 140
- Page 56 and 57: Reaction Temperature OC In-situ Ini
- Page 58 and 59: and the gas velocity is often repre
- Page 60 and 61: The mathematical model developed he
- Page 62 and 63: si sio Fraction of solid species i
- Page 64 and 65: Table 2. Differential Equations Mod
- Page 66 and 67: 1 60 I I RUN KE-5 50 T.1121K(1557'F
- Page 68 and 69: to condense excess steam, the press
- Page 70 and 71: conversion-time data.* The integrat
- Page 72 and 73: catalyzed and uncatalyzed runs were
- Page 74 and 75: CATALYTIC EFFECTS OF ALKALI METAL S
- Page 76 and 77: %me thermogravimetric measurements
- Page 78 and 79: than in steam. Figure 9 shows data
- Page 80 and 81: C - C02 REACTION C - H20 REACTION L
- Page 82 and 83: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11.
- Page 84 and 85: n 'm L u. t m - L 84
- Page 87: i 5360-096bw \ KINETICS OF POTASSIU
- Page 91 and 92: 1 I > \ i I 5360-096bw bed data. Be
- Page 93 and 94: I 1. I 5360-096bw ranging from atmo
- Page 95 and 96: uY.ku ICHlMAlIC OF MINI-FLUID BE0 R
- Page 97 and 98: 800-12-1133 -9 FIGURE IO CALCULATED
- Page 99 and 100: Mexico coal. Table 1 shows an analy
- Page 101 and 102: ', Complete results from all runs c
- Page 103 and 104: I the methanol down to atmospheric
- Page 105 and 106: TABLE 3 -----______________________
- Page 107 and 108: \ "I N z 107 c. . 0 0
- Page 109 and 110: I. INTRODUCTION DIRECT METHANATION
- Page 111 and 112: The catalyst development program fo
- Page 113 and 114: Preparing process flow diagrams and
- Page 115 and 116: \ \ i 1. 2,000 4,000 6,000 8,000 10
- Page 117 and 118: (JMS-OlBM-2). The mass spectra were
- Page 119 and 120: I I Fairbridge, R.W. (ed.) 1972, En
- Page 121 and 122: v- W V z d 3 z m 4 ? P m W c3 W m N
- Page 123 and 124: e. \ I , W 2 m 4 t- CI 99-79 noooo
- Page 125 and 126: L Table I: Compositions of High Tem
- Page 127 and 128: \ " \ I For all three coals, the pr
- Page 129 and 130: 4 , 1024 1024 3a 3b J Mineral Parti
- Page 131 and 132: The Determination of Mineral Distri
- Page 133 and 134: pyrite crystals in framboids locate
- Page 135 and 136: FIG. 1. TEM MICROGRAPH OF A HIGH VO
- Page 137 and 138: \ \ FIG. 5. SEM MICROGRAPH SHOWING
- Page 139 and 140:
\ , species. In fact, combustion ex
- Page 141 and 142:
1, It is possible to make a reasona
- Page 143 and 144:
\ i SURFACE AND BULK ENRICHMENT OF
- Page 145 and 146:
I Coal Ash Sintering Model and the
- Page 147 and 148:
5 carried out such sintering measur
- Page 149 and 150:
I this ash and other bituminous coa
- Page 151 and 152:
forming propensity. However, none o
- Page 153 and 154:
t I 153
- Page 155 and 156:
CENTRAL ELECTRICIN RESEARCH LABORAT
- Page 157 and 158:
157 18 I I a I
- Page 159 and 160:
temperature, sulfur species concent
- Page 161 and 162:
The facility is fired with coal usi
- Page 163 and 164:
Tests have been carried out to dete
- Page 165 and 166:
under which conditions sulfur speci
- Page 167 and 168:
I TITANIUM L Corn AS A TRACER FOR D
- Page 169 and 170:
E 6 i i h \ 1 1 \ on the XRF is cau
- Page 171 and 172:
\ ? CONCLUSIONS Titanium can accura
- Page 173 and 174:
NY) m * oa
- Page 175 and 176:
GFETC constructed a 0.2 square mete
- Page 177 and 178:
\: Stage 3. Sulfated ash-cemented a
- Page 179 and 180:
I FIG. 1. Initial ash coating on qu
- Page 181 and 182:
FIG 9. Limestone bed material alter
- Page 183 and 184:
(4) Since the operating temperature
- Page 185 and 186:
I I maximum particle diameter leavi
- Page 187 and 188:
! suspension chambers and cyclone f
- Page 189 and 190:
Pilot Plant of a Coal Fired Fluidiz
- Page 191 and 192:
After the fiscal year 1982, the fol
- Page 193 and 194:
MBC CBC Fig. 1 Boiler Structure 193
- Page 195 and 196:
\ i Table 2. Coal Properties Planne
- Page 197 and 198:
-2- more than 3 years, since 1977.
- Page 199 and 200:
, I B. 2 which temporarily raised t
- Page 201 and 202:
-6- abrasion rate at the bottom of
- Page 203 and 204:
\if F3.3 - Particulate Circulation
- Page 205 and 206:
\' I/O. analog 1/13. industrial I/O
- Page 207 and 208:
ACQUISITION DATA UNIT < I L- J (T)
- Page 209 and 210:
SAMPLING SYSTEM FOR FLUIDIZED BED A
- Page 211 and 212:
GAS SAMPLING WITH ORIGINAL PROBE-FI
- Page 213 and 214:
Remove the quartz tube (gas sample
- Page 215 and 216:
' ' The modifications have been com
- Page 217 and 218:
n n D 217
- Page 219 and 220:
With regard to the similarity parti
- Page 221 and 222:
i \ ' 2.2. soz Emission and NOx Emi
- Page 223 and 224:
223
- Page 225 and 226:
Figure 9: Sulphur captLTre as 0 fun
- Page 227 and 228:
P SUMMARY OF TESTS Testing complete
- Page 229 and 230:
I Table 1 Comparison of Sulfur Capt
- Page 231 and 232:
, NITROGEN OXIDE REDUCTION Single-S
- Page 233 and 234:
0 The addition of air at the 96-inc
- Page 235 and 236:
m- Y i? 4: BO n 8 c Y l0- Bo- I I I
- Page 237 and 238:
E! w 2 z e Y 100 - 3 t 5 80- 0, 40
- Page 239 and 240:
0 f 0.so o'm: 0.300 0.zo - - A 5m 4
- Page 241 and 242:
&e- -A \ \ \ : ERCENT OVERBED AIR I
- Page 243 and 244:
PARTICLE ENTRAINMENT AND NITRIC OXI
- Page 245 and 246:
i 1' 1 ! I. i Chaung (15) showed th
- Page 247 and 248:
The maximum height that a large par
- Page 249 and 250:
3.0 Nitric Oxide Reduction in the F
- Page 251 and 252:
assumed to be identical to that of
- Page 253 and 254:
Nomenclature A *t cD ‘NO $3 _ _ _
- Page 255 and 256:
TABLE 2. OPERATING CONDITIONS AND E
- Page 257 and 258:
i 1 \ ', References 1. 2. ( 3. 1 4.
- Page 259 and 260:
\ ” Y) I 259
- Page 261 and 262:
t I 100 - - I I ] , I , I , I 'ii 9
- Page 263 and 264:
Feeding of the carbonaceous materia
- Page 265 and 266:
! Table 2 Proximate and ultimate an
- Page 267 and 268:
lb, , --pp---p-- 4 p? CHAR 1 Tu-IWO
- Page 269 and 270:
I CHAR Y Y /I TIME O i ' ' ' ' 1 '
- Page 271 and 272:
could not be assumed constant. Thus
- Page 273 and 274:
\ greatly acknowledged. Literature
- Page 275 and 276:
constructed and operated to demonst
- Page 277 and 278:
The experimental procedure for the
- Page 279 and 280:
atmospheric pressure fluidized bed
- Page 281 and 282:
1' TABLE 2 Screen Analysis of Sand
- Page 283 and 284:
n RECORDER I Ill I ’ NO. NOX THER
- Page 285 and 286:
\ 285 Y 0 I- 5 B 5 3 m "9 E5 3 uz 0
- Page 287 and 288:
CHAR1 TOC 0.85 M3/k 600 0 700 V 750
- Page 289 and 290:
f Durin all the experimental runs t
- Page 291 and 292:
Assuming that large coal particles
- Page 293 and 294:
i 7 -_ 0 m\o --n 0 W i 293 a\o 0
- Page 295 and 296:
The influence of particle size dist
- Page 297 and 298:
all the initial values of x for whi
- Page 299 and 300:
\ - + 1) x. = 1 bL/n YO Defining di
- Page 301 and 302:
$ m. 1 Results and Discussion Evalu
- Page 303 and 304:
kl k2 k' KC KD m m. m P N P R R g t
- Page 305 and 306:
UNBURNT FRACTION UNBURNT FRACTION m