PDF (Lo-Res) - Smithsonian Institution Libraries
PDF (Lo-Res) - Smithsonian Institution Libraries
PDF (Lo-Res) - Smithsonian Institution Libraries
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
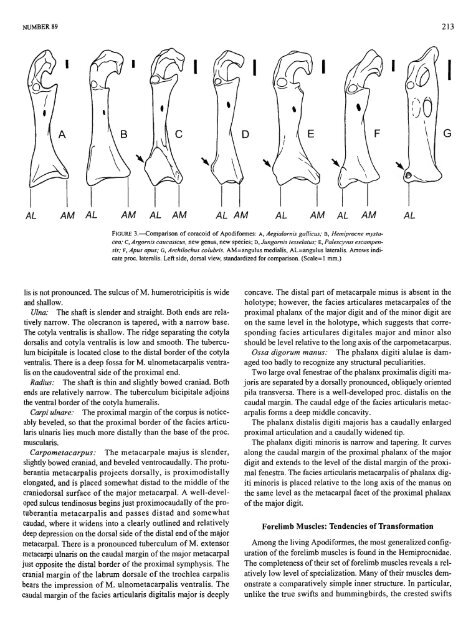
NUMBER 89 213<br />
AM AL AM AL AM AL AM AM AL AM<br />
FIGURE 3.—Comparison of coracoid of Apodiformes: A, Aegialomis gallicus; B, Hemiprocne mystacea;<br />
C, Argornis caucasicus, new genus, new species; D, Jungornis tesselatus; E, Palescyvus escampensis;<br />
F, Apus apus; G, Archilochus colubris. AM=angulus medialis, AL=angulus lateralis. Arrows indicate<br />
proc. lateralis. Left side, dorsal view, standardized for comparison. (Scale-1 mm.)<br />
lis is not pronounced. The sulcus of M. humerotricipitis is wide<br />
and shallow.<br />
Ulna: The shaft is slender and straight. Both ends are relatively<br />
narrow. The olecranon is tapered, with a narrow base.<br />
The cotyla ventralis is shallow. The ridge separating the cotyla<br />
dorsalis and cotyla ventralis is low and smooth. The tuberculum<br />
bicipitale is located close to the distal border of the cotyla<br />
ventralis. There is a deep fossa for M. ulnometacarpalis ventralis<br />
on the caudoventral side of the proximal end.<br />
Radius: The shaft is thin and slightly bowed craniad. Both<br />
ends are relatively narrow. The tuberculum bicipitale adjoins<br />
the ventral border of the cotyla humeralis.<br />
Carpi ulnare: The proximal margin of the corpus is noticeably<br />
beveled, so that the proximal border of the facies articularis<br />
ulnaris lies much more distally than the base of the proc.<br />
muscularis.<br />
Carpometacarpus: The metacarpale majus is slender,<br />
slightly bowed craniad, and beveled ventrocaudally. The protuberantia<br />
metacarpalis projects dorsally, is proximodistally<br />
elongated, and is placed somewhat distad to the middle of the<br />
craniodorsal surface of the major metacarpal. A well-developed<br />
sulcus tendinosus begins just proximocaudally of the protuberantia<br />
metacarpalis and passes distad and somewhat<br />
caudad, where it widens into a clearly outlined and relatively<br />
deep depression on the dorsal side of the distal end of the major<br />
metacarpal. There is a pronounced tuberculum of M. extensor<br />
metacarpi ulnaris on the caudal margin of the major metacarpal<br />
just opposite the distal border of the proximal symphysis. The<br />
cranial margin of the labrum dorsale of the trochlea carpalis<br />
bears the impression of M. ulnometacarpalis ventralis. The<br />
caudal margin of the facies articularis digitalis major is deeply<br />
concave. The distal part of metacarpale minus is absent in the<br />
holotype; however, the facies articulares metacarpales of the<br />
proximal phalanx of the major digit and of the minor digit are<br />
on the same level in the holotype, which suggests that corresponding<br />
facies articulares digitales major and minor also<br />
should be level relative to the long axis of the carpometacarpus.<br />
Ossa digorum manus: The phalanx digiti alulae is damaged<br />
too badly to recognize any structural peculiarities.<br />
Two large oval fenestrae of the phalanx proximalis digiti majoris<br />
are separated by a dorsally pronounced, obliquely oriented<br />
pila transversa. There is a well-developed proc. distalis on the<br />
caudal margin. The caudal edge of the facies articularis metacarpalis<br />
forms a deep middle concavity.<br />
The phalanx distalis digiti majoris has a caudally enlarged<br />
proximal articulation and a caudally widened tip.<br />
The phalanx digiti minoris is narrow and tapering. It curves<br />
along the caudal margin of the proximal phalanx of the major<br />
digit and extends to the level of the distal margin of the proximal<br />
fenestra. The facies articularis metacarpalis of phalanx digiti<br />
minoris is placed relative to the long axis of the manus on<br />
the same level as the metacarpal facet of the proximal phalanx<br />
of the major digit.<br />
Forelimb Muscles: Tendencies of Transformation<br />
Among the living Apodiformes, the most generalized configuration<br />
of the forelimb muscles is found in the Hemiprocnidae.<br />
The completeness of their set of forelimb muscles reveals a relatively<br />
low level of specialization. Many of their muscles demonstrate<br />
a comparatively simple inner structure. In particular,<br />
unlike the true swifts and hummingbirds, the crested swifts