Organ Specific Guide - Raintree Nutrition, Inc
Organ Specific Guide - Raintree Nutrition, Inc
Organ Specific Guide - Raintree Nutrition, Inc
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
AMAZON BRAIN SUPPORT<br />
Description: A synergistic formula of rainforest botanicals traditionally used in South America to support<br />
memory and brain function.<br />
Traditional uses by organ or system: Brain/CNS: For memory loss, dementia, and Alzheimer's.<br />
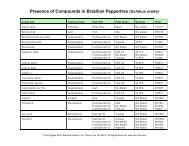
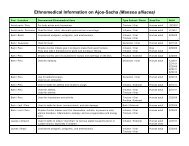
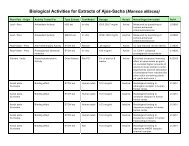
Ingredients: A proprietary blend of samambaia (Polypodium decumanum), calaguala (Polypodium leucotomos),<br />
tamamuri (Brosimum acutifolium), catuaba (Erythroxylum catuaba), muira puama (Ptychopetalum<br />
olacoides), cat’s claw (Uncaria tomentosa), suma (Pfaffia paniculata), guaraná (Paullinia cupana), nettle<br />
(Urtica dioica), and sarsaparilla (Smilax officinalis).<br />
Suggested Use: Take 2 capsules 2-3 times daily.<br />
Contraindications: Not to be used during pregnancy or while breast-feeding.<br />
Drug Interactions: None known.<br />
Other Practitioner Observations and Possible Precautions: None.<br />
Synopsis of research: (Please the online Tropical Plant Database for all cited research.)<br />
• Samambaia and calaguala are closely related Polypodium ferns which have demonstrated neuroprotective<br />
actions. In 1997, a U.S. patent was filed on a samambaia extract capable of treating brain disorders<br />
such as Alzheimer’s disease and dementia. The patent and several in vivo clinical studies indicate<br />
samambaia protects against brain cell degeneration, promotes repair of damaged brain cells, and has<br />
a protective effect to brain cells. In a double-blind placebo human trial in 2000, researchers reported<br />
patients with senile dementia improved cognitive performance, increased the blood supply to the brain,<br />
and also increased the electrical impulses in the brain. A calaguala patented product called anapsos is<br />
now used in Spain and Europe for the treatment of Alzheimer’s and dementia.<br />
• Tamamuri has been documented as a PKC inhibitor. Too much PKC enzyme is involved in a wide variety<br />
of disease processes including brain tumors and brain disorders, cancer, cardiovascular disease,<br />
arthritis, and autoimmune disorders.<br />
• Catuaba is traditionally used in Brazil as a nervine and to enhance memory. In a 2005 study catuaba was<br />
reported to provide dopaminergic-mediated antidepressant actions.<br />
• Muira puama is the subject of eight animal and human studies which reports memory enhancement,<br />
learning enhancement, antidepressant, nervine, and neuroprotective actions.<br />
• Cat's claw contains amyloid-inhibiting compounds which are the subject of three U.S. patents. Amyloid<br />
plaque in brain cells is implicated in Alzheimer's disease. In addition, another study with mice indicated<br />
that cat's claw memory enhancement action was linked to actions noted on 5-HT2 receptors.<br />
• Suma is the subject of two animal studies (in 2004 and 2000) which reported that it promoted an increase<br />
in both learning and memory in aged mice treated.<br />
• Guaraná is the subject of 6 human and animal studies concerning memory enhancement and cognitive<br />
performance. In a 2007 double-blind, placebo-controlled, multi-dose human evaluation study, guaraná<br />
improved secondary memory performance and increased alert and content mood ratings. Lower doses<br />
(75 mg) produced more positive cognitive effects than higher doses.<br />
• Nettle was found to be an effective antioxidant and possible antiapoptotic supplement promoting brain<br />
cell survival in a rat study reported in 2005.<br />
• Sarsaparilla, and several of its chemical constituents, were reported to provide protection of amyloid beta<br />
protein-induced neurotoxicity in several recent studies in rats. One of sarsparilla's main sapogenin<br />
chemicals, sarsasapogenin, was reported to improve memory by elevating the low muscarinic<br />
acetylcholine receptor density in brains of memory-deficit rats. This chemical, as well as others in<br />
sarsaparilla, are the subject of a 2004 U.S. patent which claim they are effective in the treatment of<br />
Alzheimer's disease.