Canada - World Health Organization Regional Office for Europe
Canada - World Health Organization Regional Office for Europe
Canada - World Health Organization Regional Office for Europe
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
14<br />
<strong>Health</strong> systems in transition <strong>Canada</strong><br />
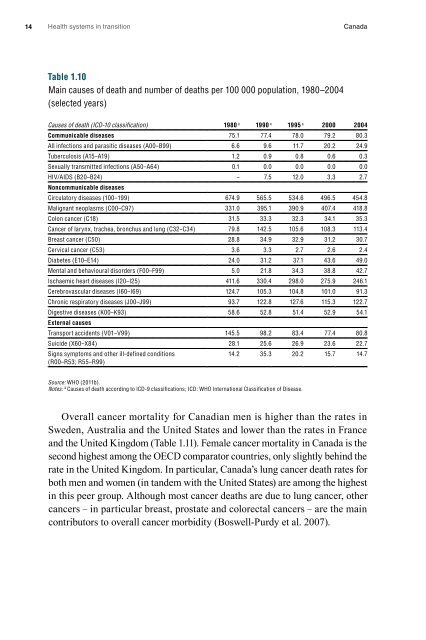
Table 1.10<br />
Main causes of death and number of deaths per 100 000 population, 1980–2004<br />
(selected years)<br />
Causes of death (ICD-10 classification) 1980 a 1990 a 1995 a 2000 2004<br />
Communicable diseases 75.1 77.4 78.0 79.2 80.3<br />
All infections and parasitic diseases (A00 – B99) 6.6 9.6 11.7 20.2 24.9<br />
Tuberculosis (A15 – A19) 1.2 0.9 0.8 0.6 0.3<br />
Sexually transmitted infections (A50 – A64) 0.1 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0<br />
HIV/AIDS (B20 – B24) – 7.5 12.0 3.3 2.7<br />
Noncommunicable diseases<br />
Circulatory diseases (100 – 199) 674.9 565.5 534.6 496.5 454.8<br />
Malignant neoplasms (C00 – C97) 331.0 395.1 390.9 407.4 418.8<br />
Colon cancer (C18) 31.5 33.3 32.3 34.1 35.3<br />
Cancer of larynx, trachea, bronchus and lung (C32 – C34) 79.8 142.5 105.6 108.3 113.4<br />
Breast cancer (C50) 28.8 34.9 32.9 31.2 30.7<br />
Cervical cancer (C53) 3.6 3.3 2.7 2.6 2.4<br />
Diabetes (E10 – E14) 24.0 31.2 37.1 43.6 49.0<br />
Mental and behavioural disorders (F00 – F99) 5.0 21.8 34.3 38.8 42.7<br />
Ischaemic heart diseases (I20 – I25) 411.6 330.4 298.0 275.9 246.1<br />
Cerebrovascular diseases (I60 – I69) 124.7 105.3 104.8 101.0 91.3<br />
Chronic respiratory diseases (J00 – J99) 93.7 122.8 127.6 115.3 122.7<br />
Digestive diseases (K00 – K93) 58.6 52.8 51.4 52.9 54.1<br />
External causes<br />
Transport accidents (V01 – V99) 145.5 98.2 83.4 77.4 80.8<br />
Suicide (X60 – X84) 28.1 25.6 26.9 23.6 22.7<br />
Signs symptoms and other ill-defined conditions<br />
(R00 – R53; R55 – R99)<br />
14.2 35.3 20.2 15.7 14.7<br />
Source: WHO (2011b).<br />
Notes: a Causes of death according to ICD-9 classifications; ICD: WHO International Classification of Disease.<br />
Overall cancer mortality <strong>for</strong> Canadian men is higher than the rates in<br />
Sweden, Australia and the United States and lower than the rates in France<br />
and the United Kingdom (Table 1.11). Female cancer mortality in <strong>Canada</strong> is the<br />
second highest among the OECD comparator countries, only slightly behind the<br />
rate in the United Kingdom. In particular, <strong>Canada</strong>’s lung cancer death rates <strong>for</strong><br />
both men and women (in tandem with the United States) are among the highest<br />
in this peer group. Although most cancer deaths are due to lung cancer, other<br />
cancers – in particular breast, prostate and colorectal cancers – are the main<br />
contributors to overall cancer morbidity (Boswell-Purdy et al. 2007).