Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy - Hyperbaric Chamber Information ...
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy - Hyperbaric Chamber Information ...
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy - Hyperbaric Chamber Information ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
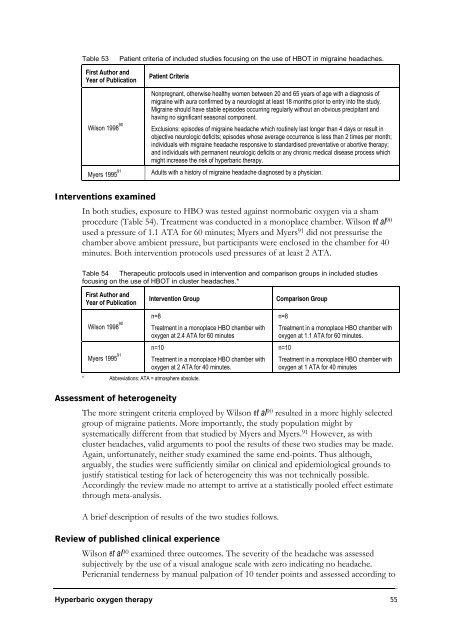
Table 53 Patient criteria of included studies focusing on the use of HBOT in migraine headaches.<br />
First Author and<br />
Year of Publication<br />
Wilson 1998 90<br />
Patient Criteria<br />
Nonpregnant, otherwise healthy women between 20 and 65 years of age with a diagnosis of<br />
migraine with aura confirmed by a neurologist at least 18 months prior to entry into the study.<br />
Migraine should have stable episodes occurring regularly without an obvious precipitant and<br />
having no significant seasonal component.<br />
Exclusions: episodes of migraine headache which routinely last longer than 4 days or result in<br />
objective neurologic deficits; episodes whose average occurrence is less than 2 times per month;<br />
individuals with migraine headache responsive to standardised preventative or abortive therapy;<br />
and individuals with permanent neurologic deficits or any chronic medical disease process which<br />
might increase the risk of hyperbaric therapy.<br />
Myers 1995 91 Adults with a history of migraine headache diagnosed by a physician.<br />
Interventions examined<br />
In both studies, exposure to HBO was tested against normobaric oxygen via a sham<br />
procedure (Table 54). Treatment was conducted in a monoplace chamber. Wilson et al90 used a pressure of 1.1 ATA for 60 minutes; Myers and Myers91 did not pressurise the<br />
chamber above ambient pressure, but participants were enclosed in the chamber for 40<br />
minutes. Both intervention protocols used pressures of at least 2 ATA.<br />
Table 54 Therapeutic protocols used in intervention and comparison groups in included studies<br />
focusing on the use of HBOT in cluster headaches.*<br />
First Author and<br />
Year of Publication<br />
Wilson 1998 90<br />
Myers 1995 91<br />
* Abbreviations: ATA = atmosphere absolute.<br />
Intervention Group Comparison Group<br />
n=8<br />
Treatment in a monoplace HBO chamber with<br />
oxygen at 2.4 ATA for 60 minutes<br />
n=10<br />
Treatment in a monoplace HBO chamber with<br />
oxygen at 2 ATA for 40 minutes.<br />
n=8<br />
Treatment in a monoplace HBO chamber with<br />
oxygen at 1.1 ATA for 60 minutes.<br />
n=10<br />
Treatment in a monoplace HBO chamber with<br />
oxygen at 1 ATA for 40 minutes<br />
Assessment of heterogeneity<br />
The more stringent criteria employed by Wilson et al90 resulted in a more highly selected<br />
group of migraine patients. More importantly, the study population might by<br />
systematically different from that studied by Myers and Myers. 91 However, as with<br />
cluster headaches, valid arguments to pool the results of these two studies may be made.<br />
Again, unfortunately, neither study examined the same end-points. Thus although,<br />
arguably, the studies were sufficiently similar on clinical and epidemiological grounds to<br />
justify statistical testing for lack of heterogeneity this was not technically possible.<br />
Accordingly the review made no attempt to arrive at a statistically pooled effect estimate<br />
through meta-analysis.<br />
A brief description of results of the two studies follows.<br />
Review of published clinical experience<br />
Wilson et al90 examined three outcomes. The severity of the headache was assessed<br />
subjectively by the use of a visual analogue scale with zero indicating no headache.<br />
Pericranial tenderness by manual palpation of 10 tender points and assessed according to<br />
<strong>Hyperbaric</strong> oxygen therapy 55