- Page 1 and 2:
BOTANY Higher Secondary Second Year
- Page 3 and 4:
Preface The most important and cruc
- Page 5 and 6:
1. Taxonomy PRACTICALS (30 periods)
- Page 7 and 8:
1. TAXONOMY OF ANGIOSPERMS Taxonomy
- Page 9 and 10:
compared to perianth with two whorl
- Page 11 and 12:
a total variety or species. To conc
- Page 13 and 14:
well known system of classification
- Page 15 and 16:
Self Evaluation I . Choose and writ
- Page 17 and 18:
Series (iii) Calyciflorae It includ
- Page 19 and 20:
Class III Monocotyledonae Seeds of
- Page 21 and 22:
5. How many families were described
- Page 23 and 24:
Flower Bracteate or ebracteate, bra
- Page 25 and 26:
A twig Sepal Epicalyx Calyx A petal
- Page 27 and 28: Self evaluation I . Choose and writ
- Page 29 and 30: Inflorescence Usually a raceme eg.
- Page 31 and 32: Calyx Ovary Gynoecium Bracteole Flo
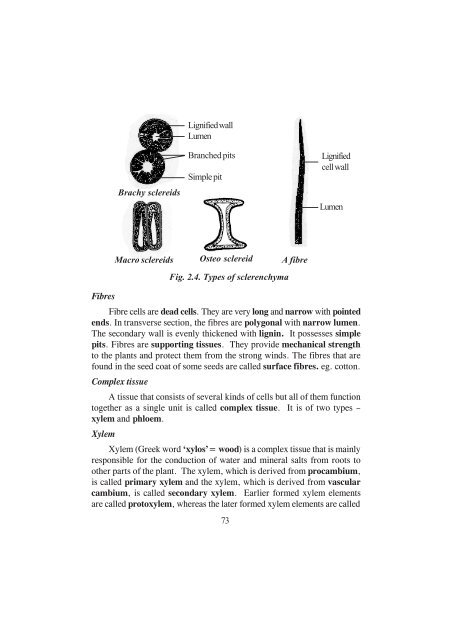
- Page 33 and 34: 5. Fibre plants Fibres obtained fro
- Page 35 and 36: 1.3.3. RUBIACEAE - the coffee famil
- Page 37 and 38: Stem Leaf Aerial, erect, branched,
- Page 39 and 40: 1. Beverage plants ECONOMIC IMPORTA
- Page 41 and 42: 1.3.4. ASTERACEAE - the sunflower f
- Page 43 and 44: Habit Root Stem Leaf Botanical desc
- Page 45 and 46: Fruit Seed A cypsela. Non-endosperm
- Page 47 and 48: Self evaluation I . Choose and writ
- Page 49 and 50: Flower Bracteate (eg. Petunia hybri
- Page 51 and 52: Stamen Epipetalous stamens T.S. of
- Page 53 and 54: Self evaluation I . Choose and writ
- Page 55 and 56: (eg. Jatropha curcas). In xerophyti
- Page 57 and 58: Perianth Tepals 5, arranged in sing
- Page 59 and 60: 1. Food plants ECONOMIC IMPORTANCE
- Page 61 and 62: MONOCOT FAMILY 1.3.7 MUSACEAE - the
- Page 63 and 64: Habit Root Stem Botanical descripti
- Page 65 and 66: Androecium Stamens 6, in two whorls
- Page 67 and 68: 1.3.8. ARECACEAE - the palm family
- Page 69 and 70: Habit Botanical description of Coco
- Page 71 and 72: Gynoecium Absent but pistillode is
- Page 73 and 74: II. Answer the following questions
- Page 75 and 76: Classification of meristem Based on
- Page 77: oval, spherical, rectangular, cylin
- Page 81 and 82: Tracheid conducting elements in ang
- Page 83 and 84: a lining layer of cytoplasm. This i
- Page 85 and 86: 2. Epidermis protects the underlyin
- Page 87 and 88: made up of barrel shaped parenchyma
- Page 89 and 90: 2.2. Anatomy of monocot and dicot r
- Page 91 and 92: The endodermal cells, which are opp
- Page 93 and 94: Cortex Cortex consists of only pare
- Page 95 and 96: II. Answer the following questions
- Page 97 and 98: Ground plan A sector enlarged Fig.
- Page 99 and 100: Ground plan A sector enlarged Fig.
- Page 101 and 102: Xylem Xylem consists of xylem fibre
- Page 103 and 104: 2.4. Anatomy of a dicot and monocot
- Page 105 and 106: Vascular tissues Vascular tissues a
- Page 107 and 108: II. Answer the following questions
- Page 109 and 110: 1. Formation of interfascicular cam
- Page 111 and 112: Formation of periderm As secondary
- Page 113 and 114: Each annual ring refers to one year
- Page 115 and 116: 8. What are complementary cells? 9.
- Page 117 and 118: chromosome has one centromere and t
- Page 119 and 120: Chromosomal puff Dark band inter ba
- Page 121 and 122: The genome size of an individual is
- Page 123 and 124: ound pollen (bbll). All the F1 hybr
- Page 125 and 126: points called chiasmata. Crossing o
- Page 127 and 128: 3.4. Recombination of chromosome Th
- Page 129 and 130:
Point or gene mutation Point mutati
- Page 131 and 132:
II. Answer the following questions
- Page 133 and 134:
127 Fig. 3.6 Chromosomal aberration
- Page 135 and 136:
Autopolyploidy Ploidy - flow chart
- Page 137 and 138:
Self evaluation I . Choose and writ
- Page 139 and 140:
cells was injected into the mouse,
- Page 141 and 142:
Replication fork Super coil DNA pol
- Page 143 and 144:
3.8. Structure of RNA and its types
- Page 145 and 146:
Role of RNA in protein synthesis Th
- Page 147 and 148:
The transfer of message present in
- Page 149 and 150:
IV. Answer the following questions
- Page 151 and 152:
to join DNA fragments. Thus the res
- Page 153 and 154:
Ti plasmid T-DNA Foreign DNA Bacter
- Page 155 and 156:
Restriction enzyme and ligase do no
- Page 157 and 158:
4.2 Transgenic plants Introduction
- Page 159 and 160:
introducing Bt toxin gene in cotton
- Page 161 and 162:
2. The number of transgenic plants
- Page 163 and 164:
Pot plant Explant Inoculation Surfa
- Page 165 and 166:
. Embryogenesis Formation of embryo
- Page 167 and 168:
II. Answer the following questions
- Page 169 and 170:
Strain A Strain B Isolation of prot
- Page 171 and 172:
The term ‘single cell protein’
- Page 173 and 174:
8. What is PEG? 9. How do you remov
- Page 175 and 176:
Many enzymes consists of a protein
- Page 177 and 178:
5.1.3. Theories explaining the mech
- Page 179 and 180:
II. Answer the following questions
- Page 181 and 182:
5.2.1. Significance of photosynthes
- Page 183 and 184:
The reactions of photosynthesis can
- Page 185 and 186:
179 Fig. 5.8. Non-cyclic photophosp
- Page 187 and 188:
Difference between cyclic and noncy
- Page 189 and 190:
power NADPH 2 . So, two molecules o
- Page 191 and 192:
Fig.5.11 Hatch-Slack pathway of CO
- Page 193 and 194:
Difference between C 3 and C 4 phot
- Page 195 and 196:
Glycine molecules enter into mitoch
- Page 197 and 198:
Among leaf factors, such as leaf ag
- Page 199 and 200:
Epiphyte eg. Vanda Aerial root Part
- Page 201 and 202:
When an insect is attracted by the
- Page 203 and 204:
11. The gas evolved during photosyn
- Page 205 and 206:
40. Explain the test tube and funne
- Page 207 and 208:
201 Fig. 5.17 Overall scheme of res
- Page 209 and 210:
Fig. 5.18 Process of Glycolysis 203
- Page 211 and 212:
decarboxylation and dehydrogenation
- Page 213 and 214:
9. The malic acid is oxidized to ox
- Page 215 and 216:
is fixed in the vertical position w
- Page 217 and 218:
Nonoxidative phase In this phase, v
- Page 219 and 220:
Respiratory quotient for anaerobic
- Page 221 and 222:
5. Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate is cle
- Page 223 and 224:
32. Write short notes on anaerobic
- Page 225 and 226:
this phase is called lag phase. It
- Page 227 and 228:
Physiological effects of auxin Auxi
- Page 229 and 230:
endosperm of coconut. Cytokinin occ
- Page 231 and 232:
4. Bakanae disease in paddy is caus
- Page 233 and 234:
5.5. Photoperiodism and vernalizati
- Page 235 and 236:
c. sunflower d. maize 4. Which of t
- Page 237 and 238:
1. To develop more food crops 2. To
- Page 239 and 240:
Clonal selection Crops like sugarca
- Page 241 and 242:
The haploid individual plant will h
- Page 243 and 244:
methods new improved crops are obta
- Page 245 and 246:
6.2. Crop diseases and their contro
- Page 247 and 248:
Pathogen The mycelium of Cercospora
- Page 249 and 250:
3. They also bring about considerab
- Page 251 and 252:
It is hoped that one day geneticall
- Page 253 and 254:
2. The genetic resources of the dev
- Page 255 and 256:
This will affect millions of uneduc
- Page 257 and 258:
additives. It depends upon crop rot
- Page 259 and 260:
COMMONLY AVAILABLE MEDICINAL PLANTS
- Page 261 and 262:
urinary infections, tuberculosis, m
- Page 263 and 264:
Groundnut oil is used to a limited