Organ Specific Guide - Raintree Nutrition, Inc
Organ Specific Guide - Raintree Nutrition, Inc
Organ Specific Guide - Raintree Nutrition, Inc
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
AMAZON MENOPAUSE SUPPORT<br />
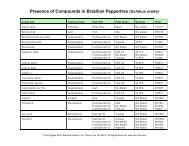
Description: A botanical formula which combines 8 plants used in traditional herbal medicine systems in<br />
South America for women during menopause.<br />
Traditional uses by organ or system: Hormonal/Reproductive: For symptoms associated with<br />
menopause.<br />
Ingredients: A proprietary blend of maca (Lepidium meyenii), suma (Pfaffia paniculata), cumaseba<br />
(Swartzia polyphylla), espinheira santa (Maytenus ilicifolia), black cohosh (Cimicifuga racemosa), chuchuhuasi<br />
(Maytenus krukovii), sarsaparilla (Smilax officinalis), muira puama (Ptychopetalum olacoides),<br />
damiana (Turnera aphrodisiaca), and passionflower (Passiflora incarnata).<br />
Suggested Use: Take 2-3 capsules twice daily or as needed.<br />
Contraindications:<br />
• Not to be used during pregnancy or while breast-feeding.<br />
• Not to be used by women with estrogen-positive cancers.<br />
Drug Interactions: None reported, however it may potentiate hypotensive medications.<br />
Other Practitioner Observations and Possible Precautions: None.<br />
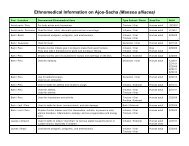
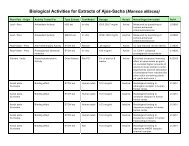
Synopsis of research: (Please the online Tropical Plant Database for all cited research.)<br />
• Maca is widely touted for hormonal balancing, endocrine and thyroid function enhancement, and even<br />
immune system enhancement. These claims are likely related to maca's amino acid and nutrient content.<br />
The endocrine system drives many functions in the body, including the production of many types of<br />
hormones. Although hormones are chemically diverse, they are constructed simply from amino acids and<br />
cholesterol. If given sufficient levels of starting materials (natural amino acids), the body may use them<br />
as needed to construct hormones which keep the body in balance.<br />
• Suma has a long history of traditional use for menopausal symptoms. The plant is a rich source of phytosterols<br />
including sitosterol, stigmasterol, and beta-ecdysterone which are believed to encourage hormone<br />
production. Researchers reported in 2003 that mice fed suma for 30 days had higher levels of the sex<br />
hormones, estradiol-17beta, progesterone and testosterone, than controls.<br />
• Cumaseba is rich is flavonoids and isoflavones. It contains a significant amount of an isoflavone<br />
chemical called biochanin A which has been well studied and documented (over 150 studies published<br />
to date). Biochanin A is a phytoestrogen which is found in other plants like red clover.<br />
• Espinheira santa has been reported with estrogenic actions. One study indicated that it interfered in<br />
fertilization and implantation in non-pregnant rats. A study in 2002 confirmed these results, again stating<br />
that a leaf extract had estrogenic actions, which suggested the anti-fertility effect may be the interference<br />
of uterine receptivity to the embryo, but did not induce abortions or have any embyrotoxic effects.<br />
• Black cohosh has shown in laboratory research that it can bind to estrogen receptors in rat uteri and<br />
pituitary glands. Another study showed it inhibited LH secretion but did not bind to estrogen receptors;<br />
but a chemical fraction did inhibit LH after a single acute injection; with single injections of estradiol<br />
showing a similar activity profile.<br />
• Chuchuhuasi is considered in Peruvian herbal medicine to be a tonic, adpatogenic, muscle relaxant,<br />
antispasmodic, aphrodisiac, analgesic, and anti-inflammatory. It is used for menopausal symptoms,<br />
menstrual balance and regulation, adrenal support, and as an overall tonic and immunostimulant.<br />
• Sarsaparilla is a rich source of phytosterols. It contains the plant steroids sarsasapogenin, smilagenin,<br />
sitosterol, stigmasterol, and pollinastanol. Some of the most recent research focuses on neuroprotective<br />
and memory enhancement actions of several of these phytosterols.<br />
• Muira puama is traditionally used in South America for menopausal symptoms and one study published<br />
in 2000 with menopausal women validates this traditional use.<br />
• Damiana has a long history of traditional use for depression, anxiety, sexual inadequacy, fatigue and<br />
menstrual irregularities.<br />
• Passionflower has a long history in herbal medicine for its calming and nervine properties and western<br />
research has validated these uses in various studies over the years.