Diagnosis and FTC by Prof. Blanke [pdf] - NTNU
Diagnosis and FTC by Prof. Blanke [pdf] - NTNU
Diagnosis and FTC by Prof. Blanke [pdf] - NTNU
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
35<br />
36<br />
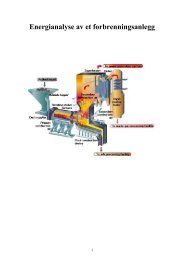
Models of dynamical systems<br />
• Notation for nonlinear system with faults<br />
The general, nonlinear case reads:<br />
dx() t<br />
= gx ( ( t), u( t), d( t), f( t)),<br />
x(0) = x0<br />
dt<br />
y() t = h( x(), t u(), t d(),()) t f t<br />
where x is state vector, u is input vector,<br />
d is disturbance vector <strong>and</strong> f(t)<br />
a fault vector.<br />
Models of dynamical systems<br />
Mogens <strong>Blanke</strong> – Spring 2006<br />
We obtain a linar model in a point of operation<br />
xudf , , , <strong>by</strong> Taylor expansion around x = x- x<br />
dx dx dx ∂g∂ ∂ ∂<br />
= + = + <br />
g<br />
+ <br />
g<br />
+ g<br />
gxudf ( , , , ) x u d+ f,<br />
dt dt dt ∂x∂u∂d∂f x(0) = x0...<br />
∂h ∂h ∂h ∂<br />
= + = ( , , , ) + + + h<br />
y y y h x u d f x u d + f<br />
∂x ∂u ∂d ∂f<br />
or<br />
x = Ax + Bu + E + <br />
xd Fxf y = Cx + Du + E + <br />
yd Fyf In the sequel, we ommit the x notation <strong>and</strong> just write x<br />
Mogens <strong>Blanke</strong> – Spring 2006<br />
18


![Diagnosis and FTC by Prof. Blanke [pdf] - NTNU](https://img.yumpu.com/12483948/18/500x640/diagnosis-and-ftc-by-prof-blanke-pdf-ntnu.jpg)