liquefaction pathways of bituminous subbituminous coals andtheir
liquefaction pathways of bituminous subbituminous coals andtheir
liquefaction pathways of bituminous subbituminous coals andtheir
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
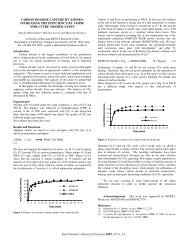
satisfactory agreement between theory and experiment, for both the<br />
lumped and MWD data, supports the validity <strong>of</strong> the explanation <strong>of</strong><br />
coal thermolytic extraction that we have proposed.<br />
conclusion<br />
A continuous-flow thrmolysis reactor, in which supercritical t-<br />
butanol contacts a differential bed <strong>of</strong> coal particles, provides<br />
sequential coal-extract samples that are analyzed by HPLC gel<br />
permeation chromatography to obtain time-dependent MWD data. The<br />
coal thermolysis experimental data support an interpretation <strong>of</strong> the<br />
results based on considering the molecular weight <strong>of</strong> extraction<br />
products as a continuous variable. This continuous-mixture theory<br />
suggests that three groups <strong>of</strong> coal components are extracted<br />
independently. At temperatures 340 OC and 360 OC the MWDs maintain<br />
a similar shape during the semibatch extraction. This indicates<br />
that first-order kinetics dominate, and that the rate coefficient is<br />
independent <strong>of</strong> molecular weight. The lumped extract concentration<br />
is monitored at the reactor exit by continuous uv-absorbance<br />
spectrophotometry. Both MWD and lumped concentration data are<br />
described by consistent expressions based on the same rate<br />
coefficient .<br />
Acknowledgements<br />
The financial support <strong>of</strong> Pittsburgh Energy Technology Center<br />
Grant No. DOE DE-FG22-90PC90288, and the University <strong>of</strong> California<br />
UERG is gratefully acknowledged.<br />
References<br />
R. Aris, I8Reactions in Continuous Mixtures," AIChE J. 35, 539<br />
(1989).<br />
Abramowitz, M. and I. A. Stegun, Handbook <strong>of</strong> Mathematical Functions,<br />
NBS, Chap. 26 (1968).<br />
Bartle, K. D., M. J. Mulligan, N. Taylor, T. G. Martin, C. E. Snape,<br />
"Molecular Mass Calibration in Size-Exclusion Chromatography <strong>of</strong> Coal<br />
Derivatives," Fuel, 63, 1556 (1984).<br />
Darivakis, G. S., W. A. Peters, J. B. Howard, "Rationalization for<br />
the Molecular Weight Distributions <strong>of</strong> Coal Pyrolysis Liquids,'* AIChE<br />
- J. 36, 1189 (1990).<br />
Ho, T. C. , R. Aris, "On Apparent Second-Order Kinetics," AIChE J.<br />
33, 1050 (1987).<br />
Zhang, C., J. M. Smith, B. J. McCoy, "Kinetics <strong>of</strong> Supercritical<br />
Fluid Extraction <strong>of</strong> Coal: Physical and Chemical Processes,*f ACS<br />
SvmDosium on SuDercritical Fluids, in press (1992).<br />
643