Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy - Hyperbaric Chamber Information ...
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy - Hyperbaric Chamber Information ...
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy - Hyperbaric Chamber Information ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
The different studies also applied varying doses of radiation to the affected region,<br />
ranging from 3,600 to 6,000 rads. Moreover, treatments were spread over differing<br />
numbers of days and used dissimilar fractions. In the study by Plenk, 117 patients were<br />
exposed to two different radiation doses and dosing schedules based on their exposure to<br />
HBO or air.<br />
Assessment of heterogeneity<br />
Due to the inadequacy with which study populations, methodologies, and intervention<br />
and comparison protocols were described, this review does not attempt to arrive at a<br />
common effect estimate through statistical methods. The results of each study are<br />
described below.<br />
Review of published clinical experience<br />
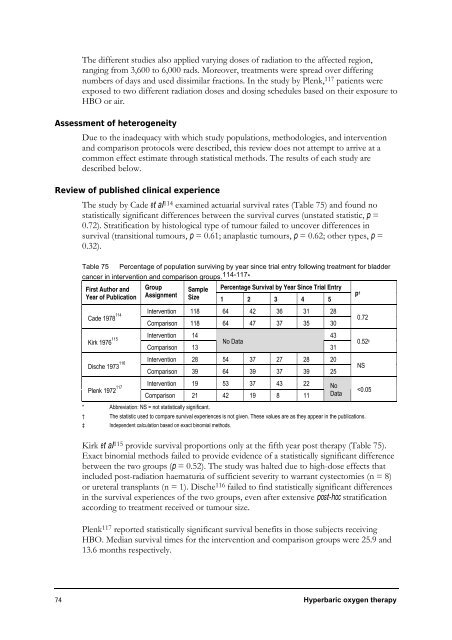
The study by Cade et al114 examined actuarial survival rates (Table 75) and found no<br />
statistically significant differences between the survival curves (unstated statistic, p =<br />
0.72). Stratification by histological type of tumour failed to uncover differences in<br />
survival (transitional tumours, p = 0.61; anaplastic tumours, p = 0.62; other types, p =<br />
0.32).<br />
Table 75 Percentage of population surviving by year since trial entry following treatment for bladder<br />
cancer in intervention and comparison groups. 114-117 *<br />
First Author and<br />
Year of Publication<br />
Group<br />
Assignment<br />
Sample<br />
Size<br />
Percentage Survival by Year Since Trial Entry<br />
1 2 3 4 5<br />
p †<br />
Cade 1978 114<br />
Kirk 1976 115<br />
Dische 1973 116<br />
Plenk 1972 117<br />
Intervention 118 64 42 36 31 28<br />
Comparison 118 64 47 37 35 30<br />
Intervention 14 43<br />
No Data<br />
Comparison 13<br />
31<br />
Intervention 28 54 37 27 28 20<br />
Comparison 39 64 39 37 39 25<br />
Intervention 19 53 37 43 22<br />
Comparison 21 42 19 8 11<br />
* Abbreviation: NS = not statistically significant.<br />
74 <strong>Hyperbaric</strong> oxygen therapy<br />
No<br />
Data<br />
† The statistic used to compare survival experiences is not given. These values are as they appear in the publications.<br />
‡ Independent calculation based on exact binomial methods.<br />
Kirk et al 115 provide survival proportions only at the fifth year post therapy (Table 75).<br />
Exact binomial methods failed to provide evidence of a statistically significant difference<br />
between the two groups (p = 0.52). The study was halted due to high-dose effects that<br />
included post-radiation haematuria of sufficient severity to warrant cystectomies (n = 8)<br />
or ureteral transplants (n = 1). Dische 116 failed to find statistically significant differences<br />
in the survival experiences of the two groups, even after extensive post-hoc stratification<br />
according to treatment received or tumour size.<br />
Plenk 117 reported statistically significant survival benefits in those subjects receiving<br />
HBO. Median survival times for the intervention and comparison groups were 25.9 and<br />
13.6 months respectively.<br />
0.72<br />
0.52 ‡<br />
NS<br />