- Page 2 and 3:
This page was intentionally left bl
- Page 4 and 5:
DISCLAIMER: The information in this
- Page 6 and 7:
TABLE OF CONTENTS Disclaimer ......
- Page 8 and 9:
Undaria pinnatifida ...............
- Page 10 and 11:
Diadumene leucolena ...............
- Page 12 and 13:
Hyboscolex longiseta ..............
- Page 14 and 15:
Watersipora subtorquata ...........
- Page 16 and 17:
Littoridinops monroensis ..........
- Page 18 and 19:
Halophiloscia couchii .............
- Page 20 and 21:
Amphibalanus amphitrite ...........
- Page 22 and 23:
Botrylloides diegensis ............
- Page 24 and 25:
Salmo trutta ......................
- Page 26 and 27:
Figure 45: Mollusca-Gastropoda: Num
- Page 28 and 29:
INTRODUCTION Overview Marine and es
- Page 30 and 31:
APPROACH AND DEFINITIONS Marine Bio
- Page 32 and 33:
Unknown: A species was classified a
- Page 34 and 35:
new species. In these cases, the pa
- Page 36 and 37:
accumulate in rocky intertidal tide
- Page 38 and 39:
the second most invaded. The Northe
- Page 40 and 41:
history of the species but not whet
- Page 42 and 43:
MAPS OF MEOW REGIONS Figure 1: Map
- Page 44 and 45:
Figure 3: Maps in geographic projec
- Page 46 and 47: Figure 5: Map of the Northwest Paci
- Page 48 and 49: Figure 7: Map of the Eastern Indo-P
- Page 50 and 51: Figure 9: Map of the Tropical Easte
- Page 52 and 53: Figure 11: Map of the Magellanic re
- Page 54 and 55: Figure 13: Map of the West Tropical
- Page 56 and 57: Figure 15: Map of the Northeast Atl
- Page 58 and 59: Figure 17: Map of the Ponto-Caspian
- Page 60 and 61: Figure 19: Map of the Southern Afri
- Page 62 and 63: Figure 21: Map of the Southern Aust
- Page 64 and 65: Figure 23: Alternate map in polar s
- Page 66 and 67: 250 200 150 100 50 0 N = 747 10 55
- Page 68 and 69: 25 20 15 10 2 6 Figure 30: Phylum B
- Page 70 and 71: 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 0 0 Figure 38: Cnidar
- Page 72 and 73: 140 120 100 Figure 46: Phylum Arthr
- Page 74 and 75: Figure 54: Arthropoda-Insecta: Numb
- Page 76 and 77: DECIPHERING SPECIES INFORMATION: KE
- Page 78 and 79: TABLES Table Key to Species Profile
- Page 80 and 81: Attribute / Level in Species Profil
- Page 82 and 83: Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 Definition
- Page 84 and 85: Ecosystems Table 4: Definitions for
- Page 86 and 87: Major Habitat Type: Level 1 Ecosyst
- Page 88 and 89: Depth Table 5: Definitions for the
- Page 90 and 91: Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 Definition
- Page 92 and 93: Salinity Table 7: Definitions for t
- Page 94 and 95: Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 Level 4 Exp
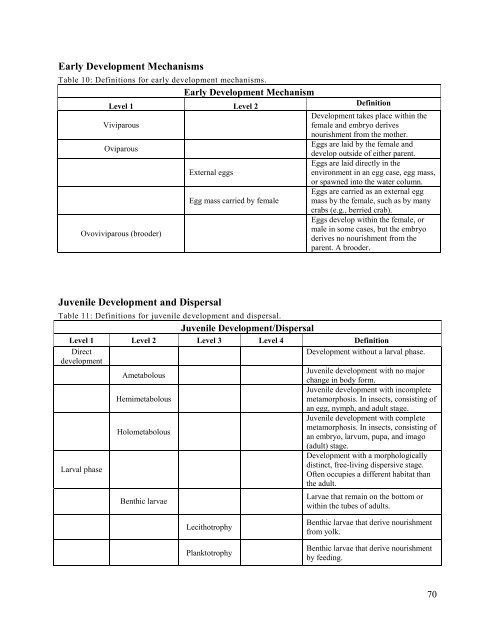
- Page 98 and 99: Juvenile Development/Dispersal Leve
- Page 100 and 101: Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 Level 4 Def
- Page 102 and 103: Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 Level 4 Def
- Page 104 and 105: 77 This page was intentionally left
- Page 106 and 107: Claviceps purpurea var. spartinae P
- Page 108 and 109: Cytospora rhizophorae Print Date: 9
- Page 110 and 111: Etheirophora blepharospora Print Da
- Page 112 and 113: 85 This page was intentionally left
- Page 114 and 115: Bonamia ostreae Print Date: 9/9/201
- Page 116 and 117: Haplosporidium nelsoni Print Date:
- Page 118 and 119: 91 This page was intentionally left
- Page 120 and 121: Ancistrocoma pelseneeri Print Date:
- Page 122 and 123: Ancistrum cyclidioides Print Date:
- Page 124 and 125: Boveria teredinidi Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 126 and 127: Conidophrys pilisuctor Print Date:
- Page 128 and 129: Cothurnia limnoriae Print Date: 9/9
- Page 130 and 131: Eufolliculina lignicola Print Date:
- Page 132 and 133: Lagenophrys cochinensis Print Date:
- Page 134 and 135: Lobochona prorates Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 136 and 137: Mirofolliculina limnoriae Print Dat
- Page 138 and 139: Sphenophyra dosiniae Print Date: 9/
- Page 140 and 141: 113 This page was intentionally lef
- Page 142 and 143: Haynesina germanica Print Date: 9/9
- Page 144 and 145: Trochammina hadai Print Date: 9/9/2
- Page 146 and 147:
119 This page was intentionally lef
- Page 148 and 149:
Attheya armata Print Date: 9/9/2012
- Page 150 and 151:
Pseudo-nitzschia americana Print Da
- Page 152 and 153:
125 This page was intentionally lef
- Page 154 and 155:
Ascophyllum nodosum Print Date: 9/9
- Page 156 and 157:
Cutleria multifida Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 158 and 159:
Desmarestia ligulata Print Date: 9/
- Page 160 and 161:
Dictyota flabellata Print Date: 9/9
- Page 162 and 163:
Elachista nigra Print Date: 9/9/201
- Page 164 and 165:
Fucus cottonii Print Date: 9/9/2012
- Page 166 and 167:
Macrocystis pyrifera Print Date: 9/
- Page 168 and 169:
Microspongium globosum Print Date:
- Page 170 and 171:
Nemacystus decipiens Print Date: 9/
- Page 172 and 173:
Pylaiella littoralis Print Date: 9/
- Page 174 and 175:
Ralfsia bornetii Print Date: 9/9/20
- Page 176 and 177:
Saccharina japonica Print Date: 9/9
- Page 178 and 179:
Saccharina longissima Print Date: 9
- Page 180 and 181:
Sargassum horneri Print Date: 9/9/2
- Page 182 and 183:
Sargassum muticum Print Date: 9/9/2
- Page 184 and 185:
Striaria attenuata Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 186 and 187:
Undaria pinnatifida Print Date: 9/9
- Page 188 and 189:
161 This page was intentionally lef
- Page 190 and 191:
Cephaloidophora communis Print Date
- Page 192 and 193:
165 This page was intentionally lef
- Page 194 and 195:
Alexandrium margalefi Print Date: 9
- Page 196 and 197:
Alexandrium tamutum Print Date: 9/9
- Page 198 and 199:
Dinophysis caudata Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 200 and 201:
Heterocapsa circularisquama Print D
- Page 202 and 203:
Peridiniopsis penardiforme Print Da
- Page 204 and 205:
Perkinsus marinus Print Date: 9/9/2
- Page 206 and 207:
179 This page was intentionally lef
- Page 208 and 209:
Acanthophora spicifera Print Date:
- Page 210 and 211:
Aglaothamnion tenuissimum Print Dat
- Page 212 and 213:
Asparagopsis armata Print Date: 9/9
- Page 214 and 215:
Asparagopsis taxiformis Print Date:
- Page 216 and 217:
Bonnemaisonia hamifera Print Date:
- Page 218 and 219:
Callithamnion corymbosum Print Date
- Page 220 and 221:
Caulacanthus ustulatus Print Date:
- Page 222 and 223:
Ceramium cimbricum Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 224 and 225:
Ceramium giacconei Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 226 and 227:
Ceramium kondoi Print Date: 9/9/201
- Page 228 and 229:
Ceramium sinicola Print Date: 9/9/2
- Page 230 and 231:
Chroodactylon ornatum Print Date: 9
- Page 232 and 233:
Corynomorpha prismatica Print Date:
- Page 234 and 235:
Dasya sessilis Print Date: 9/9/2012
- Page 236 and 237:
Eucheuma denticulatum Print Date: 9
- Page 238 and 239:
Gelidium vagum Print Date: 9/9/2012
- Page 240 and 241:
Gracilaria salicornia Print Date: 9
- Page 242 and 243:
Gracilaria tikvahiae Print Date: 9/
- Page 244 and 245:
Gracilaria vermiculophylla Print Da
- Page 246 and 247:
Grateloupia lanceolata Print Date:
- Page 248 and 249:
Grateloupia turuturu Print Date: 9/
- Page 250 and 251:
Hypnea musciformis Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 252 and 253:
Kappaphycus alvarezii Print Date: 9
- Page 254 and 255:
Kappaphycus striatus Print Date: 9/
- Page 256 and 257:
Lomentaria hakodatensis Print Date:
- Page 258 and 259:
Neosiphonia harveyi Print Date: 9/9
- Page 260 and 261:
Polysiphonia brodiei Print Date: 9/
- Page 262 and 263:
Polysiphonia denudata Print Date: 9
- Page 264 and 265:
237 This page was intentionally lef
- Page 266 and 267:
Avrainvillea amadelpha Print Date:
- Page 268 and 269:
Bryopsis sp. (Cohen and Carlton, 19
- Page 270 and 271:
Caulerpa taxifolia Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 272 and 273:
Codium fragile fragile Print Date:
- Page 274 and 275:
Udotea argentea Print Date: 9/9/201
- Page 276 and 277:
Ulva californica Print Date: 9/9/20
- Page 278 and 279:
Ulva expansa Print Date: 9/9/2012 E
- Page 280 and 281:
Ulva lactuca Print Date: 9/9/2012 E
- Page 282 and 283:
Ulva pertusa Print Date: 9/9/2012 E
- Page 284 and 285:
Ulva rigida Print Date: 9/9/2012 Es
- Page 286 and 287:
259 This page was intentionally lef
- Page 288 and 289:
Ammophila arenaria Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 290 and 291:
Bruguiera sexangula Print Date: 9/9
- Page 292 and 293:
Conocarpus erectus Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 294 and 295:
Halophila decipiens Print Date: 9/9
- Page 296 and 297:
Limosella australis Print Date: 9/9
- Page 298 and 299:
Rhizophora mangle Print Date: 9/9/2
- Page 300 and 301:
Spartina alterniflora Print Date: 9
- Page 302 and 303:
Spartina anglica Print Date: 9/9/20
- Page 304 and 305:
Spartina densiflora Print Date: 9/9
- Page 306 and 307:
Spartina patens Print Date: 9/9/201
- Page 308 and 309:
Zostera japonica Print Date: 9/9/20
- Page 310 and 311:
283 This page was intentionally lef
- Page 312 and 313:
Chalinula loosanoffi Print Date: 9/
- Page 314 and 315:
Clathria prolifera Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 316 and 317:
Cliona thoosina Print Date: 9/9/201
- Page 318 and 319:
Gelliodes fibrosa Print Date: 9/9/2
- Page 320 and 321:
Halichondria bowerbanki Print Date:
- Page 322 and 323:
Halichondria coerulea Print Date: 9
- Page 324 and 325:
Halichondria melanodocia Print Date
- Page 326 and 327:
Haliclona caerulea Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 328 and 329:
Monanchora sp. (Carlton and Eldredg
- Page 330 and 331:
Mycale cecilia Print Date: 9/9/2012
- Page 332 and 333:
Mycale grandis Print Date: 9/9/2012
- Page 334 and 335:
Mycale parishi Print Date: 9/9/2012
- Page 336 and 337:
Prosuberites sp. (Hartman, 1975) Pr
- Page 338 and 339:
Suberites aurantiacus Print Date: 9
- Page 340 and 341:
313 This page was intentionally lef
- Page 342 and 343:
Aiptasia cf. insignis Print Date: 9
- Page 344 and 345:
Aiptasiomorpha minima Print Date: 9
- Page 346 and 347:
Bunodeopsis sp. A (Engle and Richar
- Page 348 and 349:
Carijoa riisei Print Date: 9/9/2012
- Page 350 and 351:
Culicia rachelfitzhardingeae Print
- Page 352 and 353:
Diadumene cincta Print Date: 9/9/20
- Page 354 and 355:
Diadumene franciscana Print Date: 9
- Page 356 and 357:
Diadumene leucolena Print Date: 9/9
- Page 358 and 359:
Diadumene lineata Print Date: 9/9/2
- Page 360 and 361:
Nematostella vectensis Print Date:
- Page 362 and 363:
Synandwakia hozawai Print Date: 9/9
- Page 364 and 365:
337 This page was intentionally lef
- Page 366 and 367:
Copula sivickisi Print Date: 9/9/20
- Page 368 and 369:
341 This page was intentionally lef
- Page 370 and 371:
Amphinema sp. (Rees, 2000) Print Da
- Page 372 and 373:
Bimeria vestita Print Date: 9/9/201
- Page 374 and 375:
Blackfordia virginica Print Date: 9
- Page 376 and 377:
Bougainvillia muscus Print Date: 9/
- Page 378 and 379:
Cladonema pacificum Print Date: 9/9
- Page 380 and 381:
Cladonema radiatum Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 382 and 383:
Clava multicornis Print Date: 9/9/2
- Page 384 and 385:
Clytia hemisphaerica Print Date: 9/
- Page 386 and 387:
Cordylophora caspia Print Date: 9/9
- Page 388 and 389:
Corymorpha sp. (Cohen and Carlton,
- Page 390 and 391:
Garveia franciscana Print Date: 9/9
- Page 392 and 393:
Garveia sp. (Carlton and Eldredge,
- Page 394 and 395:
Gonothyraea loveni Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 396 and 397:
Laomedea calceolifera Print Date: 9
- Page 398 and 399:
Laomedea flexuosa Print Date: 9/9/2
- Page 400 and 401:
Maeotias marginata Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 402 and 403:
Moerisia sp. (Rees and Gershwin, 20
- Page 404 and 405:
Obelia bidentata Print Date: 9/9/20
- Page 406 and 407:
Obelia dichotoma Cmplx Print Date:
- Page 408 and 409:
Pennaria disticha Print Date: 9/9/2
- Page 410 and 411:
Pinauay crocea Print Date: 9/9/2012
- Page 412 and 413:
Podocorynoides minima Print Date: 9
- Page 414 and 415:
Thuiaria thuiarioides Print Date: 9
- Page 416 and 417:
Turritopsis nutricula Cmplx Print D
- Page 418 and 419:
391 This page was intentionally lef
- Page 420 and 421:
Anomalorhiza shawi Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 422 and 423:
Aurelia sp. (Carlton and Eldredge,
- Page 424 and 425:
Aurelia sp. 1 (Dawson et al., 2005)
- Page 426 and 427:
Cassiopea andromeda Print Date: 9/9
- Page 428 and 429:
Cassiopea sp. 3 (Holland et al., 20
- Page 430 and 431:
Phyllorhiza punctata Print Date: 9/
- Page 432 and 433:
405 This page was intentionally lef
- Page 434 and 435:
Vallicula multiformis Print Date: 9
- Page 436 and 437:
409 This page was intentionally lef
- Page 438 and 439:
Camallanus cotti Print Date: 9/9/20
- Page 440 and 441:
413 This page was intentionally lef
- Page 442 and 443:
Ascocotyle tenuicollis Print Date:
- Page 444 and 445:
Bothriocephalus acheilognathi Print
- Page 446 and 447:
Cercaria batillariae Print Date: 9/
- Page 448 and 449:
Gyrodactylus anguillae Print Date:
- Page 450 and 451:
Khawia iowensis Print Date: 9/9/201
- Page 452 and 453:
Koinostylochus ostreophagus Print D
- Page 454 and 455:
Neobenedenia melleni Print Date: 9/
- Page 456 and 457:
Neoheterobothrium hirame Print Date
- Page 458 and 459:
Salsuginus seculus Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 460 and 461:
Stylochoplana limnoriae Print Date:
- Page 462 and 463:
Taenioplana teredini Print Date: 9/
- Page 464 and 465:
437 This page was intentionally lef
- Page 466 and 467:
Chaetogaster diaphanus Print Date:
- Page 468 and 469:
Limnodriloides monothecus Print Dat
- Page 470 and 471:
Monopylephorus evertus Print Date:
- Page 472 and 473:
Myzobdella lugubris Print Date: 9/9
- Page 474 and 475:
Paranais frici Print Date: 9/9/2012
- Page 476 and 477:
Tubificoides brownae Print Date: 9/
- Page 478 and 479:
Tubificoides diazi Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 480 and 481:
Tubificoides wasselli Print Date: 9
- Page 482 and 483:
455 This page was intentionally lef
- Page 484 and 485:
Alitta succinea Print Date: 9/9/201
- Page 486 and 487:
Amaeana sp. (Cohen et al., 2005) Pr
- Page 488 and 489:
Amblyosyllis speciosa Print Date: 9
- Page 490 and 491:
Amphiglena mediterranea Print Date:
- Page 492 and 493:
Axiothella quadrimaculata Print Dat
- Page 494 and 495:
Bispira sp. A (Cohen et al., 2002)
- Page 496 and 497:
Boccardiella hamata Print Date: 9/9
- Page 498 and 499:
Boccardiella ligerica Print Date: 9
- Page 500 and 501:
Branchiomma bairdi Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 502 and 503:
Branchiomma japonica Print Date: 9/
- Page 504 and 505:
Brevicirrosyllis weismanni Print Da
- Page 506 and 507:
Caulleriella acicula Print Date: 9/
- Page 508 and 509:
Chaetopterus variopedatus Cmplx Pri
- Page 510 and 511:
Clymenella torquata Print Date: 9/9
- Page 512 and 513:
Crucigera websteri Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 514 and 515:
Demonax sp. A (Cohen et al., 2002)
- Page 516 and 517:
Dipolydora commensalis Print Date:
- Page 518 and 519:
Dipolydora normalis Print Date: 9/9
- Page 520 and 521:
Eumida sanguinea Print Date: 9/9/20
- Page 522 and 523:
Eusyllis japonica Print Date: 9/9/2
- Page 524 and 525:
Exogone longicornis Print Date: 9/9
- Page 526 and 527:
Ficopomatus enigmaticus Print Date:
- Page 528 and 529:
Ficopomatus miamiensis Print Date:
- Page 530 and 531:
Geminosyllis ohma Print Date: 9/9/2
- Page 532 and 533:
Hesionura australiensis Print Date:
- Page 534 and 535:
Heteromastus filiformis Cmplx Print
- Page 536 and 537:
Hobsonia florida Print Date: 9/9/20
- Page 538 and 539:
Hyboscolex longiseta Print Date: 9/
- Page 540 and 541:
Hydroides brachyacanthus Print Date
- Page 542 and 543:
Hydroides cruciger Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 544 and 545:
Hydroides dianthus Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 546 and 547:
Hydroides diramphus Print Date: 9/9
- Page 548 and 549:
Hydroides elegans Print Date: 9/9/2
- Page 550 and 551:
Hydroides ezoensis Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 552 and 553:
Hydroides norvegicus Print Date: 9/
- Page 554 and 555:
Janua pagenstecheri Print Date: 9/9
- Page 556 and 557:
Kuwaita heteropoda Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 558 and 559:
Laonome sp. SF1 Norris (CANOD, 2009
- Page 560 and 561:
Linopherus microcephala Print Date:
- Page 562 and 563:
Magelona capensis Print Date: 9/9/2
- Page 564 and 565:
Manayunkia aestuarina Print Date: 9
- Page 566 and 567:
Marenzelleria viridis Print Date: 9
- Page 568 and 569:
Marphysa conferta Print Date: 9/9/2
- Page 570 and 571:
Microspio granulata Print Date: 9/9
- Page 572 and 573:
Myrianida pachycera Print Date: 9/9
- Page 574 and 575:
Neanthes arenaceodentata Print Date
- Page 576 and 577:
Neoamphitrite sp. A (Cohen et al.,
- Page 578 and 579:
Neodexiospira brasiliensis Print Da
- Page 580 and 581:
Nicolea sp. A (Cohen et al., 2002)
- Page 582 and 583:
Nicolea zostericola Print Date: 9/9
- Page 584 and 585:
Ophryotrocha adherens Print Date: 9
- Page 586 and 587:
Ophryotrocha labronica pacifica Pri
- Page 588 and 589:
Perinereis aibuhitensis Print Date:
- Page 590 and 591:
Perkinsyllis spinisetosa Print Date
- Page 592 and 593:
Pileolaria militaris Print Date: 9/
- Page 594 and 595:
Plakosyllis brevipes Print Date: 9/
- Page 596 and 597:
Polydora cornuta Print Date: 9/9/20
- Page 598 and 599:
Polydora limicola Print Date: 9/9/2
- Page 600 and 601:
Polydora nuchalis Print Date: 9/9/2
- Page 602 and 603:
Polydora websteri Print Date: 9/9/2
- Page 604 and 605:
Procerastea nematodes Print Date: 9
- Page 606 and 607:
Protodorvillea biarticulata Print D
- Page 608 and 609:
Protodorvillea egena Print Date: 9/
- Page 610 and 611:
Protodriloides chaetifer Print Date
- Page 612 and 613:
Pseudopolydora antennata Print Date
- Page 614 and 615:
Pseudopolydora bassarginensis Print
- Page 616 and 617:
Pseudopotamilla occelata Print Date
- Page 618 and 619:
Pseudovermilia occidentalis Print D
- Page 620 and 621:
Sabaco elongatus Print Date: 9/9/20
- Page 622 and 623:
Sabellastarte spectabilis Print Dat
- Page 624 and 625:
Salmacina tribranchiata Print Date:
- Page 626 and 627:
Salvatoria mediodentata Print Date:
- Page 628 and 629:
Scolelepis victoriensis Print Date:
- Page 630 and 631:
Scyphoproctus djiboutiensis Print D
- Page 632 and 633:
Serpula watsoni Print Date: 9/9/201
- Page 634 and 635:
Sphaerosyllis riseri Print Date: 9/
- Page 636 and 637:
Spio blakei Print Date: 9/9/2012 Es
- Page 638 and 639:
Spirobranchus kraussii Print Date:
- Page 640 and 641:
Streblospio benedicti Cmplx Print D
- Page 642 and 643:
Syllides bansei Print Date: 9/9/201
- Page 644 and 645:
Typosyllis nipponica Print Date: 9/
- Page 646 and 647:
619 This page was intentionally lef
- Page 648 and 649:
Aetea anguina Print Date: 9/9/2012
- Page 650 and 651:
Aetea truncata Print Date: 9/9/2012
- Page 652 and 653:
Aeverrillia armata Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 654 and 655:
Amathia convoluta Print Date: 9/9/2
- Page 656 and 657:
Amathia distans Print Date: 9/9/201
- Page 658 and 659:
Anguinella palmata Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 660 and 661:
Aspidelectra cf. melolontha Print D
- Page 662 and 663:
Bowerbankia gracilis Cmplx Print Da
- Page 664 and 665:
Bowerbankia imbricata Print Date: 9
- Page 666 and 667:
Bugula californica Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 668 and 669:
Bugula dentata Print Date: 9/9/2012
- Page 670 and 671:
Bugula flabellata Print Date: 9/9/2
- Page 672 and 673:
Bugula fulva Print Date: 9/9/2012 E
- Page 674 and 675:
Bugula minima Print Date: 9/9/2012
- Page 676 and 677:
Bugula neritina Cmplx Print Date: 9
- Page 678 and 679:
Bugula sp. 1 (Cohen et al., 1998) P
- Page 680 and 681:
Bugula sp. 2 (Cohen et al., 1998) P
- Page 682 and 683:
Bugula stolonifera Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 684 and 685:
Caberea boryi Print Date: 9/9/2012
- Page 686 and 687:
Caulibugula caliculata Print Date:
- Page 688 and 689:
Caulibugula dendrograpta Print Date
- Page 690 and 691:
Conopeum seurati Print Date: 9/9/20
- Page 692 and 693:
Conopeum tenuissimum Print Date: 9/
- Page 694 and 695:
Cryptosula pallasiana Print Date: 9
- Page 696 and 697:
Electra tenella Print Date: 9/9/201
- Page 698 and 699:
Escharoides excavata Print Date: 9/
- Page 700 and 701:
Hippopodina tahitiensis Print Date:
- Page 702 and 703:
Membranipora chesapeakensis Print D
- Page 704 and 705:
Membraniporopsis tubigerum Print Da
- Page 706 and 707:
Nolella stipata Print Date: 9/9/201
- Page 708 and 709:
Savignyella lafontii Print Date: 9/
- Page 710 and 711:
Schizoporella errata Print Date: 9/
- Page 712 and 713:
Schizoporella japonica Print Date:
- Page 714 and 715:
Schizoporella sp. (Carlton and Eldr
- Page 716 and 717:
Schizoporella unicornis Print Date:
- Page 718 and 719:
Synnotum aegyptiacum Print Date: 9/
- Page 720 and 721:
Triticella sp. B (Hewitt, 1993) Pri
- Page 722 and 723:
Trypostega venusta Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 724 and 725:
Victorella pavida Print Date: 9/9/2
- Page 726 and 727:
Watersipora arcuata Print Date: 9/9
- Page 728 and 729:
Watersipora edmondsoni Print Date:
- Page 730 and 731:
Watersipora sp. (Mackie et al., 200
- Page 732 and 733:
Watersipora subtorquata Print Date:
- Page 734 and 735:
Zoobotryon verticillatum Print Date
- Page 736 and 737:
709 This page was intentionally lef
- Page 738 and 739:
Phoronis hippocrepia Print Date: 9/
- Page 740 and 741:
713 This page was intentionally lef
- Page 742 and 743:
Barentsia benedeni Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 744 and 745:
Barentsia sp. (Carlton and Eldredge
- Page 746 and 747:
719 This page was intentionally lef
- Page 748 and 749:
Abra sp. A (Coles et al., 1997) Pri
- Page 750 and 751:
Anomia nobilis Print Date: 9/9/2012
- Page 752 and 753:
Argopecten irradians Print Date: 9/
- Page 754 and 755:
Bankia bipalmulata Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 756 and 757:
Chama fibula Print Date: 9/9/2012 E
- Page 758 and 759:
Chama lazarus Print Date: 9/9/2012
- Page 760 and 761:
Chama macerophylla Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 762 and 763:
Chama pacifica Print Date: 9/9/2012
- Page 764 and 765:
Corbicula fluminea Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 766 and 767:
Corbula amurensis Print Date: 9/9/2
- Page 768 and 769:
Crassostrea gigas Print Date: 9/9/2
- Page 770 and 771:
Crassostrea virginica Print Date: 9
- Page 772 and 773:
Gemma gemma Print Date: 9/9/2012 Es
- Page 774 and 775:
Geukensia demissa Print Date: 9/9/2
- Page 776 and 777:
Hiatella arctica Print Date: 9/9/20
- Page 778 and 779:
Laternula marilina Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 780 and 781:
Limnoperna fortunei Print Date: 9/9
- Page 782 and 783:
Limnoperna securis Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 784 and 785:
Lioconcha fastigiata Print Date: 9/
- Page 786 and 787:
Lyrodus affinis Print Date: 9/9/201
- Page 788 and 789:
Lyrodus pedicellatus Print Date: 9/
- Page 790 and 791:
Lyrodus takanoshimensis Print Date:
- Page 792 and 793:
Macoma petalum Print Date: 9/9/2012
- Page 794 and 795:
Martesia striata Print Date: 9/9/20
- Page 796 and 797:
Mercenaria mercenaria Print Date: 9
- Page 798 and 799:
Meretrix petechialis Print Date: 9/
- Page 800 and 801:
Musculista senhousia Print Date: 9/
- Page 802 and 803:
Mya arenaria Print Date: 9/29/2012
- Page 804 and 805:
Mytilopsis leucophaeata Print Date:
- Page 806 and 807:
Mytilopsis sallei Print Date: 9/9/2
- Page 808 and 809:
Mytilus galloprovincialis Print Dat
- Page 810 and 811:
Neotrapezium liratum Print Date: 9/
- Page 812 and 813:
Nuttallia obscurata Print Date: 9/9
- Page 814 and 815:
Ostrea edulis Print Date: 9/9/2012
- Page 816 and 817:
Ostrea lurida Print Date: 9/9/2012
- Page 818 and 819:
Panopea generosa Print Date: 9/9/20
- Page 820 and 821:
Patinopecten yessoensis Print Date:
- Page 822 and 823:
Pecten maximus Print Date: 9/9/2012
- Page 824 and 825:
Perna viridis Print Date: 9/9/2012
- Page 826 and 827:
Petricola lithophaga Print Date: 9/
- Page 828 and 829:
Petricolaria pholadiformis Print Da
- Page 830 and 831:
Phacosoma gibba Print Date: 9/9/201
- Page 832 and 833:
Potamocorbula laevis Print Date: 9/
- Page 834 and 835:
Saccostrea cucullata Print Date: 9/
- Page 836 and 837:
Sphenia coreanica Print Date: 9/9/2
- Page 838 and 839:
Spisula solidissima Print Date: 9/9
- Page 840 and 841:
Teredo bartschi Print Date: 9/9/201
- Page 842 and 843:
Teredo clappi Print Date: 9/9/2012
- Page 844 and 845:
Teredo fulleri Print Date: 9/9/2012
- Page 846 and 847:
Teredo furcifera Print Date: 9/9/20
- Page 848 and 849:
Teredo navalis Print Date: 9/9/2012
- Page 850 and 851:
Theora lubrica Print Date: 9/9/2012
- Page 852 and 853:
Venerupis philippinarum Print Date:
- Page 854 and 855:
827 This page was intentionally lef
- Page 856 and 857:
Alderia modesta Print Date: 9/9/201
- Page 858 and 859:
Amphithalamus inclusus Print Date:
- Page 860 and 861:
Assiminea parasitologica Print Date
- Page 862 and 863:
Babakina festiva Print Date: 9/9/20
- Page 864 and 865:
Batillaria attramentaria Print Date
- Page 866 and 867:
Boonea cincta Print Date: 9/9/2012
- Page 868 and 869:
Bostrycapulus calyptraeiformis Prin
- Page 870 and 871:
Busycotypus canaliculatus Print Dat
- Page 872 and 873:
Caloria indica Print Date: 9/9/2012
- Page 874 and 875:
Catriona rickettsi Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 876 and 877:
Cecina manchurica Print Date: 9/9/2
- Page 878 and 879:
Chrysallida trachis Print Date: 9/9
- Page 880 and 881:
Crepidula convexa Print Date: 9/9/2
- Page 882 and 883:
Crepidula fornicata Print Date: 9/9
- Page 884 and 885:
Crepidula onyx Print Date: 9/9/2012
- Page 886 and 887:
Crepidula plana Print Date: 9/9/201
- Page 888 and 889:
Crucibulum spinosum Print Date: 9/9
- Page 890 and 891:
Cuthona columbiana Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 892 and 893:
Cuthona perca Print Date: 9/9/2012
- Page 894 and 895:
Diodora rueppellii Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 896 and 897:
Evalea cf. americana Print Date: 9/
- Page 898 and 899:
Folinella navisa Print Date: 9/9/20
- Page 900 and 901:
Haliotis fulgens Print Date: 9/9/20
- Page 902 and 903:
Haliotis iris Print Date: 9/9/2012
- Page 904 and 905:
Haliotis kamtschatkana Print Date:
- Page 906 and 907:
Haliotis laevigata Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 908 and 909:
Haliotis rufescens Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 910 and 911:
Haliotis tuberculata Print Date: 9/
- Page 912 and 913:
Haminoea japonica Print Date: 9/9/2
- Page 914 and 915:
Ilyanassa obsoleta Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 916 and 917:
Iolaea eucosmia Print Date: 9/9/201
- Page 918 and 919:
Laguncula pulchella Print Date: 9/9
- Page 920 and 921:
Littoridinops monroensis Print Date
- Page 922 and 923:
Littorina littorea Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 924 and 925:
Littorina saxatilis Print Date: 9/9
- Page 926 and 927:
Melanoides tuberculata Print Date:
- Page 928 and 929:
Myosotella myosotis Print Date: 9/9
- Page 930 and 931:
Nassarius fraterculus Print Date: 9
- Page 932 and 933:
Nassarius sinarus Print Date: 9/9/2
- Page 934 and 935:
Ocenebra inornata Print Date: 9/9/2
- Page 936 and 937:
Odetta bisuturalis Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 938 and 939:
Okenia eolida Print Date: 9/9/2012
- Page 940 and 941:
Okenia pellucida Print Date: 9/9/20
- Page 942 and 943:
Peristichia pedroana Print Date: 9/
- Page 944 and 945:
Philine auriformis Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 946 and 947:
Philine orientalis Print Date: 9/29
- Page 948 and 949:
Phyllodesmium poindimiei Print Date
- Page 950 and 951:
Potamopyrgus antipodarum Print Date
- Page 952 and 953:
Pyrgophorus coronatus Print Date: 9
- Page 954 and 955:
Sakuraeolis enosimensis Print Date:
- Page 956 and 957:
Stenothyra sp. (Tamaki et al., 2002
- Page 958 and 959:
Tarebia granifera Print Date: 9/9/2
- Page 960 and 961:
Tenellia adspersa Print Date: 9/9/2
- Page 962 and 963:
Thylaeodus sp. (Carlton and Eldredg
- Page 964 and 965:
Umbonium thomasi Print Date: 9/9/20
- Page 966 and 967:
Urosalpinx cinerea Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 968 and 969:
Vermetus alii Print Date: 9/9/2012
- Page 970 and 971:
943 This page was intentionally lef
- Page 972 and 973:
Nebalia sp. (Cohen and Carlton, 199
- Page 974 and 975:
947 This page was intentionally lef
- Page 976 and 977:
Ampelisca abdita Print Date: 9/9/20
- Page 978 and 979:
Ampithoe lacertosa Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 980 and 981:
Ampithoe longimana Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 982 and 983:
Ampithoe sp. (Cohen and Carlton, 19
- Page 984 and 985:
Ampithoe valida Print Date: 9/9/201
- Page 986 and 987:
Aoroides secundus Print Date: 9/9/2
- Page 988 and 989:
Caprella danilevskii Print Date: 9/
- Page 990 and 991:
Caprella drepanochir Print Date: 9/
- Page 992 and 993:
Caprella equilibra Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 994 and 995:
Caprella mutica Print Date: 9/9/201
- Page 996 and 997:
Caprella penantis Print Date: 9/9/2
- Page 998 and 999:
Caprella scaura Print Date: 9/9/201
- Page 1000 and 1001:
Caprella simia Print Date: 9/9/2012
- Page 1002 and 1003:
Centromedon pumilus Print Date: 9/9
- Page 1004 and 1005:
Cheiriphotis megacheles Print Date:
- Page 1006 and 1007:
Chelura terebrans Print Date: 9/9/2
- Page 1008 and 1009:
Corophium alienense Print Date: 9/9
- Page 1010 and 1011:
Corophium heteroceratum Print Date:
- Page 1012 and 1013:
Elasmopus rapax Print Date: 9/9/201
- Page 1014 and 1015:
Eochelidium sp. A (Chapman, 2007) P
- Page 1016 and 1017:
Ericthonius brasiliensis Print Date
- Page 1018 and 1019:
Gammarus daiberi Print Date: 9/9/20
- Page 1020 and 1021:
Gammarus mucronatus Print Date: 9/9
- Page 1022 and 1023:
Grandidierella bispinosa Print Date
- Page 1024 and 1025:
Grandidierella japonica Print Date:
- Page 1026 and 1027:
Incisocalliope derzhavini Print Dat
- Page 1028 and 1029:
Jassa falcata Print Date: 9/9/2012
- Page 1030 and 1031:
Jassa marmorata Print Date: 9/9/201
- Page 1032 and 1033:
Jassa slatteryi Print Date: 9/9/201
- Page 1034 and 1035:
Laticorophium baconi Print Date: 9/
- Page 1036 and 1037:
Leucothoe micronesiae Print Date: 9
- Page 1038 and 1039:
Leucothoe spinicarpa Cmplx Print Da
- Page 1040 and 1041:
Liljeborgia sp. (Cohen et al., 2002
- Page 1042 and 1043:
Melita nitida Print Date: 9/9/2012
- Page 1044 and 1045:
Melita rylovae Print Date: 9/9/2012
- Page 1046 and 1047:
Metopella sp. (Cohen et al., 2002)
- Page 1048 and 1049:
Microdeutopus gryllotalpa Print Dat
- Page 1050 and 1051:
Microjassa sp. (deRivera et al., 20
- Page 1052 and 1053:
Monocorophium acherusicum Print Dat
- Page 1054 and 1055:
Monocorophium insidiosum Print Date
- Page 1056 and 1057:
Monocorophium uenoi Print Date: 9/9
- Page 1058 and 1059:
Paracaprella pusilla Print Date: 9/
- Page 1060 and 1061:
Paracorophium sp. (Chapman, 2007) P
- Page 1062 and 1063:
Paradexamine sp. (Chapman, 2007) Pr
- Page 1064 and 1065:
Paraleucothoe sp. (Carlton and Eldr
- Page 1066 and 1067:
Podocerus brasiliensis Print Date:
- Page 1068 and 1069:
Stenothoe gallensis Print Date: 9/9
- Page 1070 and 1071:
Stenothoe valida Print Date: 9/9/20
- Page 1072 and 1073:
Transorchestia enigmatica Print Dat
- Page 1074 and 1075:
Tropichelura insulae Print Date: 9/
- Page 1076 and 1077:
1049 This page was intentionally le
- Page 1078 and 1079:
Nannastacus sp. (Carlton and Eldred
- Page 1080 and 1081:
Nippoleucon hinumensis Print Date:
- Page 1082 and 1083:
Scherocumella sp. (Carlton and Eldr
- Page 1084 and 1085:
1057 This page was intentionally le
- Page 1086 and 1087:
Alloniscus oahuensis Print Date: 9/
- Page 1088 and 1089:
Armadilloniscus ellipticus Print Da
- Page 1090 and 1091:
Boreosignum wilsoni Print Date: 9/9
- Page 1092 and 1093:
Buchnerillo sp. (Carlton and Eldred
- Page 1094 and 1095:
Caecijaera horvathi Print Date: 9/9
- Page 1096 and 1097:
Dynoides dentisinus Print Date: 9/9
- Page 1098 and 1099:
Eurylana arcuata Print Date: 9/9/20
- Page 1100 and 1101:
Exosphaeroma sp. (Carlton and Eldre
- Page 1102 and 1103:
Gnorimosphaeroma rayi Print Date: 9
- Page 1104 and 1105:
Halophiloscia couchii Print Date: 9
- Page 1106 and 1107:
Iais californica Print Date: 9/9/20
- Page 1108 and 1109:
Ligia exotica Print Date: 9/9/2012
- Page 1110 and 1111:
Limnoria quadripunctata Print Date:
- Page 1112 and 1113:
Limnoria tripunctata Print Date: 9/
- Page 1114 and 1115:
Littorophiloscia culebrae Print Dat
- Page 1116 and 1117:
Mesanthura sp. (Carlton and Eldredg
- Page 1118 and 1119:
Munna sp. A (Cohen and Carlton, 199
- Page 1120 and 1121:
Niambia capensis Print Date: 9/9/20
- Page 1122 and 1123:
Olibrinus truncatus Print Date: 9/9
- Page 1124 and 1125:
Orthione griffenis Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 1126 and 1127:
Paracerceis sculpta Print Date: 9/9
- Page 1128 and 1129:
Paradella dianae Print Date: 9/9/20
- Page 1130 and 1131:
Paralimnoria andrewsi Print Date: 9
- Page 1132 and 1133:
Paranthura japonica Print Date: 9/9
- Page 1134 and 1135:
Pistorius bidens Print Date: 9/9/20
- Page 1136 and 1137:
Platyarthrus aiasensis Print Date:
- Page 1138 and 1139:
Porcellio dilatatus Print Date: 9/9
- Page 1140 and 1141:
Porcellio laevis Print Date: 9/9/20
- Page 1142 and 1143:
Porcellio lamellatus Print Date: 9/
- Page 1144 and 1145:
Porcellio scaber Print Date: 9/9/20
- Page 1146 and 1147:
Pseudosphaeroma sp. (Bruce and Wetz
- Page 1148 and 1149:
Sphaeroma quoianum Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 1150 and 1151:
Sphaeroma walkeri Print Date: 9/9/2
- Page 1152 and 1153:
Synidotea laevidorsalis Print Date:
- Page 1154 and 1155:
1127 This page was intentionally le
- Page 1156 and 1157:
Deltamysis holmquistae Print Date:
- Page 1158 and 1159:
Holmesimysis costata Print Date: 9/
- Page 1160 and 1161:
Hyperacanthomysis longirostris Prin
- Page 1162 and 1163:
Neomysis japonica Print Date: 9/9/2
- Page 1164 and 1165:
Orientomysis aspera Print Date: 9/9
- Page 1166 and 1167:
Orientomysis hwanhaiensis Print Dat
- Page 1168 and 1169:
1141 This page was intentionally le
- Page 1170 and 1171:
Apseudes sp. (Carlton and Eldredge,
- Page 1172 and 1173:
Parapseudes pedispinis Print Date:
- Page 1174 and 1175:
Sinelobus stanfordi Cmplx Print Dat
- Page 1176 and 1177:
1149 This page was intentionally le
- Page 1178 and 1179:
Acantholobulus pacificus Print Date
- Page 1180 and 1181:
Callinectes sapidus Print Date: 9/9
- Page 1182 and 1183:
Carcinus aestuarii Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 1184 and 1185:
Carcinus maenas Print Date: 10/2/20
- Page 1186 and 1187:
Deiratonotus cristatum Print Date:
- Page 1188 and 1189:
Eriocheir sinensis Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 1190 and 1191:
Exopalaemon carinicauda Print Date:
- Page 1192 and 1193:
Fenneropenaeus chinensis Print Date
- Page 1194 and 1195:
Fenneropenaeus merguiensis Print Da
- Page 1196 and 1197:
Glabropilumnus seminudus Print Date
- Page 1198 and 1199:
Homarus americanus Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 1200 and 1201:
Homarus gammarus Print Date: 9/9/20
- Page 1202 and 1203:
Hyastenus spinosus Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 1204 and 1205:
Litopenaeus stylirostris Print Date
- Page 1206 and 1207:
Litopenaeus vannamei Print Date: 9/
- Page 1208 and 1209:
Macrobrachium lar Print Date: 9/9/2
- Page 1210 and 1211:
Macrobrachium rosenbergii Print Dat
- Page 1212 and 1213:
Marsupenaeus japonicus Print Date:
- Page 1214 and 1215:
Metacarcinus magister Print Date: 9
- Page 1216 and 1217:
Metadromia wilsoni Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 1218 and 1219:
Metopograpsus oceanicus Print Date:
- Page 1220 and 1221:
Nanosesarma minutum Print Date: 9/9
- Page 1222 and 1223:
Pachygrapsus fakaravensis Print Dat
- Page 1224 and 1225:
Palaemon macrodactylus Print Date:
- Page 1226 and 1227:
Panopeus lacustris Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 1228 and 1229:
Pilumnus oahuensis Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 1230 and 1231:
Pyromaia tuberculata Print Date: 9/
- Page 1232 and 1233:
Rhithropanopeus harrisii Print Date
- Page 1234 and 1235:
Scylla serrata Print Date: 9/9/2012
- Page 1236 and 1237:
1209 This page was intentionally le
- Page 1238 and 1239:
Gonodactylaceus falcatus Print Date
- Page 1240 and 1241:
1213 This page was intentionally le
- Page 1242 and 1243:
Acartiella sinensis Print Date: 9/9
- Page 1244 and 1245:
Caligus sclerotinosus Print Date: 9
- Page 1246 and 1247:
Enhydrosoma lacunae Print Date: 9/9
- Page 1248 and 1249:
Eurytemora affinis Cmplx Print Date
- Page 1250 and 1251:
Harpacticella paradoxa Print Date:
- Page 1252 and 1253:
Limnoithona sinensis Print Date: 9/
- Page 1254 and 1255:
Limnoithona tetraspina Print Date:
- Page 1256 and 1257:
Mytilicola orientalis Print Date: 9
- Page 1258 and 1259:
Neotachidius triangularis Print Dat
- Page 1260 and 1261:
Oithona davisae Print Date: 9/9/201
- Page 1262 and 1263:
Pachypygus gibber Print Date: 9/9/2
- Page 1264 and 1265:
Psammopsyllus stri Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 1266 and 1267:
Pseudodiaptomus forbesi Print Date:
- Page 1268 and 1269:
Pseudodiaptomus inopinus Print Date
- Page 1270 and 1271:
Pseudodiaptomus marinus Print Date:
- Page 1272 and 1273:
Pseudomyicola spinosus Print Date:
- Page 1274 and 1275:
Sarsamphiascus parvus Print Date: 9
- Page 1276 and 1277:
Sinocalanus doerrii Print Date: 9/9
- Page 1278 and 1279:
Stephos pacificus Print Date: 9/9/2
- Page 1280 and 1281:
Stephos sp. (Ruiz et al. 2000) Prin
- Page 1282 and 1283:
Teredicola typica Print Date: 9/9/2
- Page 1284 and 1285:
Tortanus dextrilobatus Print Date:
- Page 1286 and 1287:
1259 This page was intentionally le
- Page 1288 and 1289:
Amphibalanus amphitrite Print Date:
- Page 1290 and 1291:
Amphibalanus eburneus Print Date: 9
- Page 1292 and 1293:
Amphibalanus improvisus Print Date:
- Page 1294 and 1295:
Amphibalanus reticulatus Print Date
- Page 1296 and 1297:
Amphibalanus subalbidus Print Date:
- Page 1298 and 1299:
Amphibalanus variegatus Print Date:
- Page 1300 and 1301:
Amphibalanus venustus Print Date: 9
- Page 1302 and 1303:
Amphibalanus zhujiangensis Print Da
- Page 1304 and 1305:
Balanus glandula Print Date: 9/9/20
- Page 1306 and 1307:
Balanus perforatus Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 1308 and 1309:
Chthamalus proteus Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 1310 and 1311:
Megabalanus coccopoma Print Date: 9
- Page 1312 and 1313:
Megabalanus tintinnabulum Print Dat
- Page 1314 and 1315:
Megabalanus zebra Print Date: 9/9/2
- Page 1316 and 1317:
1289 This page was intentionally le
- Page 1318 and 1319:
Aspidoconcha limnoriae Print Date:
- Page 1320 and 1321:
Eusarsiella zostericola Print Date:
- Page 1322 and 1323:
Redekea californica Print Date: 9/9
- Page 1324 and 1325:
Spinileberis quadriaculeata Print D
- Page 1326 and 1327:
1299 This page was intentionally le
- Page 1328 and 1329:
Ammothella pacifica Print Date: 9/9
- Page 1330 and 1331:
Anoplodactylus arescus Print Date:
- Page 1332 and 1333:
Anoplodactylus californicus Print D
- Page 1334 and 1335:
Anoplodactylus digitatus Print Date
- Page 1336 and 1337:
Anoplodactylus erectus Print Date:
- Page 1338 and 1339:
Anoplodactylus marshallensis Print
- Page 1340 and 1341:
Anoplodactylus pycnosoma Print Date
- Page 1342 and 1343:
Endeis biseriata Print Date: 9/9/20
- Page 1344 and 1345:
Endeis nodosa Print Date: 9/9/2012
- Page 1346 and 1347:
Endeis procera Print Date: 9/9/2012
- Page 1348 and 1349:
Pigrogromitus timsanus Print Date:
- Page 1350 and 1351:
Tanystylum rehderi Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 1352 and 1353:
1325 This page was intentionally le
- Page 1354 and 1355:
Anisolabis maritima Print Date: 9/9
- Page 1356 and 1357:
Atrichopogon jacobsoni Print Date:
- Page 1358 and 1359:
Atrichopogon sp. (Carlton & Eldredg
- Page 1360 and 1361:
Brachydeutera ibari Print Date: 9/9
- Page 1362 and 1363:
Canaceoides angulatus Print Date: 9
- Page 1364 and 1365:
Cercyon fimbriatum Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 1366 and 1367:
Ceropsilopa coquilletti Print Date:
- Page 1368 and 1369:
Clasiopella uncinata Print Date: 9/
- Page 1370 and 1371:
Cricotopus bicinctus Print Date: 9/
- Page 1372 and 1373:
Crocothemis servilia Print Date: 9/
- Page 1374 and 1375:
Cyclodinus mundulus Print Date: 9/9
- Page 1376 and 1377:
Dolichopus exsul Print Date: 9/9/20
- Page 1378 and 1379:
Donaceus nigronotatus Print Date: 9
- Page 1380 and 1381:
Enallagma civile Print Date: 9/9/20
- Page 1382 and 1383:
Enochrus sayi Print Date: 9/9/2012
- Page 1384 and 1385:
Ephydra gracilis Print Date: 9/9/20
- Page 1386 and 1387:
Ephydra millbrae Print Date: 9/9/20
- Page 1388 and 1389:
Goeldichironomus holoprasinus Print
- Page 1390 and 1391:
Hecamede granifera Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 1392 and 1393:
Hostis guamensis Print Date: 9/9/20
- Page 1394 and 1395:
Ischnura ramburii Print Date: 9/9/2
- Page 1396 and 1397:
Kleidotoma bryani Print Date: 9/9/2
- Page 1398 and 1399:
Medetera grisescens Print Date: 9/9
- Page 1400 and 1401:
Mesovelia amoena Print Date: 9/9/20
- Page 1402 and 1403:
Mesovelia mulsanti Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 1404 and 1405:
Micracanthia humilis Print Date: 9/
- Page 1406 and 1407:
Mosillus tibialis Print Date: 9/9/2
- Page 1408 and 1409:
Orasiopa mera Print Date: 9/9/2012
- Page 1410 and 1411:
Parathroscinus murphyi Print Date:
- Page 1412 and 1413:
Paratissa pollinosa Print Date: 9/9
- Page 1414 and 1415:
Placopsidella marquesana Print Date
- Page 1416 and 1417:
Procanace williamsi Print Date: 9/9
- Page 1418 and 1419:
Prokelisia marginata Print Date: 9/
- Page 1420 and 1421:
Pselactus spadix Print Date: 9/9/20
- Page 1422 and 1423:
Psilopa girschneri Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 1424 and 1425:
Psychoda salicornia Print Date: 9/9
- Page 1426 and 1427:
Scatella stagnalis Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 1428 and 1429:
Syntormon flexible Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 1430 and 1431:
Telmatogeton japonicus Print Date:
- Page 1432 and 1433:
Tethina willistoni Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 1434 and 1435:
Thambemyia borealis Print Date: 9/9
- Page 1436 and 1437:
Tramea lacerata Print Date: 9/9/201
- Page 1438 and 1439:
Trichocorixa reticulata Print Date:
- Page 1440 and 1441:
Trigonotylus uhleri Print Date: 9/9
- Page 1442 and 1443:
Tropisternus salsamentus Print Date
- Page 1444 and 1445:
1417 This page was intentionally le
- Page 1446 and 1447:
Ophiactis savignyi Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 1448 and 1449:
Strongylocentrotus intermedius Prin
- Page 1450 and 1451:
1423 This page was intentionally le
- Page 1452 and 1453:
Ascidia archaia Print Date: 9/9/201
- Page 1454 and 1455:
Ascidia sp. (Lambert and Lambert, 1
- Page 1456 and 1457:
Ascidia species A (Carlton and Eldr
- Page 1458 and 1459:
Ascidia species B (Carlton and Eldr
- Page 1460 and 1461:
Ascidia sydneiensis Print Date: 9/9
- Page 1462 and 1463:
Ascidia zara Print Date: 9/9/2012 E
- Page 1464 and 1465:
Ascidiella aspersa Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 1466 and 1467:
Bostrichobranchus pilularis Print D
- Page 1468 and 1469:
Botrylloides diegensis Print Date:
- Page 1470 and 1471:
Botrylloides perspicuus Print Date:
- Page 1472 and 1473:
Botrylloides simodensis Print Date:
- Page 1474 and 1475:
Botrylloides sp. (Carlton and Eldre
- Page 1476 and 1477:
Botrylloides sp. A Lambert (CANOD,
- Page 1478 and 1479:
Botrylloides violaceus Print Date:
- Page 1480 and 1481:
Botryllus schlosseri Print Date: 9/
- Page 1482 and 1483:
Botryllus sp. (Carlton and Eldredge
- Page 1484 and 1485:
Botryllus sp. A Lambert (CANOD, 200
- Page 1486 and 1487:
Ciona intestinalis Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 1488 and 1489:
Ciona savignyi Print Date: 9/9/2012
- Page 1490 and 1491:
Cnemidocarpa irene Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 1492 and 1493:
Corella minuta Print Date: 9/9/2012
- Page 1494 and 1495:
Didemnum candidum Cmplx Print Date:
- Page 1496 and 1497:
Didemnum perlucidum Print Date: 9/9
- Page 1498 and 1499:
Didemnum psammatode Print Date: 9/9
- Page 1500 and 1501:
Didemnum vexillum Print Date: 9/9/2
- Page 1502 and 1503:
Diplosoma listerianum Print Date: 9
- Page 1504 and 1505:
Ecteinascidia imperfecta Print Date
- Page 1506 and 1507:
Eusynstyela hartmeyeri Print Date:
- Page 1508 and 1509:
Halocynthia roretzi Print Date: 9/9
- Page 1510 and 1511:
Herdmania mauritiana Print Date: 9/
- Page 1512 and 1513:
Herdmania momus Print Date: 9/9/201
- Page 1514 and 1515:
Herdmania pallida Print Date: 9/9/2
- Page 1516 and 1517:
Lissoclinum fragile Print Date: 9/9
- Page 1518 and 1519:
Microcosmus exasperatus Print Date:
- Page 1520 and 1521:
Microcosmus squamiger Print Date: 9
- Page 1522 and 1523:
Molgula ficus Print Date: 9/9/2012
- Page 1524 and 1525:
Molgula manhattensis Print Date: 9/
- Page 1526 and 1527:
Perophora japonica Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 1528 and 1529:
Phallusia nigra Print Date: 9/9/201
- Page 1530 and 1531:
Polyandrocarpa sagamiensis Print Da
- Page 1532 and 1533:
Polyandrocarpa zorritensis Print Da
- Page 1534 and 1535:
Polyclinum constellatum Print Date:
- Page 1536 and 1537:
Styela canopus Print Date: 9/9/2012
- Page 1538 and 1539:
Styela clava Print Date: 9/9/2012 E
- Page 1540 and 1541:
Styela plicata Print Date: 9/9/2012
- Page 1542 and 1543:
Symplegma brakenhielmi Print Date:
- Page 1544 and 1545:
Symplegma reptans Print Date: 9/9/2
- Page 1546 and 1547:
Symplegma sp. (Carlton and Eldredge
- Page 1548 and 1549:
1521 This page was intentionally le
- Page 1550 and 1551:
Abudefduf vaigiensis Print Date: 9/
- Page 1552 and 1553:
Acanthogobius flavimanus Print Date
- Page 1554 and 1555:
Acanthorhodeus macropterus Print Da
- Page 1556 and 1557:
Acipenser gueldenstaedtii Print Dat
- Page 1558 and 1559:
Acipenser nudiventris Print Date: 9
- Page 1560 and 1561:
Acipenser sinensis Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 1562 and 1563:
Acipenser sturio Print Date: 9/9/20
- Page 1564 and 1565:
Alosa sapidissima Print Date: 9/9/2
- Page 1566 and 1567:
Ameiurus melas Print Date: 9/9/2012
- Page 1568 and 1569:
Anguilla anguilla Print Date: 9/9/2
- Page 1570 and 1571:
Anguilla australis Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 1572 and 1573:
Anguilla marmorata Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 1574 and 1575:
Anguilla rostrata Print Date: 9/9/2
- Page 1576 and 1577:
Centropyge flavissima Print Date: 9
- Page 1578 and 1579:
Cephalopholis argus Print Date: 9/9
- Page 1580 and 1581:
Chrysiptera taupou Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 1582 and 1583:
Clarias batrachus Print Date: 9/9/2
- Page 1584 and 1585:
Cynoscion nebulosus Print Date: 9/9
- Page 1586 and 1587:
Cyprinus carpio Print Date: 9/9/201
- Page 1588 and 1589:
Dorosoma petenense Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 1590 and 1591:
Favonigobius sp. (Carlton and Eldre
- Page 1592 and 1593:
Fundulus diaphanus Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 1594 and 1595:
Gambusia affinis Print Date: 9/9/20
- Page 1596 and 1597:
Herklotsichthys quadrimaculatus Pri
- Page 1598 and 1599:
Hypomesus nipponensis Print Date: 9
- Page 1600 and 1601:
Ictalurus furcatus Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 1602 and 1603:
Ictalurus punctatus Print Date: 9/9
- Page 1604 and 1605:
Lateolabrax sp. (Yokogawa and Seki,
- Page 1606 and 1607:
Lates calcarifer Print Date: 9/9/20
- Page 1608 and 1609:
Limia vittata Print Date: 9/9/2012
- Page 1610 and 1611:
Lucania parva Print Date: 9/9/2012
- Page 1612 and 1613:
Lutjanus fulvus Print Date: 9/9/201
- Page 1614 and 1615:
Lutjanus gibbus Print Date: 9/9/201
- Page 1616 and 1617:
Lutjanus kasmira Print Date: 9/9/20
- Page 1618 and 1619:
Menidia beryllina Print Date: 9/9/2
- Page 1620 and 1621:
Morone saxatilis Print Date: 9/9/20
- Page 1622 and 1623:
Mugilogobius cavifrons Print Date:
- Page 1624 and 1625:
Odontesthes bonariensis Print Date:
- Page 1626 and 1627:
Omobranchus ferox Print Date: 9/9/2
- Page 1628 and 1629:
Omobranchus rotundiceps Print Date:
- Page 1630 and 1631:
Oncorhynchus kisutch Print Date: 9/
- Page 1632 and 1633:
Oncorhynchus mykiss Print Date: 9/9
- Page 1634 and 1635:
Oreochromis aureus Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 1636 and 1637:
Oreochromis mossambicus Print Date:
- Page 1638 and 1639:
Oreochromis niloticus Print Date: 9
- Page 1640 and 1641:
Parablennius thysanius Print Date:
- Page 1642 and 1643:
Paralichthys dentatus Print Date: 9
- Page 1644 and 1645:
Paralichthys lethostigma Print Date
- Page 1646 and 1647:
Parambassis ranga Print Date: 9/9/2
- Page 1648 and 1649:
Perca flavescens Print Date: 9/9/20
- Page 1650 and 1651:
Poecilia latipinna Print Date: 9/9/
- Page 1652 and 1653:
Poecilia mexicana Print Date: 9/9/2
- Page 1654 and 1655:
Poecilia reticulata Print Date: 9/9
- Page 1656 and 1657:
Psetta maxima Print Date: 9/9/2012
- Page 1658 and 1659:
Salmo salar Print Date: 9/9/2012 Es
- Page 1660 and 1661:
Salmo trutta Print Date: 9/9/2012 E
- Page 1662 and 1663:
Salvelinus fontinalis Print Date: 9
- Page 1664 and 1665:
Sardinella marquesensis Print Date:
- Page 1666 and 1667:
Sarotherodon melanotheron Print Dat
- Page 1668 and 1669:
Sciaenops ocellatus Print Date: 9/9
- Page 1670 and 1671:
Takifugu rubripes Print Date: 9/9/2
- Page 1672 and 1673:
Tridentiger barbatus Print Date: 9/
- Page 1674 and 1675:
Tridentiger bifasciatus Print Date:
- Page 1676 and 1677:
Tridentiger trigonocephalus Print D
- Page 1678 and 1679:
Upeneus vittatus Print Date: 9/9/20
- Page 1680 and 1681:
Valamugil engeli Print Date: 9/9/20
- Page 1682 and 1683:
Ahyong, S.T. 2001. Revision of the
- Page 1684 and 1685:
Aquenal Pty. Ltd. 2002. Final repor
- Page 1686 and 1687:
Ayres, P. 1991. Introduced Pacific
- Page 1688 and 1689:
Beasley, C.R., Fernandes, C.M., Gom
- Page 1690 and 1691:
Blake, J.A., Hecker, B., Grassle, J
- Page 1692 and 1693:
Brasher, A.M.D., Luton, C.D., Goodb
- Page 1694 and 1695:
Busby, M.S., Barnhart, R.A., and Pe
- Page 1696 and 1697:
Carlton, J.T. 1987. Patterns of tra
- Page 1698 and 1699:
Castanos, C., Pascual, M., and Cama
- Page 1700 and 1701:
Chen, R., Watanabe, S., and Yokota,
- Page 1702 and 1703:
Wastewater Department, Environmenta
- Page 1704 and 1705:
Museum Technical Report. No. 15. Be
- Page 1706 and 1707:
Cragg, S.M., Jumel M.-C., Al-Horani
- Page 1708 and 1709:
Daly, H.V. 2007a. Orders of interti
- Page 1710 and 1711:
wood-boring isopods, Limnoria tripu
- Page 1712 and 1713:
Dudley, P.L. and Illg, P.L. 1991. M
- Page 1714 and 1715:
Environmental Protection Agency. 20
- Page 1716 and 1717:
Farrapeira, C.M.R. 2010b. Shallow w
- Page 1718 and 1719:
Foster, N. and Feder, H.M. 2000a. B
- Page 1720 and 1721:
Garci, M.E., Trigo, J.E., Pascual,
- Page 1722 and 1723:
Godwin, L.S. 2003. Hull fouling of
- Page 1724 and 1725:
Griffiths, C.L., Robinson, T.B., an
- Page 1726 and 1727:
Port Valdez/Prince William Sound, A
- Page 1728 and 1729:
morphological and physiological con
- Page 1730 and 1731:
Ho, J. 2005. Symbiotic copepods as
- Page 1732 and 1733:
Hutchins, L.W. 1952. Species record
- Page 1734 and 1735:
Ishikawa, T. and Tachihara, K. 2008
- Page 1736 and 1737:
Jeong S.J., Yu O.H., and Suh H.L. 2
- Page 1738 and 1739:
Kawahara, T. 1969. Studies on the m
- Page 1740 and 1741:
Kitanishi, S., Yamamoto, T., and Na
- Page 1742 and 1743:
Krug, P.J. 2009. Not my “type”:
- Page 1744 and 1745:
Melphidippidae., edited by Cobb, D.
- Page 1746 and 1747:
Lewis, J.E. and Norris, J.N. 1987.
- Page 1748 and 1749:
Lowry, J.K. 2000. Taxonomic status
- Page 1750 and 1751:
Marquet, G., Taiki, N., Chadderton,
- Page 1752 and 1753:
McCauley, J.E. 1972. A preliminary
- Page 1754 and 1755:
Menzies, R.J. 1951b. A new genus an
- Page 1756 and 1757:
Miura, T., Iwakiri, M., Morioka, M.
- Page 1758 and 1759:
Morton, A. and Volpe, J. 2003. A de
- Page 1760 and 1761:
Neill, P.E., Alcalde, O., Faugeron,
- Page 1762 and 1763:
Paracerceis sculpta species summary
- Page 1764 and 1765:
Noda, T. 1999. Within- and between-
- Page 1766 and 1767:
O'Kelly, C.J., Kurihara, A., Shiple
- Page 1768 and 1769:
Paavola, M., Olenin, S., and Leppko
- Page 1770 and 1771:
Piepenburg et al., 2011. Towards a
- Page 1772 and 1773:
Prabowo, R.E. and Yamaguchi, T. 200
- Page 1774 and 1775:
Randall, J.E. and Kulbicki, M. 2006
- Page 1776 and 1777:
Rizzo, A.E. and Amaral, A.C.Z. 2001
- Page 1778 and 1779:
Ruiz, G.M., Fofonoff, P.W., Carlton
- Page 1780 and 1781:
SCAMIT (Southern California Associa
- Page 1782 and 1783:
Senanan, W., Tangkrock-Olan, N., Pa
- Page 1784 and 1785:
Silva, P.C., Basson, P.W., and Moe,
- Page 1786 and 1787:
B.S., Jorge, M.A., Lonbana, A., Lou
- Page 1788 and 1789:
Takaoka Biological Club. 2006. Sea
- Page 1790 and 1791:
Toda, H. and Yamamoto, T. 1991. Dis
- Page 1792 and 1793:
Invertebrates from the United State
- Page 1794 and 1795:
Van Syoc, R.J. 1992. Living and fos
- Page 1796 and 1797:
Wasson, K. and Mariscal, R.N. 2007.
- Page 1798 and 1799:
Williams, G.D. 1997. The physical,
- Page 1800 and 1801:
Yakovlev Y. M. 2002. Animal kingdom
- Page 1802 and 1803:
Yoo, M.S. and Kajihara, T. 1983. Re
- Page 1804 and 1805:
Zvyagintsev, A.Y. 2005. Marine Foul
- Page 1806 and 1807:
NIES Acartiella sinensis Avent et a
- Page 1808 and 1809:
Lee and Reusser (PCEIS), 2012 Light
- Page 1810 and 1811:
Ass. Res. Lit. Org. Osaka Bay, 1986
- Page 1812 and 1813:
Bagaveeva and Zvyagintsev, 1999 Cal
- Page 1814 and 1815:
Nelson et al., 2007 OBIS Tovar-Hern
- Page 1816 and 1817:
Gordon, 2009 Inglis et al., 2006d M
- Page 1818 and 1819:
Lambert, 2002 Lambert, 2003b Lee an
- Page 1820 and 1821:
McDonald, 2007 Padula and Absalão,
- Page 1822 and 1823:
Aladin et al., 2006b Bardi and Marq
- Page 1824 and 1825:
Lee and Reusser (PCEIS), 2012 Liu,
- Page 1826 and 1827:
Carlton, 2003 Carlton and Cohen, 19
- Page 1828 and 1829:
OBIS Pierri et al., 2010 Zenetos et
- Page 1830 and 1831:
Lee and Reusser (PCEIS), 2012 Meado
- Page 1832 and 1833:
Vassilenko, 2006 Wasson et al., 200
- Page 1834 and 1835:
Lee and Reusser (PCEIS), 2012 Liu,
- Page 1836 and 1837:
California Department of Fish and G
- Page 1838 and 1839:
Lambert and Lambert, 1998 Lambert a
- Page 1840 and 1841:
Neves and da Rocha, 2008 Paulay et
- Page 1842 and 1843:
EPA, 2008 Fairey et al., 2002 GBIF
- Page 1844 and 1845:
Emmett et al., 1991 Everett et al.,
- Page 1846 and 1847:
Lee and Reusser (PCEIS), 2012 Leung
- Page 1848 and 1849:
Iwasaki et al., 2004b Lee and Reuss
- Page 1850 and 1851:
Fautin and Hand, 2007 Furota et al.
- Page 1852 and 1853:
Berkeley, 1927 Berkeley and Berkele
- Page 1854 and 1855:
Deonier, 1972 Englund et al., 2000a
- Page 1856 and 1857:
The Bay Institute, 2004 USGS-NAS Wa
- Page 1858 and 1859:
Hinton and Emmett, 2000 Lee and Reu
- Page 1860 and 1861:
Carlton, 1969 Carlton, 1979 Carlton
- Page 1862 and 1863:
SCAMIT, 2008a Shluker, 2003 Shouse
- Page 1864 and 1865:
CANOD, 2009 CIESM, 2006 DAISIE Gibs
- Page 1866 and 1867:
Coan et al., 2000 Coles et al., 200
- Page 1868 and 1869:
Dept. Env. Water Heritage and Arts
- Page 1870 and 1871:
Cohen and Carlton, 1995 Cohen et al
- Page 1872 and 1873:
Mead et al., 2011 Mills, 2001a OBIS
- Page 1874 and 1875:
Zongguo, 2001 Lates calcarifer #Mas
- Page 1876 and 1877:
MEI, 2008 Nabeshima, 2007 Okamoto,
- Page 1878 and 1879:
Shimura et al., 2007 USGS-NAS WoRMS
- Page 1880 and 1881:
Bishop Museum, 2000 Carlton and Eld
- Page 1882 and 1883:
DAISIE Doi et al., 2011 GBIF Kerckh
- Page 1884 and 1885:
Liu, 2008 MEI, 2008 Morris et al.,
- Page 1886 and 1887:
deRivera et al., 2007 Microspio gra
- Page 1888 and 1889:
Lowry, 2000 Markmann, 1986 Meacham,
- Page 1890 and 1891:
Wonham and Carlton, 2005 Yoklavich
- Page 1892 and 1893:
Ricketts et al., 1985 Rudy and Rudy
- Page 1894 and 1895:
Asai et al., 1997 Asakura, 1992 Ass
- Page 1896 and 1897:
Carlton and Eldredge, 2009 Lee and
- Page 1898 and 1899:
Sytsma et al., 2004a T N & Associat
- Page 1900 and 1901:
GBIF Hirakawa, 1989 Light et al., 2
- Page 1902 and 1903:
Coles et al., 2002a Coles et al., 1
- Page 1904 and 1905:
Jamieson et al., 1998 Lee and Reuss
- Page 1906 and 1907:
Paavola et al., 2005 Ruiz et al., 2
- Page 1908 and 1909:
Wells et al., 2009 Yokogawa and Nab
- Page 1910 and 1911:
Carlton and Eldredge, 2009 Child, 1
- Page 1912 and 1913:
Cohen et al., 2002 Coles et al., 20
- Page 1914 and 1915:
Ward et al., 2000 Ward et al., 2001
- Page 1916 and 1917:
Joydas and Damodaran, 2004 Lee and
- Page 1918 and 1919:
WADOE, 2002 Welch, 2005 WoRMS Zvyag
- Page 1920 and 1921:
Nichols and Thompson, 1985b Ruiz et
- Page 1922 and 1923:
Miller et al., 2007 OBIS Tokida and
- Page 1924 and 1925:
Nelson et al., 2007 OBIS Scylla ser
- Page 1926 and 1927:
Boyd et al., 2002 Brusca et al., 20
- Page 1928 and 1929:
Dept. of Navy, 2000 Eldredge and De
- Page 1930 and 1931:
Van Name, 1945 Zongguo, 2001 Styela
- Page 1932 and 1933:
#Master Comment Furota et al., 2008
- Page 1934 and 1935:
OBIS Indo-Pacific Molluscan Databas
- Page 1936 and 1937:
Hieb et al., 2004 Light et al., 200
- Page 1938 and 1939:
Lee and Reusser (PCEIS), 2012 OBIS
- Page 1940 and 1941:
Venerupis philippinarum Barnhart et
- Page 1942:
Soule et al., 2007 Streftaris et al