- Page 1 and 2:
)i 1 reesonably complete and accura
- Page 3 and 4:
3 inquire about the component of ve
- Page 5 and 6:
4 I I 5 To find (t2)av, we assume t
- Page 7 and 8:
\ vnich, it is noted can be negativ
- Page 9 and 10:
I 7 than or smaller than the second
- Page 11 and 12:
i I i I I I ) ) i L , I I . INT1:OD
- Page 13 and 14:
13 field per electron is and per co
- Page 15 and 16:
. 11. 5. CharRe-Transfer and Ion-Mo
- Page 17 and 18:
17 In the followin:: sections much
- Page 19 and 20:
above. With that EIN, an estimate o
- Page 21 and 22:
21 region in w!iich large, nighlv l
- Page 23 and 24:
i ’ understanding: 23 (a) Electro
- Page 25 and 26:
Obviously, the secondary ion must h
- Page 27 and 28:
27 (22) Franklin, J. L., Munson, M.
- Page 29 and 30:
Tables 1-6 present examples of rela
- Page 31 and 32:
Table 8 Some Ions Formed by Process
- Page 33 and 34:
33 velocity of the reacting partn r
- Page 35 and 36:
35 must be added to the Langevin cr
- Page 37 and 38:
37 In our laboratory a microwave di
- Page 39 and 40:
+ . 4 . r 39 as well as N in a cor0
- Page 41 and 42:
ION-MOIECULE REACTION RATES MEASUFI
- Page 43 and 44:
43 excitntion 2onditions so that th
- Page 45 and 46:
45 In 2 like manner Fig. 3, showing
- Page 47:
47 Absorption Spectra of Transient
- Page 50 and 51:
50 maximum fiela. In this manner, a
- Page 52 and 53:
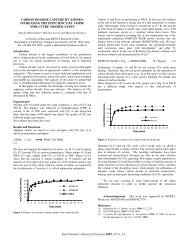
52 3 % %- %- 5- a- 7 h W P H 0 L v)
- Page 54 and 55:
References I I . A.B.Callear, J.A.G
- Page 56 and 57:
._ . _-.. - , , . . ,. . The Pyrex
- Page 58 and 59:
58 0 0 0 VI J > I cv . u H a
- Page 60:
.... . 0 2 e I / m 0 H F4 : 1
- Page 63 and 64:
\ 0.9 0.8 0.7 06 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 01
- Page 65 and 66:
65 ' cause of the reduction in the
- Page 67 and 68:
INTRODUCTION I' Attachment of polar
- Page 69 and 70:
I 69 EXPERIMENTAL The mass spectrom
- Page 71 and 72:
+ Figure 1 Mixed water and methanol
- Page 73 and 74:
73 ' , radius might be expected bec
- Page 75 and 76:
75 Negative Ion Mass Spectra of Som
- Page 77 and 78:
A b 1 1 I H I I I FILAMEN T CONTINU
- Page 79 and 80:
79 for positive and negative ions,
- Page 81 and 82:
51 out to answer some of the questi
- Page 83 and 84:
93 INTERACTIONS OF EXCITED SPECIES
- Page 85 and 86:
L 4 I*C z 0'2 = a, a U x I m 4 m 0
- Page 87 and 88:
I L I, ; > > E Fig. 3 I50 200 150 1
- Page 89 and 90:
I 300 r 1 - 200 i io ;' a cn I I. 0
- Page 91 and 92:
where DISCUSSION OF XESULTS PERTAIN
- Page 93 and 94:
93 where the bar indicates values c
- Page 95 and 96:
'I i 'I 0 2. 4 6 8 2 [ N]* x' I 0-2
- Page 97 and 98:
Fig. 14 IO 8 6 4F [NO] x IO-" (mole
- Page 99 and 100:
for chemiluminescent excitation in
- Page 101 and 102:
101 Chemiluminescent Reactions of E
- Page 103 and 104:
103 All gases were taken directly f
- Page 106 and 107:
10; He: + N2 -. 2He + h': (8) whi!?
- Page 108 and 109:
description for both diffusion and
- Page 110 and 111:
B. Ions and Electrons I Consider a
- Page 112 and 113:
' 112 axial diffusion through the d
- Page 114 and 115:
the tube walls occurs continuously
- Page 116 and 117:
E2R M ' $6"
- Page 118 and 119:
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9- 10. u. -
- Page 120 and 121:
120 . Dlschorge zone Reactor zone 1
- Page 122 and 123:
122 In radiation chemistry the cust
- Page 124 and 125:
124 4. chemistry seem limited essen
- Page 126 and 127:
126 Conversion of Mixtures into Mor
- Page 128 and 129:
Hydrazine Synthesis in A Silent dle
- Page 130 and 131:
{;I . - . .. . - .., . . .. _- .. .
- Page 132 and 133:
1 \ \ \ , \ , \ \ Pmer hnrity K.W.
- Page 134 and 135:
. I operating fact that the sloGe i
- Page 136 and 137:
_- of ' . 8. - 7 6, Residence Time
- Page 138 and 139:
135 Ionic Reactions in Corona Disch
- Page 140 and 141:
GAS OUT GAS IN i.ho QUADRUPOLE MASS
- Page 142 and 143:
- + ( ~ ~ + 0 H ) ~ O ~ ( H~o)~H+ +
- Page 144 and 145:
144 i I , , , , . + 1- u 3c w Inu c
- Page 146 and 147:
146 SYNTHESIS OF ORGANIC COIGhTDS B
- Page 148 and 149:
mi5 a- dz CI n I a I n +4 - 0 -I- k
- Page 150 and 151:
0 z cu I I I
- Page 152:
I- I - t d m a .rl Y x c, t-' d k
- Page 155 and 156:
, 155 This result is significant in
- Page 157 and 158:
Compound Bond he rgy Li I 82 UBr 10
- Page 159 and 160:
, ”..’ 3or 25 - 5 20 - s 3 w Y
- Page 161 and 162:
I 161 THE GLOW DISCHARGE DEPOSITION
- Page 163 and 164:
Fig. 1 Process Apparatus -__l.ll__
- Page 165 and 166:
v) t- at- InIo Io0 t-Q) loo lcua O
- Page 167 and 168:
This study is only an approximation
- Page 169 and 170:
Mole Reaction Material ratio time e
- Page 171 and 172:
\ i (4) Effect of System Pressure T
- Page 173 and 174:
173 Pressure. Since pressure is a c
- Page 175 and 176:
175 Table VI X-RAY DATA OF DEPOSIT
- Page 177 and 178:
177 Another source of weakness is t
- Page 179 and 180:
179 PLATING IN A CORONA DISCHARGE R
- Page 181 and 182:
\ 3 , ,\ 110 v 60 CPS MANOMETER . F
- Page 183 and 184:
I i , \ I i & a - P Fig. 3 Reaction
- Page 185 and 186:
\ \' C 0 .d * d .- C U d 0) c( 1) L
- Page 187 and 188:
I i I . Q) I, s w 0 v) Y 0 a w W a
- Page 189 and 190:
I (b) Polarized Light Fig. 6 Cross
- Page 191 and 192:
i m v) Y C i! u o) 23 a a- + 191 m
- Page 193 and 194:
i, d C .d c c W Q ) 0 0 L1Y 0 000 0
- Page 195 and 196:
i e 4 0 wcr -4 4 al 0 0 0 c) cr 13:
- Page 197 and 198:
\ E ‘ 1 TIME FOR RUN 13-1 14-1 -
- Page 199 and 200:
199 a red heat in this cell using d
- Page 201 and 202:
\ , t j \ I, v) 2 Y . C 0 u m .I C
- Page 203 and 204:
203 VAPOR PHASE FORMATION OF NONCRY
- Page 205 and 206:
BELL JAR STANC TO VACUUM SYSTEM U T
- Page 207 and 208:
207 of the boron oxide film, the fi
- Page 209 and 210:
i I, 4 I.( Y I- * 0 i f i 3 0.t I I
- Page 211 and 212:
211 The Reacticn 3f Oxygen with Car
- Page 213 and 214:
2 E, W t- a Z 9 I- a 2 X 0 I50 too
- Page 215 and 216:
'i' 100 50 IC 21 5 2.0 2.5 SURFACE
- Page 217 and 218:
I- z W 0 w a a 100 80 60 40 20 215
- Page 219 and 220:
s., Literature Cited Berkley, C. ,
- Page 221 and 222:
7 h \ F 221 600°C and 1 atmosphere
- Page 223 and 224:
223 e I'
- Page 225 and 226:
R L ' -1 9mm O.D. 5mm I.D. 45mm 0.D
- Page 227 and 228:
Figure 5.- Paschen's law curves. 2-
- Page 229 and 230:
\ '? I The water-free product gases
- Page 231 and 232:
N I + 0" ON i I + 0 u / 0 0 I 0 cu
- Page 233 and 234:
- 233 SOME PROBLEMS OF THE KINETICS
- Page 235 and 236:
.. . :. ,. .I , . i ? .. . , ... .
- Page 237 and 238:
237 Table 2 Experimental Variables
- Page 239 and 240:
239 Zhbie I Eerccnt Consumption of
- Page 241 and 242:
241 Discussion The systematic varia
- Page 243 and 244:
I \ 1 243 FORMATION OF HYDROCARBONS
- Page 245 and 246:
h z - a o m a 20 T IME, minutes . F
- Page 247 and 248:
I 1 I I I I 0 I 2 3 4 5 TIME, minut
- Page 249 and 250:
The next five coluws in table 1 sho
- Page 251 and 252:
\ .\ t 251 Given the existence of t
- Page 253 and 254:
I L 253 Epple, R. P. and C. M. Apt.
- Page 255 and 256:
1 ' Fig. 1 Schematic of flow discha
- Page 257 and 258:
5' . ' I 1 257 co, with excess H2,
- Page 259 and 260:
1 1 1 moo 1400 1300 c V' I IPOO I I
- Page 261 and 262:
i 25i The Dlssocfatior of ToIuere V
- Page 263 and 264:
L ! , c PRODUCTS FROM A 28 MC. DISC
- Page 265 and 266:
'\ J ?. , .. . : PRODUCT FORMATION
- Page 267 and 268:
'9 / I '\ "1 BENZYL CATION AND RADI
- Page 269 and 270:
a
- Page 271 and 272:
271 tube serve? as the high voltare
- Page 273 and 274:
273 ion (1L.). Zxcitei-ion by colli
- Page 275 and 276:
Apparatus and Procedure 275 EXPERIM
- Page 277 and 278:
. 277 6. A freshly prepared sam le
- Page 279 and 280:
observed. The polystyrene (10% solu
- Page 281 and 282:
i i (12) c (11) (14) I 281 LITERATU
- Page 283 and 284:
FLOW- METER I ADDITIVE SUPPLY * ,28
- Page 285 and 286:
285 TABLE 2 Effect of Haloqenated A
- Page 287 and 288:
ANALYTICAL RESULTS Some evidence wa
- Page 289 and 290:
DISCUSSION 289 The salient features
- Page 291 and 292:
? ~ MENBERSHIP IN THE DIVISION OF F
- Page 293 and 294:
292 flow of the reactant gas stream
- Page 295 and 296:
294 have suitable residence times i
- Page 297 and 298:
0 E < h( E l! d K c 0 .- Y 0 t u t
- Page 299 and 300:
298 yields of many chemical product
- Page 301 and 302:
- ;i Y . 15. Pressure lOmm 5 > 10-
- Page 303 and 304:
302 the best and in many practical
- Page 305 and 306:
GENERATION AND MEASUREMENT OF AUDIO
- Page 307 and 308:
. The transformer secondary and the
- Page 309 and 310:
Vaccum-Tube Amplifier The mobile co
- Page 311 and 312:
310 f = Power supply frequency in c
- Page 313:
FUFARCI! INSTITUTE OF TFYDLC UNIVER
- Page 316 and 317:
J # I / 4) I . . '8 r4 0 r( P
- Page 318 and 319:
317 i Cuencb svsten w.nnar;itus use
- Page 320 and 321:
epcrte? the noss~kil.itv of nroduct
- Page 322 and 323:
1' b t +
- Page 324 and 325:
323 ....... - . . . . . . . . . . .
- Page 326 and 327:
1 \ i I i , / / / 8 3 1 325 To205 +
- Page 328 and 329:
- .- - - . - - . . . - . 327 n + c
- Page 330 and 331:
' POWER PLASMA GAS l e , ' I ! I I
- Page 332 and 333:
331 f'ENI?AL PF'FCLCCFC Dernis, P.R
- Page 334 and 335:
i J 333 ; mosphere (as opposed to a
- Page 336 and 337:
; it raised the question, still &?z
- Page 338 and 339:
p .I V I .= - - HCN/C(CALC. WITH C
- Page 340 and 341:
1 1 339 atmospheric ressure and ach
- Page 342 and 343:
RESULTS 341 Composition Dependence
- Page 344 and 345:
0.09 0.08 0.07 9 0.06 2 U - .$ 0.05
- Page 346 and 347:
II \ to the Slot So that less of th
- Page 348 and 349:
i 4 2 HYDROCARBON-NITROGEN REACTION
- Page 350 and 351:
I 1 349 c M m ; a e, k M x
- Page 352 and 353:
1.0 I - a. I n TEMPERATURE - OK Fig
- Page 354 and 355:
353 the experimental results in the
- Page 356 and 357:
,) 355 The ceaswed conversion cf ni
- Page 358 and 359: 1 6 357 Freezing. 3jpotnesise thzf
- Page 360 and 361: 359 \ Frozen Compositior: Calcillat
- Page 362 and 363: I 1 \ 361 -. ne reaction proceecis
- Page 364 and 365: \ 36 3 ' h, I 26. H. Purnell, Gas C
- Page 366 and 367: In experiments on the direct conver
- Page 368 and 369: 367 used as blnders, with different
- Page 370 and 371: 369 ' i 1. REFERENCES Berber, John
- Page 372 and 373: Distribution and yield rates of pro
- Page 374 and 375: . . I . I 370 . . . . ., . . .. . .
- Page 376 and 377: 4 372 090- > E w - m c N O - 0 z :
- Page 378 and 379: A-Feed tank 6-Thermocracker GReceiv
- Page 380 and 381: 80 \ 0 70 60 e 40 a U VI 9 30 20 10
- Page 382 and 383: COAL DEASH& AND HIGH-PURITY COKE Wa
- Page 384 and 385: 3Pn _. -. - L -J:,J.-;~~~L, ):as se
- Page 386 and 387: S ~ l ~ o n~pg:ading r is the resul
- Page 388 and 389: The range ~f temperatures and gener
- Page 390 and 391: . .. 386 9 * - r. Y 2 .' d a f' r.
- Page 392 and 393: .) .L m 388 I
- Page 394 and 395: TABLE 4 390 DELAYED COKING OF DEASH
- Page 396 and 397: , ! I- on '---
- Page 398 and 399: 394 The present method is to keep t
- Page 400 and 401: 396 ‘c erperature, while the pres
- Page 402 and 403: 2, '! ! Proximate Analysis, wt $ Mo
- Page 404 and 405: 0 IS 0 14 LL 9 013 e \ 3 b- m *- 01
- Page 406 and 407: 402 HYDROGEN CYANIDE PRODUCED FROM
- Page 410 and 411: 4 OL. ' , I. . TesCs. With.Coals .o
- Page 412 and 413: Table 3.- Product Gas Analyses and
- Page 414 and 415: 410 BIBLIOGRAPHY 1. American Public
- Page 416 and 417: Figure 2. Enclosure surrounding hyd
- Page 418 and 419: 0 0 f v) C 0 u m I z 2 c 2 r d J w
- Page 420 and 421: 0. E c .4 7 .. .c . I ( - Low tempe
- Page 422 and 423: 418 cual. A mjor aa\;antage or' the
- Page 424 and 425: 420 Ir ?Y ? ? 9 9 9 pc rod n o c o
- Page 426 and 427: 422 Table 3. Room-texperature M'dss
- Page 428 and 429: 424 state, depending on the strengt
- Page 430 and 431: Table 4. Room-?;ergerature isomer s
- Page 432 and 433: I' 1.3 . /o 9 IO 9 6 a 425 F F 33 I
- Page 434 and 435: Brooks J.D. and Sternhell S. (1957)
- Page 436 and 437: (52) Gib3 T.C. and Greenwood N.N. (
- Page 438 and 439: 434 transducer vas then introduced
- Page 440 and 441: 436 yield is quite similar. The con
- Page 442 and 443: ?-!??? 0 mv, Uh\OhIe . . . . eirlrl
- Page 444 and 445: 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 4
- Page 446 and 447: 442 CHEMICAL REACTIONS IN A CORONA
- Page 448 and 449: helium 444 CORONA REACTOR SYSTEM Fi
- Page 450 and 451: 446 The ultraviolet spectrum. for t
- Page 452 and 453: Biphenyl Fraction 448 The low molec
- Page 454 and 455: LUd The actual structural definitio
- Page 456 and 457: I I I I I In m 9 In 2 , I: r- In m
- Page 458 and 459:
’. 454 Mechanism I The available
- Page 460 and 461:
456 , , . The relatively low yield
- Page 462 and 463:
458 h/lethylacetylene, allene and b
- Page 464 and 465:
Introduction VAPOR PHASE DECOMPOSIT
- Page 466 and 467:
462 more efficient hydrogenation. T
- Page 468 and 469:
464 place in parallel with fragment
- Page 470 and 471:
466 P rl 0, k 7 rnI rn al k a I hl
- Page 472 and 473:
458 TABLE I. COMPOSI'IION OF GASEOU
- Page 474 and 475:
REFERENCES 1. C. Hirayama and D. A.
- Page 476 and 477:
i 472 Reciprocal Arc Enthalpy ,-> F
- Page 478 and 479:
474 be pumped down without altering
- Page 480 and 481:
476 Instead a hydrogen deficient fi
- Page 482 and 483:
i 478
- Page 484 and 485:
480 FATTY ACIDS AND n-ALKANES IN GR
- Page 486 and 487:
482 TA5L,E 2. - Carbon number distr
- Page 488 and 489:
6. 7. a. 9. 484 Lawlor, D. L., and
- Page 490 and 491:
' I ' Sample No. 6 ' 12 IO 8 6 z 4
- Page 492 and 493:
. 488 uiolecular weight of which ca
- Page 494 and 495:
Xississippi (Sample GS). Stock solu
- Page 496 and 497:
492 found at 5.7 and 4.9& for the W
- Page 498 and 499:
494 mechanisms. However, the voltad
- Page 500 and 501:
For pure polynuclcar arom.i;ic hydr
- Page 502 and 503:
- '-'. . ' . . values are listed in
- Page 504 and 505:
500 (1;) Ten, T. 17.: a;1d,Dic;
- Page 506 and 507:
- ~ Resistivity Czlculation 2: 1 j:
- Page 508 and 509:
504 o ' C 0s 2 0 v x i 8 2 0 ! P -
- Page 510 and 511:
506 i
- Page 512 and 513:
d 601 L P LL
- Page 516 and 517:
I I I I I I I I m W N W N 0 (D ? 0
- Page 518 and 519:
514 was heated under nitrogen in a
- Page 520 and 521:
The line broadening at 79OK of the
- Page 522 and 523:
13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21.
- Page 524 and 525:
W L, Z 6 m (1: 0 6 d j o 2 ' 1 0.0
- Page 526 and 527:
Coals 522 Studies of the 1600 cm-l
- Page 528 and 529:
L in ole i c a c id - 0' Two sample
- Page 530 and 531:
526 Table 1.- Ultimate analyses of
- Page 532 and 533:
528 6. Friedel, R. A., and H. Retco
- Page 534 and 535:
egeneration. The system can be seen
- Page 536 and 537:
532 and can be expressed in terms o
- Page 538 and 539:
534 in the vapor increases with inc
- Page 540 and 541:
NH3 NH3 NH3 NH3 Pyridine Pyridine P
- Page 542 and 543:
Mole Ratio of Test No. Quinoline to
- Page 544 and 545:
IXPROFJCTION D; M. Mason Institute
- Page 546 and 547:
-4:c~rciiny to recent studies o ;i4
- Page 548 and 549:
544 Table 1. LIGHT EMISSION OF Y"TR
- Page 550 and 551:
emission in a few cases may be by d
- Page 552 and 553:
LITERATUR2 CITED i. C. -. .' * il.
- Page 554 and 555:
co, CH,,OR 1 - OTHER ADDITIVE FRITT
- Page 556 and 557:
FRIT 'TED CO, CH,.OR 4 ___ OTHER AD
- Page 558 and 559:
340 350 300 400 4 50 500 600 700 80
- Page 560 and 561:
0 554 WITH COOLING (PLATE AT 40°C)
- Page 562 and 563:
5 56 then t = to when e = 0 2) the
- Page 564 and 565:
5 58 The surface heat transfer coef
- Page 566 and 567:
Discussion and Results 560 Three br
- Page 568 and 569:
__- ._ 562 Table I THERMAL AND PHYS
- Page 570:
ln 4 I 0 4J v \ 1.0 0.8 0.6 L - 0.4